AAF International PORTA Scrubber User Manual
Page 7
5.6 General System Maintenance
Ducts, external PORTA-Scrubber surfaces, latches, blower, and
other system infrastructure should be checked at least every 6
months. Internal surfaces shall be examined whenever filters are
replaced. Examine all components for the following:
5.6.1 Cleanliness: Sweep and vacuum all standing dust or
dirt in the system. If using cleaning solvents, be mindful of the
impact of solvents on the performance and life of the chemical
media and take appropriate precautions to protect the system.
5.6.2 Water: The system should be completely dry at all times.
The presence of standing water, condensation, or dampness
is detrimental to the performance and life of the system.
Determine and remove the cause for the presence of water in
the system, dry the system, and examine all components for
the presence of molds and other biological growth. Remove
all contamination, clean and sterilize as necessary.
5.6.3 Filter System Integrity: Ensure that the unit contains the
appropriate filter elements, both particulate and gas-phase, and
that these elements are correctly installed. Check for missing or
improperly installed components and review the system seals.
Check for air leaks at joints and seams and replace gaskets,
worn hardware, and seal with caulk as necessary.
5.6.4 Duct and System Integrity: Examine the entire system
to ensure that contaminated air cannot leak around the filter
system. Check all perimeter seals and repair as necessary.
5.6.5 Corrosion: If metal components are corroded repair the
corrosion and provide protective coatings as necessary. Be
mindful of the impact of painting on the performance and life
of the chemical media, and take appropriate precautions to
protect the system. Determine the source of the corrosion
and rectify.
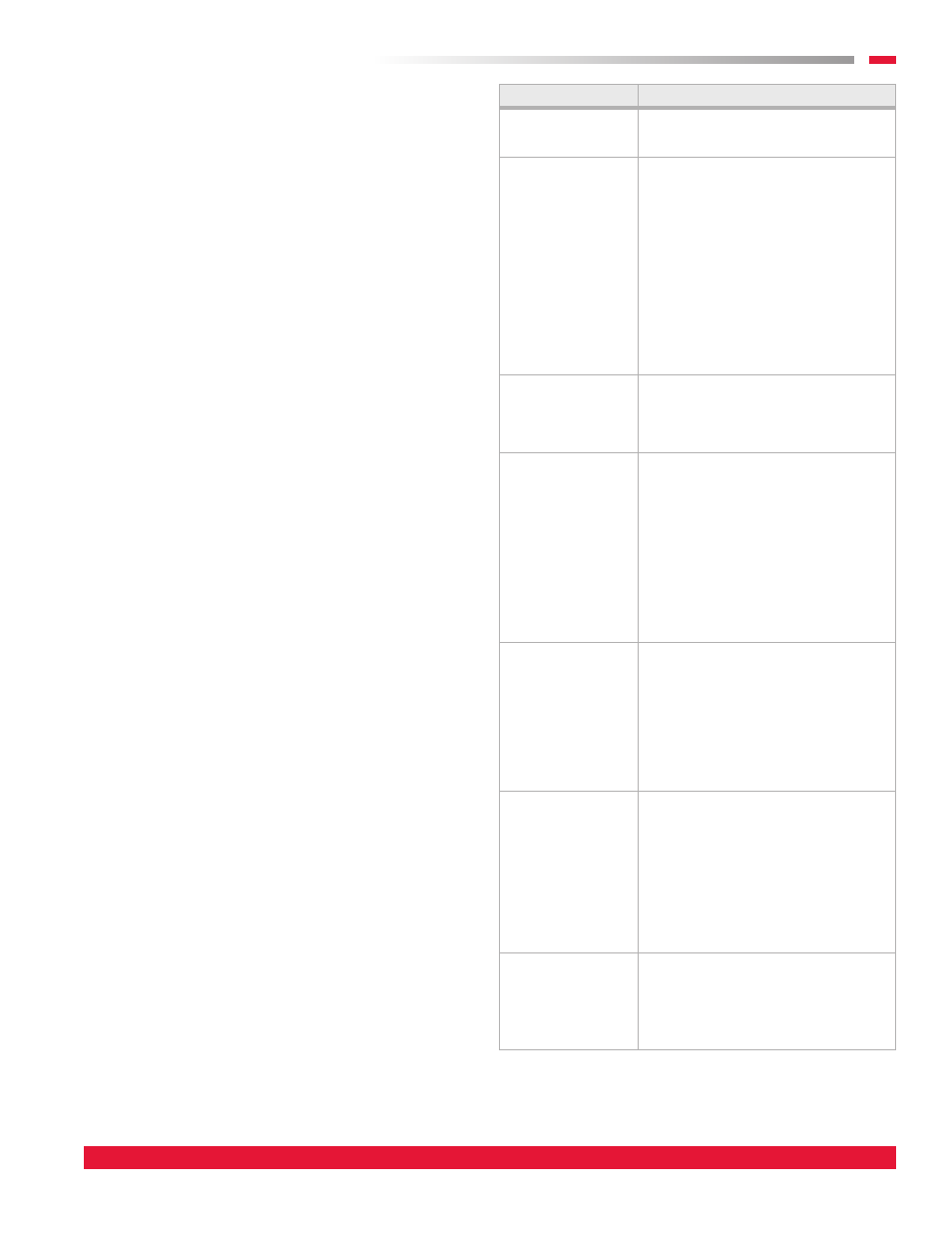
6.0 Troubleshooting
Potential problems and causes listed are in no order of
importance or priority. The causes are only a list of the most
common items to check to correct a problem. If you find the
cause of a problem, DO NOT assume it is the only cause of that
problem. Different problems can have the same cause.
Problem
Cause
Odors and Smells
1. Chemical media is spent.
2. Missing or damaged filters.
3. Incorrect media installed.
Airflow (CFM) Too Low 1. Blower wheel turning in wrong direction.
2. Actual system static pressure is higher
than expected.
3. Motor speed (RPM) too low.
4. Dampers or valves not adjusted properly.
5. Leaks or obstructions in duct work.
6. Filters dirty.
7. Inlet and/or discharge guards are clogged.
8. Duct elbow too close to blower discharge.
9. Improperly designed duct work.
10. Condensation of moisture blinding the
particulate and/or chemical media.
11. Presence of moisture in the filters
combined with freezing temperatures can
cause the filters to become impassible.
Airflow (CFM) Too High 1. Actual system static pressure is lower
than expected.
2. Motor speed (RPM) too high.
3. Filters not in place.
4. Dampers or valves not adjusted properly.
Excessive Vibration
1. Loose mounting bolts, wheel set screws,
taper-lock hubs.
2. Worn or corroded blower wheel.
3. Accumulation of foreign material on
blower wheel.
4. Bent motor shaft.
5. Worn motor bearings.
6. Motor out of balance.
7. Inadequate structural support.
8. Support structure not sufficiently
cross braced.
9. Weak or resonant foundation.
10. Foundation not flat and level.
Motor Overheating NOTE: A normal motor will operate at 174ºF.
1. Actual system static pressure is lower
than expected.
2. Voltage supplied to motor is too high or
too low.
3. Motor speed (RPM) too high or
defective motor.
4. Air density higher than expected.
5. Motor wired correctly or loose wiring
connections.
Excessive Noise
1. Wheel rubbing inside of housing.
2. Worn or corroded blower wheel.
3. Accumulation of foreign material on
blower wheel.
4. Loose mounting bolts, wheel set screws,
or taper-lock hubs.
5. Bent motor shaft.
6. Worn motor bearings.
7. Motor out of balance.
8. Motor bearings need lubrication.
9. System resonance or pulsation.
Fan Doesn’t Operate
1. Motor wired incorrectly or loose wiring
connections.
2. Incorrect voltage supply.
3. Defective fuses or circuit breakers.
4. Power turned off elsewhere.
5. Defective motor
7
