4 sata controller, Sata controller, Raid function (if the sata function is assembled) – Kontron MSMSA104EX User Manual
Page 12: 4sata controller, 1 raid function
MSMSA104EX
/ SATA Controller
www.kontron.com
10
4
SATA Controller
The Silicon Image Sil3132 is a two-port PCI Express to SATA controller. The Sil3132 is designed to provide multiple
port SATA connectivity with minimal host overhead and host to device latency. The Sil3132 supports a 1-lane 2.5Gb7s
PCI Express BUS and the SATA Generation 2 transfer rate of 3.0G7b (300MB/s).
4.1 RAID Function
(if the SATA function is assembled)
RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks:
RAID technology manages multiple disk drives to enhance I/O performance and provide redundancy in order to
withstand the failure of any individual member, without loss of data. SATA Raid provides two RAID Set types, Striped
(RAID 0), Mirrored (RAID 1), Mirroring and Striping (RAID 10) and Parity RAID (RAID 5).
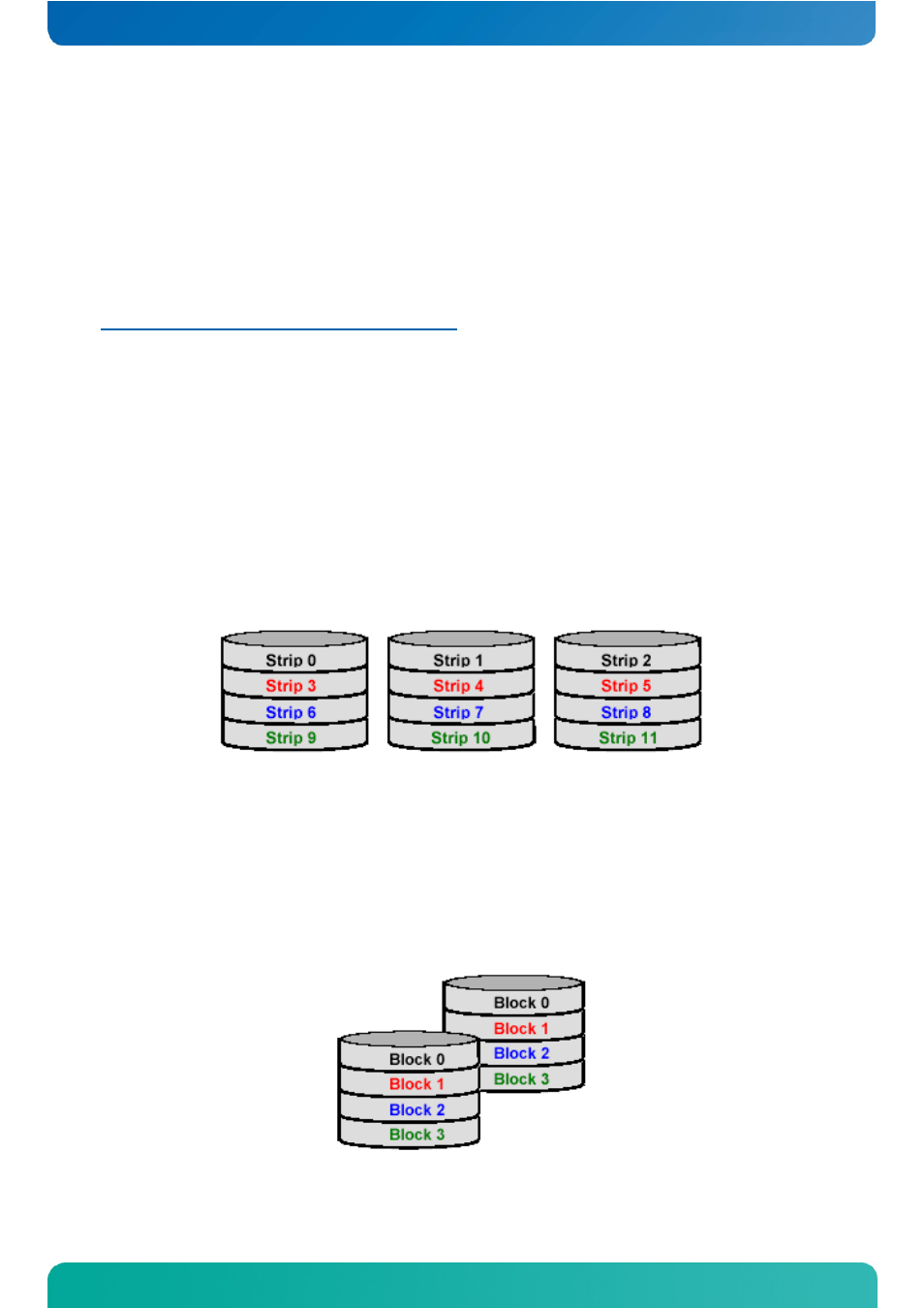
Disk Striping (RAID 0)
Striping is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. While Striping is discussed as a RAID Set
type, it actually does not provide fault tolerance. With modern SATA and ATA BUS mastering technology, multiple I/O
operations can be done in parallel, enhancing performance. Striping arrays use multiple disks to form a larger virtual
disk. This figure shows a stripe set using three disks with stripe one written to disk one, stripe two to disk two, and so
forth. RAID 0 sets can include two, three, four or five drives. If the sizes of the disk segments are different, the
smallest disk segment will limit the size of the RAID Group.
Disk Mirroring (RAID 1)
Disk mirroring creates an identical twin for a selected disk by having the data simultaneously written to two disks. This
redundancy provides instantaneous protection from a single disk failure. If a read failure occurs on one drive, the
system reads the data from the other drive. RAID 1 sets are typically comprised of two drives, and a third drive can be
allocated as a spare in case one of the drives in the set fails. Additional drives can be configured as part of a mirrored
set, but without much added benefit. If the sizes of the disk segments are different, the smallest disk segment will
limit the overall size of RAID Group.
