Dyras BPSS-4128 User Manual
Page 5
9
8
Should you happen to measure a blood pressure differing from the normal, healthy pressure, or
if you have any doubt in respect of the measured value, please have your blood pressure
checked by a specialist doctor for diagnostic purposes, so that you can control the value
measured by the appliance. We recommend that you take the appliance with you and ask for
the advice of the doctor.
• Do not use the appliance near to appliances emitting electromagnetic waves (e.g. mobile phones or microwave ovens).
They can disturb the appliance resulting in faulty measurement and incorrect values.
• If after switching on nothing appears on the display, check whether the batteries have been correctly inserted and that
they are correctly touching the battery contacts in the battery compartment.
• Please keep the appliance in its box when it is not in use, this way you can protect it against possible damage during
storage.
Please keep this instruction manual. If you give the device to anyone else,
you must give them this instruction manual, too!
MAIN COMPONENTS
1. Velcro cuff
2. LCD-display
3. On-/Off switch, “START/STOP” button
4. Memory recall buttons ”MEM”
5. Battery compartment
6. Battery compartment cover
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT BLOOD PRESSURE
Blood circulation ensures an appropriate supply of oxygen to the body. Blood pressure is the pressure the blood exerts on
the artery wall. The systolic value (upper value) can be measured when the myocardium contracts and forces blood into the
arteries. The diastolic value (lower value) is measured when the myocardium relaxes and blood flows from the veins into the
heart.
The BPSS-4128 classifies values obtained according to WHO (World Health Organization) recommendations and assigns
these into corresponding categories. Should either systolic or diastolic value fall into a higher category, the whole
measurement must be given a higher classification.
In the human body, blood pressure increases naturally with age. This is the result of aging of the blood vessels. Increased
blood pressure can be further aggravated by smoking, regular consumption of alcohol and drinks containing caffeine,
extreme salt consumption, stress and lack of regular exercise. Also latent diseases such as problems with the kidneys or a
high level of cholesterol (LDL) can cause increased blood pressure, because they result in the blood vessels losing flexibility.
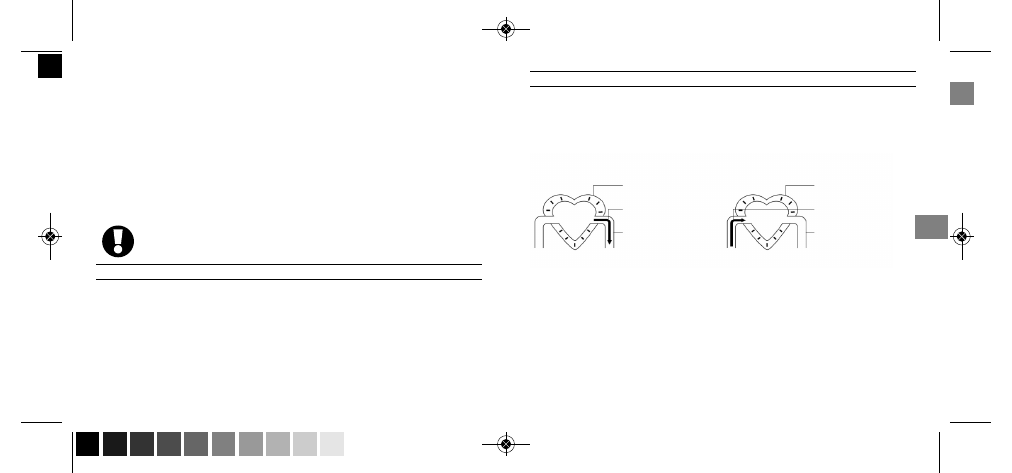
Systolic blood pressure
Myocardium contracts
Blood flows out
Pressure rises in
the blood vessels
Higher pressure
Myocardium relaxes
Blood flows back to the heart
Pressure decreases
in the blood vessels
Lower pressure
Diastolic blood pressure
EN
User'sManual code BPSS-4128_5lang:User's Manual for BPSS-4128 2010.12.15. 14:25 Page 8 (Black plate)
