Dell POWEREDGE R720 User Manual
Page 12
The high-level steps of the procedure are as follows:
•
Obtain a baseline wear indicator
•
Run the intended application for an extended time period
•
Re-check the wear indicator
•
Calculate wear over time
1. Make sure DIPM is disabled to ensure that the data collected is accurate.
2. Temporarily move the drive to a NON-Windows (Linux) SMART-capable system.
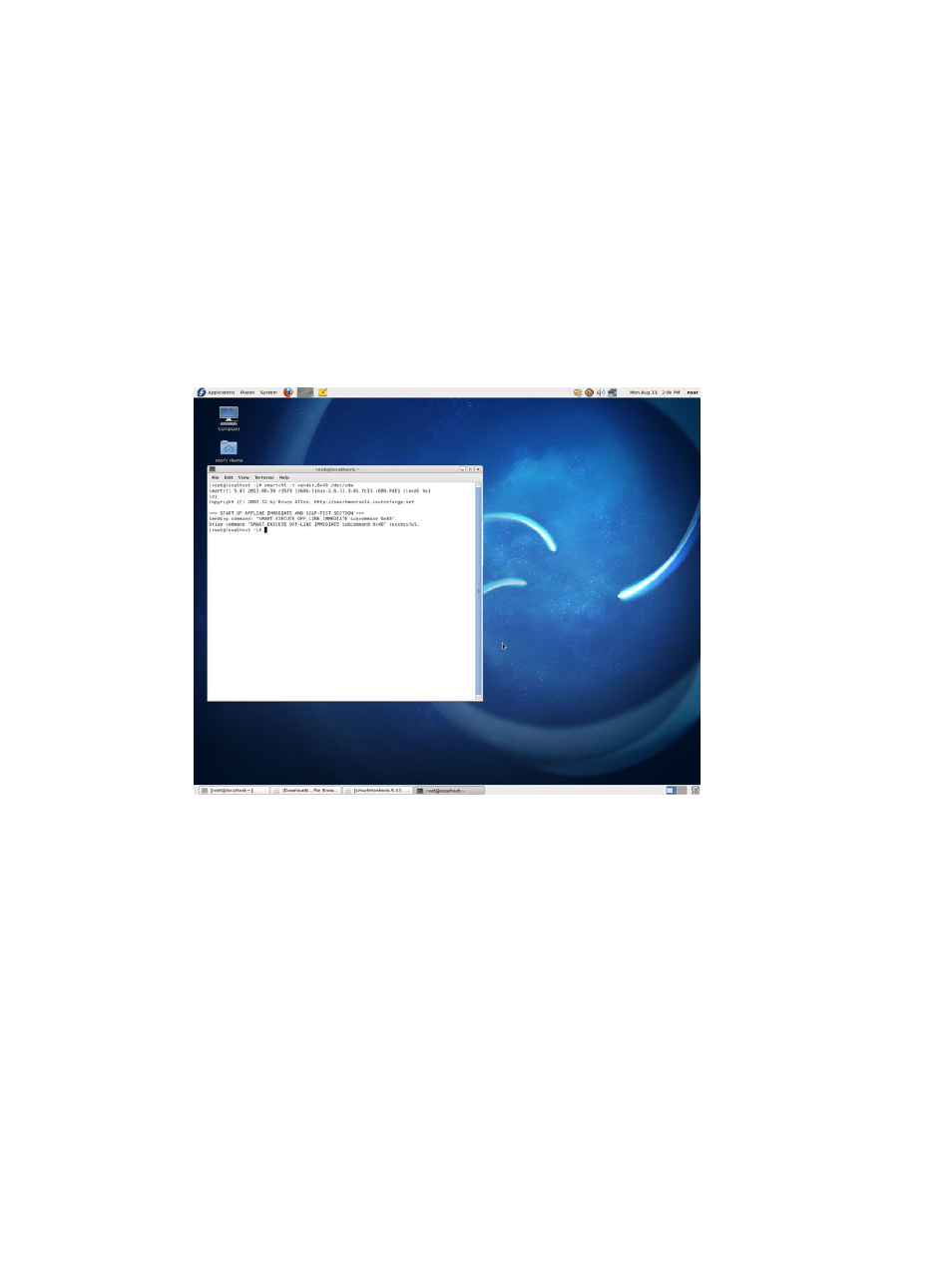
3. Issue the SMART EXECUTE OFF-LINE IMMEDIATE (D4h) sub-command 40h to reset the E4h (workload timer)
attribute.
– For example, utilizing smartctl version 5.43 in a Linux OS where the drive under test is /dev/sda you can
enter the following command line:
smartctl –t vendor,0x40 /dev/sda.
Figure 7. Resetting the SMART workload timer attribute
4. Return the drive to the Windows system where the workload will be measured.
5. Run the workload to be evaluated for at least 60 minutes (otherwise the drive wear attributes will not be available).
– For this example, the workload was run for about 22 hours.
– Iometer was used with a transfer size of 1MB with 100% random writes.
6. Do a clean system power down. Use either the ATA STANDBY IMMEDIATE command or leave the drive in the
system for 10 minutes prior to shutting down the system. This ensures that the drive will store all the drive wear
SMART attributes to persistent memory within the drive.
7. Return the drive to a non-Windows (Linux) SMART-capable system (the same system environment of step 2).
8. Read the drive wear attributes with the SMART READ DATA (D0h) command within 60 minutes after power-up.
– For example, a drive in a system with smartctl version 5.43 captures the SMART Read Data by running the
following command line:
smartctl –A /dev/sda.
12
