Using solve, Comp), K rules governing equations when using solve – Casio fx-115ES User Manual
Page 31
E-29
s
(or=)
10=
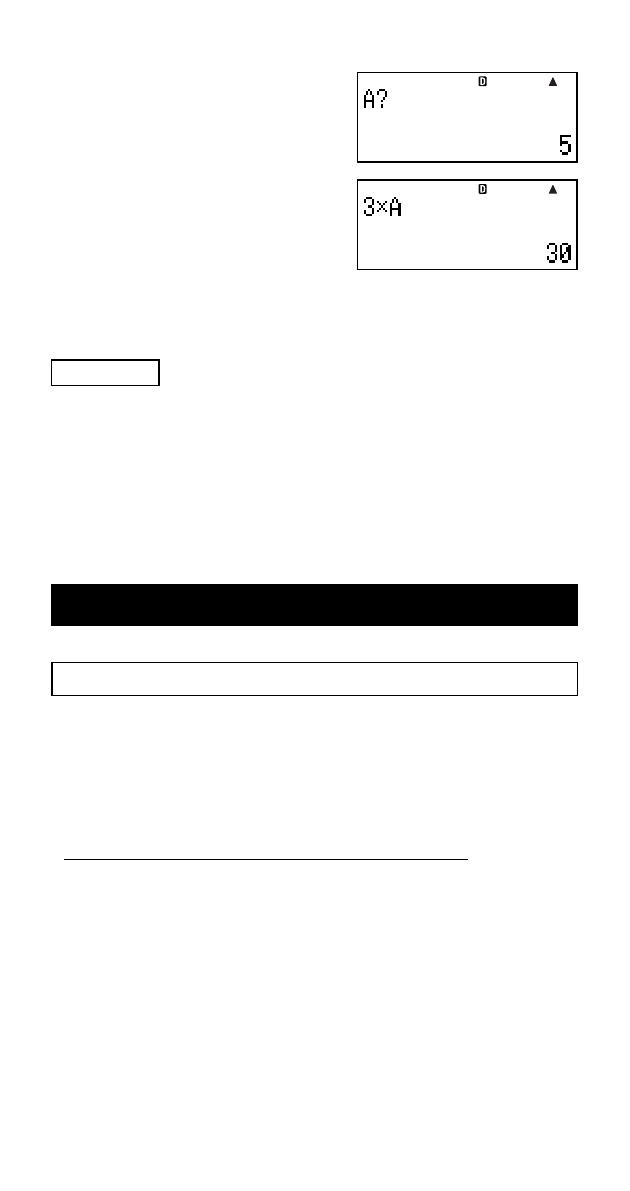
• To exit CALC, press A.
• If the expression you are using contains more than one variable,
an input prompt appears for each one.
Appendix
<#016> Calculate an
+1
= an +
2
n
(a
1
= 1) as the value of an changes
from a
2
to a
5
. (Results: a
2
= 3, a
3
= 7, a
4
= 13,
a
5
= 21)
*1
Assigns 1 to a
1
.
*2 Assigns 1 to
n
.
*3
Value of a
2
*4 Assigns value to a
2
.
*5
Assigns 2 to
n
.
*6 Value of a
3
*7
Value of a
4
*8 Value of a
5
Using SOLVE
(COMP)
SOLVE uses Newton’s Method of approximation to solve an equation.
You can use SOLVE in the COMP Mode (N1) only.
k Rules Governing Equations when Using
SOLVE
• You can use the following types of syntax for the solution variable.
Example: Y = X + 5, Y (Solves for Y.);
XB = C + D, B (Solves for B.)
The following shows the syntax for the log function.
Y = X
× log(2
(When the variable specification “,X” is omitted,
the equation Y = X
× log
10
2 is solved for X.)
Y = X
× log(2,Y (When the variable specification “,Y” is included,
the equation Y = X
× log
10
2 is solved for Y.)
Y = X
× log(2,Y) (When the variable specification “,X” is omitted,
the equation Y = X
× log
2
Y is solved for X.)
• Unless you specify otherwise, an equation is solved for X.
Example: Y = X + 5, X = sin(M), X + 3 = B + C,
XY + C (Treated as XY + C = 0.)
• SOLVE cannot be used to solve an equation that contains an
integral, derivative,
Σ
( function, Pol( function, Rec( function, or
multi-statement.
