Acceleration guide values – Retsch AS 200 control - natural frequency User Manual
Page 23
Retsch GmbH
23
Acceleration guide values
In the technical literature* on plant engineering sieve bottom
acceleration in „g“ is designated as the sieve characteristic
value K , and the relationship between the sieve characterisitc
value and sieving effect is described as follows:
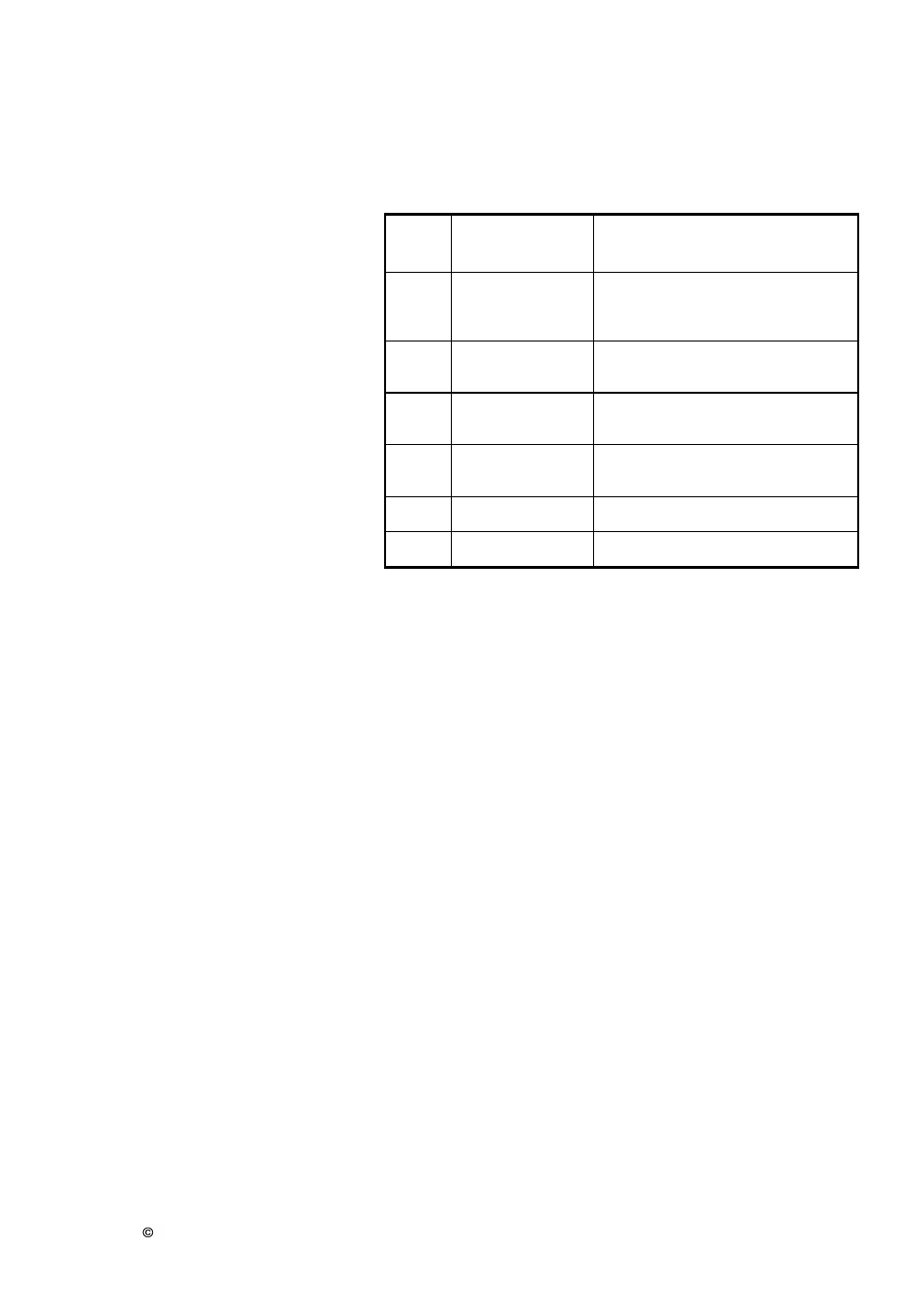
K
(„g“)
Sieved
material
movement
Sieving evaluation
1,0
No throwing,
flowing or sliding
movement
Very sluggish sieving effect, sieve
bottom is quickly blocked
1,5
Poor lifting of
sieved material
Sluggish sieving effect, sieve
bottom blocked slowly
1,8
Very flat throwing
action
Very gentle sieving for easily
sievable material
2,3
Flat to slightly
steep throwing
action
Gentle sieving for material difficult
to sieve
3,5
Steep throwing
action
Precise sieving
4
Very steep
throwing action
Very precise and loosening sieving
action
We have taken the liberty of supplementing the information
with the associated amplitudes for the two most common
mains frequencies in the world.
These data can be regarded only as guide values for small
quantities of sieved material if, owing to its distribution
characteristics, the material moves mainly under single grain
conditions on the sieve bottom.
However, under the usual thick layer conditions (multiple grain
layers) in the laboratory the impulses transmitted from the
sieve bottom are damped, and the sieve bottom of the
analytical sieve also vibrates. Therefore in laboratory practice
higher K-values are necessary than those resulting from
individual grain dynamics. In practice this means that the
above recommendations should be multiplied by a factor of 1.5
– 2.
*
Höffl, K.
Milling and classifying machines
Springer-Verlag 1986
