Behringer T1953 User Manual
Page 8
8
TUBE ULTRAGAIN T1953
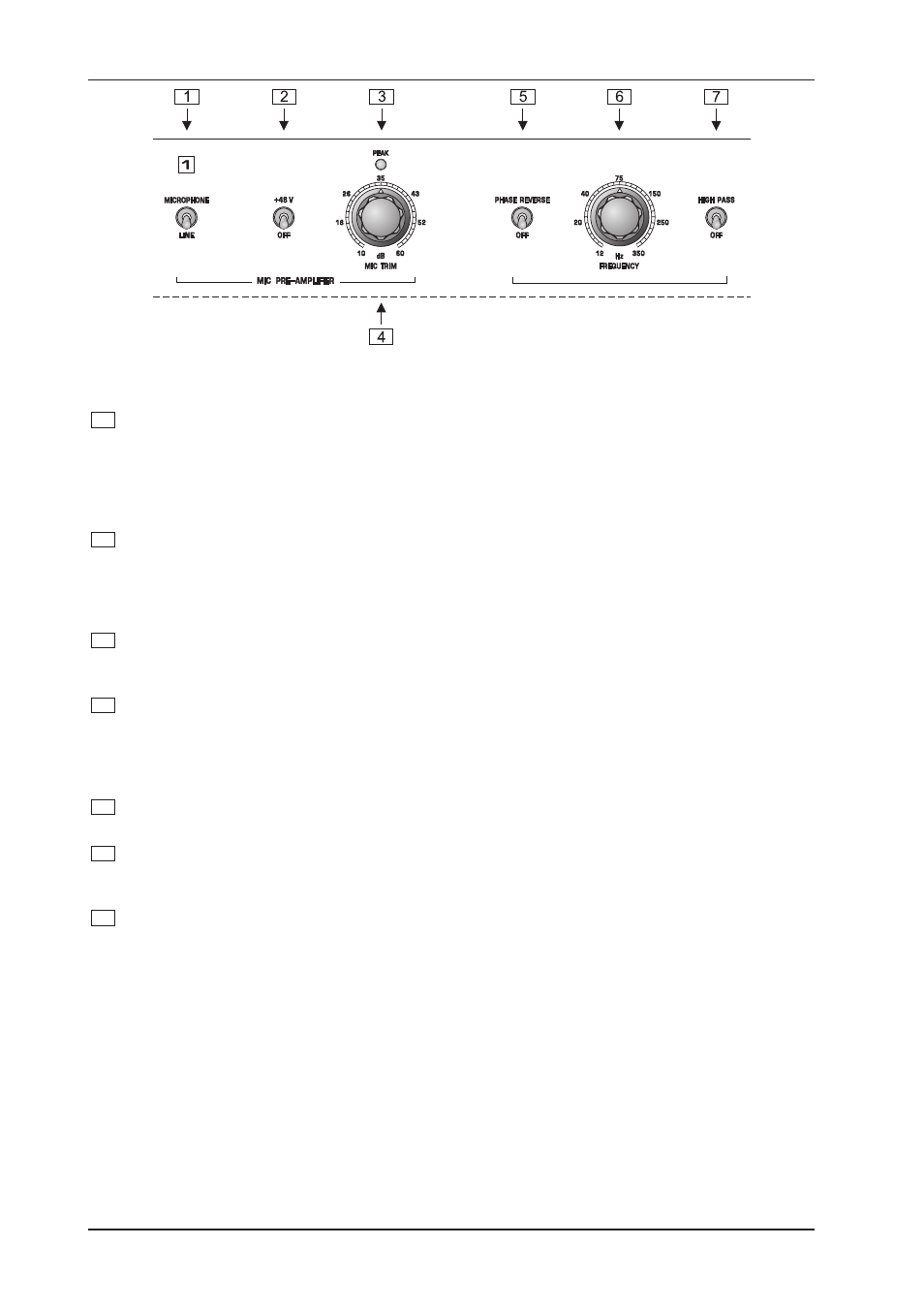
Fig. 1.2: Control elements on the front panel
1
Use the MIC/LINE switch to toggle between MIC and LINE modes. When the switch in up position, the
unit works in MIC mode (now you can activate the +48 V switch if required; in LINE mode this function
is disabled). The newly developed UTC circuitry is active in both modes.
+
Please note that the input phone jack is disabled in MIC mode, i.e. you must use the XLR
connector to access the microphone amp.
2
This +48 V switch activates the +48 V phantom power circuit that uses the signal leads to supply
condenser microphones with the required operating voltage.
+
Please check the connected signal source for matching specifications before you switch
phantom power on, so as to avoid damage to the microphone, etc.
3
The CLIP LED signals that a level of at least +18 dBu is present after the microphone amp stage. With
too high a level the CLIP LED warns you to reduce the gain with the MIC TRIM control, so as to avoid
distortion caused by overloading. During normal operation, the LED should not light up at all.
4
The MIC TRIM control is enabled in MIC mode only and allows for applying gain from 10 to 60 dB to the
input signal. In view of the extremely high gain levels that can be applied, you should verify that the gain
control is properly set before you power up the unit. In case of doubt, set the control fully counter-
clockwise, and start from there slowly raising the gain. High gain settings and the resulting levels can
damage subsequent devices.
5
With the PHASE REVERSE switch the input signal is reversed in phase by 180°. This function is
available both in MIC and LINE modes.
6
When the high pass filter is in high position, the FREQUENCY control defines the filters cut-off
frequency. With a setting range from 12 to 350 Hz the filters main task is to eliminate bottom-end
rumble noise, etc.
7
The HIGH PASS switch activates/deactivates the filter.
1. INTRODUCTION
