9 phantom power – Behringer T1953 User Manual
Page 19
19
TUBE ULTRAGAIN T1953
V
ideo
T
ape
Compact
Disc
Analog
Records
FM
Radio
Digital
T
ape
(16
Bit)
Analog
T
ape
dB
100
75
50
25
Analog
Mixing
Console
Fig. 4.8: Dynamic range of various media
4.9 Phantom power
Condenser microphones need a specific supply voltage polarizing the condenser diaphragm. This voltage can
be furnished from an internal battery, or an external power supply that is either connected directly to the
microphone or supplies the voltage through the microphone cable. In practice, this technique is usually referred
to as +48 V or phantom power supply, and uses the microphone cable to carry both the audio signal and the
supply voltage required for the microphone.
Please read this chapter thoroughly: phantom power can damage the microphone, if used improperly.
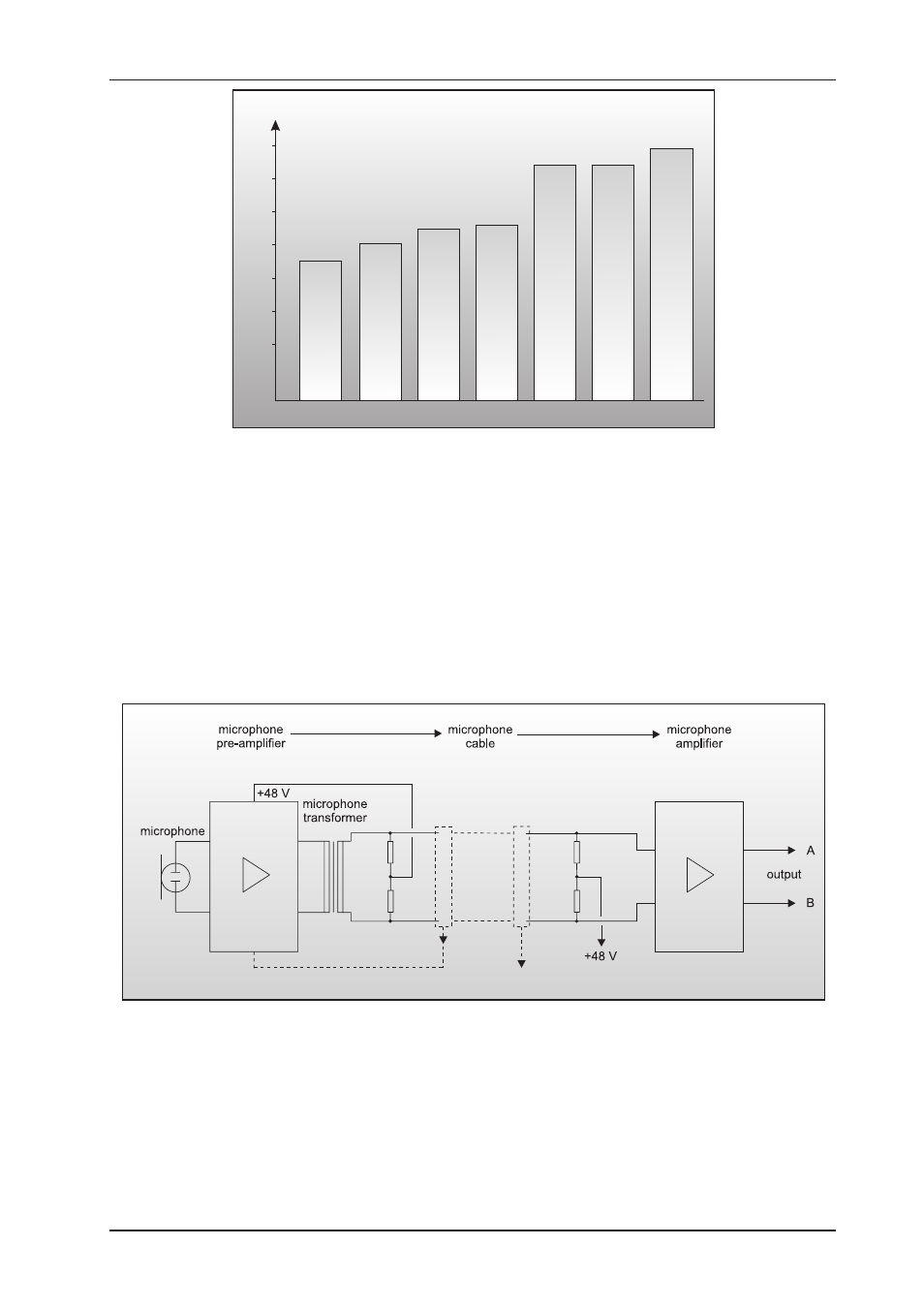
Fig. 4.9: Functional diagram of phantom power supply
We speak of phantom power when a microphone cable is used to carry several signals, with a DC voltage
layered on the actual audio signal. The typical phantom DC voltage is +48 V, which is applied both to the
positive (pin 2) and negative inputs (pin 3) of the XLR connector, using current-limiting resistors. As the
phantom voltage is split up in a balanced configuration among the signal leads, there is no need to apply it
directly to the microphone transducer or the microphone itself, where it could damage the transducer and/or
capsule. In an unbalanced configuration, DC voltage would be applied directly, which would inevitably lead to
disturbing noise or could even damage the electronics.
4. TECHNICAL BACKGROUND
