How write-once and rewritable dvds work – Sony RDR-GX7 User Manual
Page 8
3
During DVD recording, a powerful laser beam, stronger than that used for playback,
heats up the recording material, changing it to represent the data. Write-once DVDs use
chemical change, while rewritableDVDs make use of phase change.
8
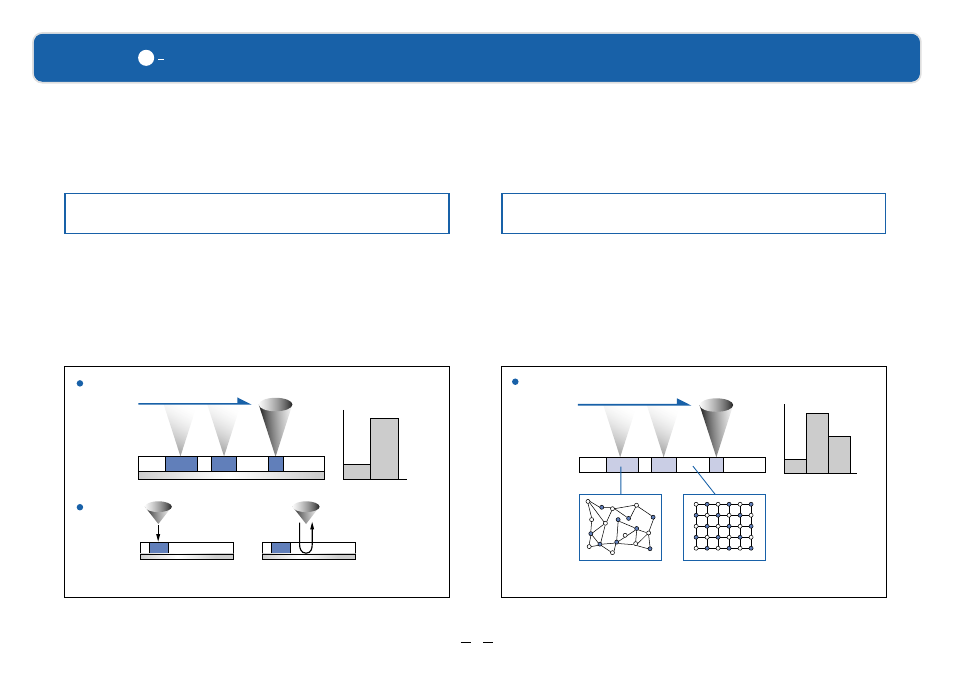
How Write-once and Rewritable DVDs work.
During recording, a powerful laser beam is focused on the organic dye
recording material, and the heat from the laser changes the chemical
structure of the dye. During playback, the playback laser can sense which
parts of the dye have been changed by heat and which haven’t. Through this
process the [0] and [1] of a digital signal can be represented. However,
changes in the dye structure are permanent, so the disc cannot be rewritten.
In write-once recording,
the organic dye is chemically changed.
Recording material layer
Reflective layer
Playback
Recording
Playback of an area
heated by the laser
Laser
Playback of an area
not heated by the laser
Laser pickup
Required laser output during
recording and playback
Recording time
Playback
The recording material used is in crystalline form before recording.
When it is heated by the powerful laser, it becomes amorphous and
loses its crystalline structure. However, weaker laser light can be used to
slowly heat it to return it to its original crystalline form. In this way, the disc
can be rewritten over and over.
In rewritable recording,
the phase of the recording material is changed.
Recording time
Recording material layer
(Reflective layer)
Playback Recording
Erasing
Amorphous structure
Crystalline structure
Laser
Laser pickup
Required laser output during
recording and playback
Amorphous and crystalline
structures have different
reflective ratios, so the [0] and
[1] of Through this process
the [0] and [1] of a digital signal
can be represented.
Differences in
writable DVD
1
1
