1 cr1000 vapor pressure example – Campbell Scientific HMP60 Temperature and Relative Humidity Probe User Manual
Page 21
HMP60 Temperature and Relative Humidity Probe
VaporPressure() instruction to calculate vapor pressure from temperature and
relative humidity measurements (see Section 7.6.1). Edlog dataloggers must
first calculate the saturation vapor pressure and then calculate vapor pressure
(see Section 7.6.2).
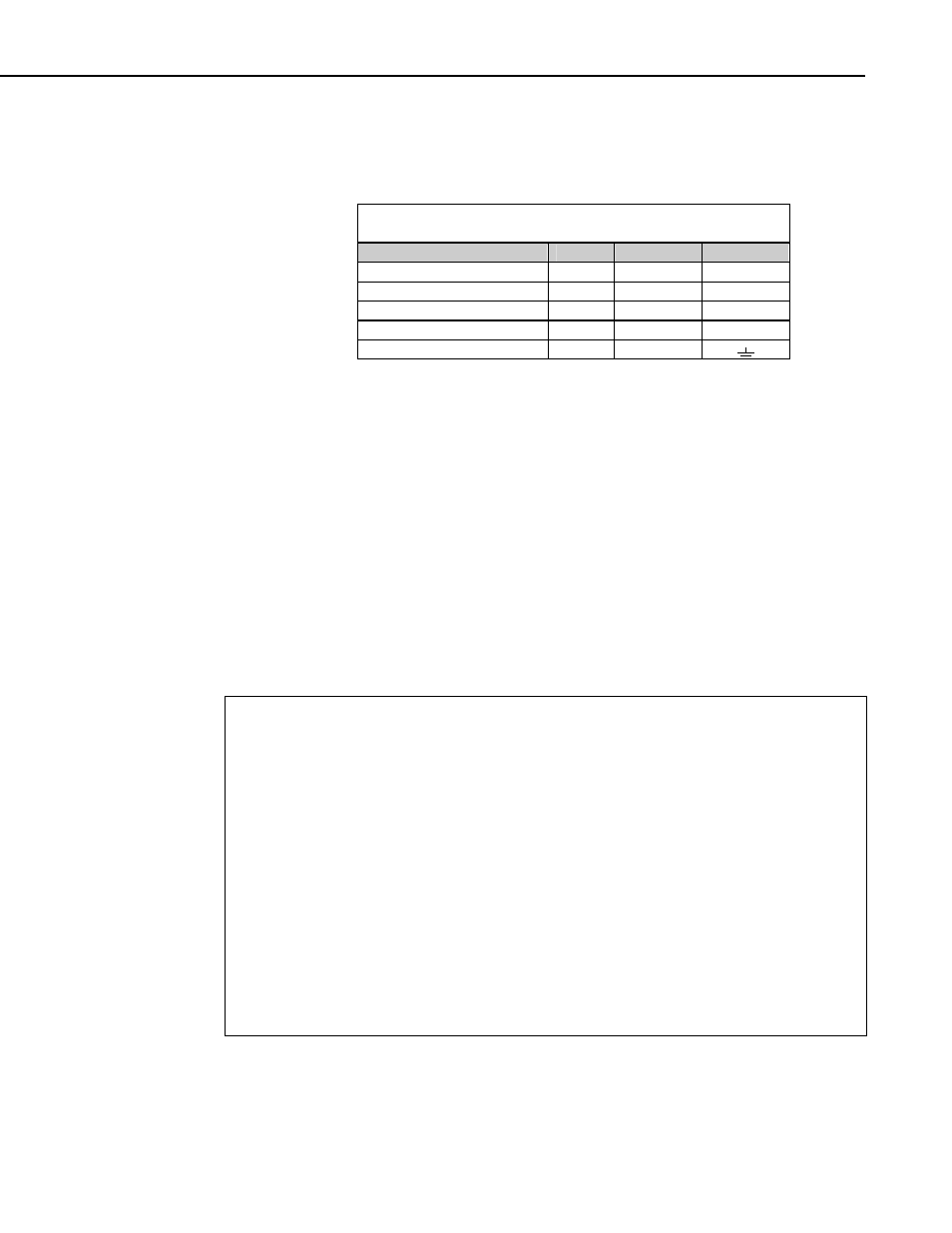
TABLE 7-5. Wiring for Vapor Pressure Examples
Description
Color
CR10(X)
CR1000
Temperature
Black
SE 3 (2H)
SE 1 (1H)
Relative Humidity
White
SE 4 (2L)
SE 2 (2H)
Signal & Power Reference
Blue
G
G
Power
Brown
12 V
12 V
Shield Clear
G
7.6.1 CR1000 Vapor Pressure Example
The VaporPressure() instruction has the following syntax:
VaporPressure(Dest,Temp,RH)
Where:
Dest—the variable in which the results of the instruction will be stored.
Temp—the program variable that contains the value for the temperature sensor.
The temperature measurement must be in degrees Celsius.
RH—the program variable that contains the value for the relative humidity
sensor. The relative humidity measurement must be in percent of RH.
'CR1000
Public AirTC
Public RH
Public VP
DataTable(Table1,True,-1)
DataInterval(0,60,Min,0)
Average(1,AirTC,FP2,0)
Sample(1,RH,FP2)
Average(1,VP, FP2,0)
EndTable
BeginProg
Scan(5,Sec,1,0)
'HMP60 Temperature & Relative Humidity Sensor measurements AirTC and RH:
VoltSE(AirTC,1,mV2500,1,0,0,_60Hz,0.1,-40.0)
VoltSE(RH,1,mV2500,2,0,0,_60Hz,0.1,0)
If (RH>100) And (RH<108) Then RH=100
VaporPressure(VP,AirTC,RH)
CallTable(Table1)
NextScan
EndProg
15
