3. typical soil water potential, r, And v – Campbell Scientific 227-L Delmhorst Cylindrical Soil Moisture Block User Manual
Page 16
227 Delmhorst Cylindrical Soil Moisture Block
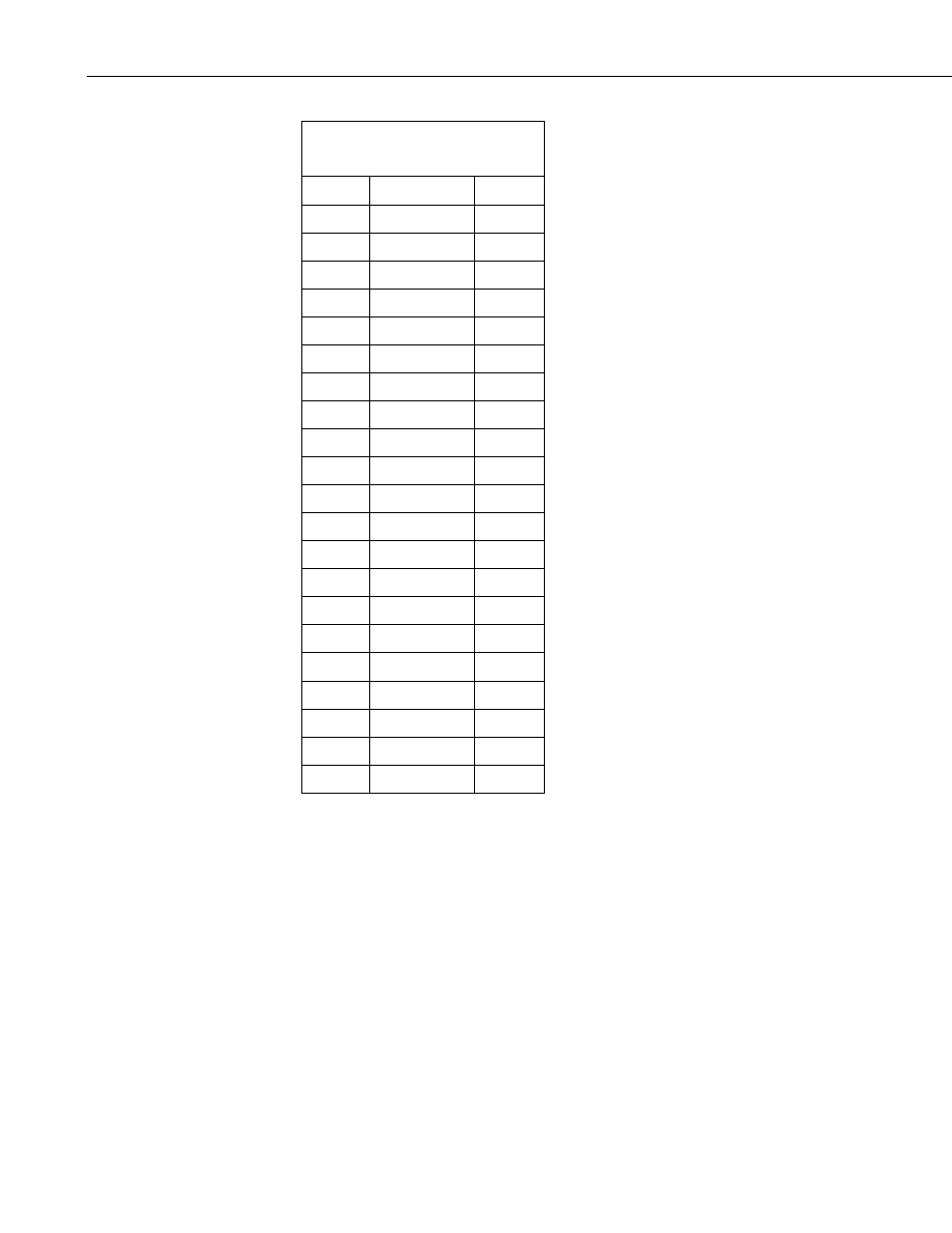
TABLE 7-3. Typical Soil Water
Potential, R
s
and V
s
/ V
x
BARS R
s
(kohms)
V
s
/V
x
0.1 0.060
0.0566
0.2 0.130
0.1150
0.3 0.260
0.2063
0.4 0.370
0.2701
0.5 0.540
0.3506
0.6 0.750
0.4286
0.7 0.860
0.4624
0.8 1.100
0.5238
0.9 1.400
0.5833
1.0 1.700
0.6296
1.5 3.400
0.7727
1.8 4.000
0.8000
2.0 5.000
0.8333
3.0 7.200
0.8780
6.0 12.500 0.9259
10.0 17.000
0.9444
11.0 22.200
0.9569
12.0 22.400
0.9573
13.0 30.000
0.9677
14.0 32.500
0.9701
15.0 35.000
0.9722
For the typical resistance values listed in TABLE 7-3, soil water potential
(bars) is calculated from sensor resistance (R
s
) using a 5th order polynomial
(FIGURE 7-2 and TABLE 7-4). The nonlinear relationship of R
s
to bars rules
out averaging R
s
directly.
The polynomial is entered as an expression in CRBasic or by Edlog instruction
Polynomial (P55). The polynomial to calculate soil water potential is fit to the
0.1 to 10 bar range using a least square fit. TABLE 7-4 lists the coefficients
and equation for the 0.1 to 10 bar polynomial.
10
- 014A Met One Wind Speed Sensor (36 pages)
- 020C Wind Direction Sensor (26 pages)
- 024A-L Met One Wind Direction Sensor (30 pages)
- 03001-L R.M. Young Wind Sentry Set (34 pages)
- 03002, 03101, and 03301 R. M. Young Wind Sentry Sensors (40 pages)
- 034A-L WindSet (16 pages)
- 034B-L Met One Windset (34 pages)
- 036, 038 Spark Gapped Junction Box (6 pages)
- 05103, 05103-45, 05106, and 05305 R. M. Young Wind Monitors (30 pages)
- 083E Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensor (22 pages)
- 0871LH1 Freezing Rain Sensor (31 pages)
- 092 Barometric Pressure Sensor (24 pages)
- 10164-L Water Sampler Control Cable for use with Isco and Sigma Autosamplers (18 pages)
- 107-L Temperature Probe (28 pages)
- 108-LC Temperature Probe for MetData1 (12 pages)
- 108-L Temperature Probe (30 pages)
- 109-L Temperature Probe (30 pages)
- 109SS Temperature Probe (32 pages)
- 110PV Surface Temperature Probe (32 pages)
- 21108 RF450 Demo Kit (14 pages)
- 223-L Delmhorst Cylindrical Soil Moisture Block (28 pages)
- 229 Water Matric Potential Sensor and CE4/CE8 (34 pages)
- 237-L Leaf Wetness Sensor (14 pages)
- 247-L Conductivity and Temperature (18 pages)
- 253-L and 257-L (Watermark 200) Soil Matric Potential Sensors (36 pages)
- 25458 DIN-Rail Terminal Kit (10 pages)
- 255-100 Novalynx Analog Output Evaporation Gauge (16 pages)
- 260-953 Alter-Type Wind Screen for Tipping Bucket Rain Gages (14 pages)
- 27106T Gill Propeller Anemometer (18 pages)
- 30066 Battery Terminal Bus (1 page)
- 380, 385, 380M, 385M Met One Rain Gages (22 pages)
- 3WHB10K 3-Wire Half-Bridge Terminal Input Module (14 pages)
- 43347 RTD Temperature Probe and 43502 Aspirated Radiation Shield (40 pages)
- 4386 Battery Terminal Bus (1 page)
- 4WFB120, 4WFB350, 4WFB1K 4-Wire Full Bridge Terminal Input Module (22 pages)
- 4WFBS120, 4WFBS350, 4WFBS1K 4 Wire Full Bridge Terminal Input Modules (46 pages)
- 4WPB100, 4WPB1K PRT Terminal Input Modules (16 pages)
- 52202 Electrically Heated Rain and Snow Gage (16 pages)
- 9522B Iridium Satellite Modem and COM9522B Interface Modem (46 pages)
- A100LK Anemometer (18 pages)
- A150 Desiccated Case (12 pages)
- A21REL-12 Relay Driver (10 pages)
- A6REL-12 Relay Driver (12 pages)
- AL200 ALERT2 Encoder, Modulator, and Sensor Interface (44 pages)
