Operation – Power Jacks C-Series User Manual
Page 17
www.powerjacks.com
17
5
Operation
5.2.11
Shock Loads on a Screw Jack
Shock loads should be eliminated or reduced to a minimum, if they cannot be avoided, the screw
jack model selected should be rated at twice the required static load.
For severe shock load applications, use the E-Series, S-Series or M-series screw jacks, the load
bearings here can be replaced with heat-treated steel thrust rings which is an option available
from Power Jacks. Note this will increase the input torque by approximately 100%.
5.2.12 Axial Backlash in a Screw Jack
5.2.12.1 Backlash in Standard Machine Screw Jacks
Machine screw jacks have backlash due not only to normal manufacturing tolerances, but to the
fact that there must be some clearances to prevent binding and galling when the screw jack unit
is under load. Usually, the axial backlash is not a problem unless the load on the screw jack unit
changes between compression and tension. If a problem does exist, then a unit with the anti-
backlash feature should be considered.
5.2.12.2 Screw Jacks with the Anti-Backlash Device
The anti-backlash device reduces the axial backlash between the lead screw and nut assembly
to a regulated minimum. As the backlash will increase as the lead screw thread on the gear
wears the anti-backlash device can be adjusted to remove this normal condition.
5.2.13
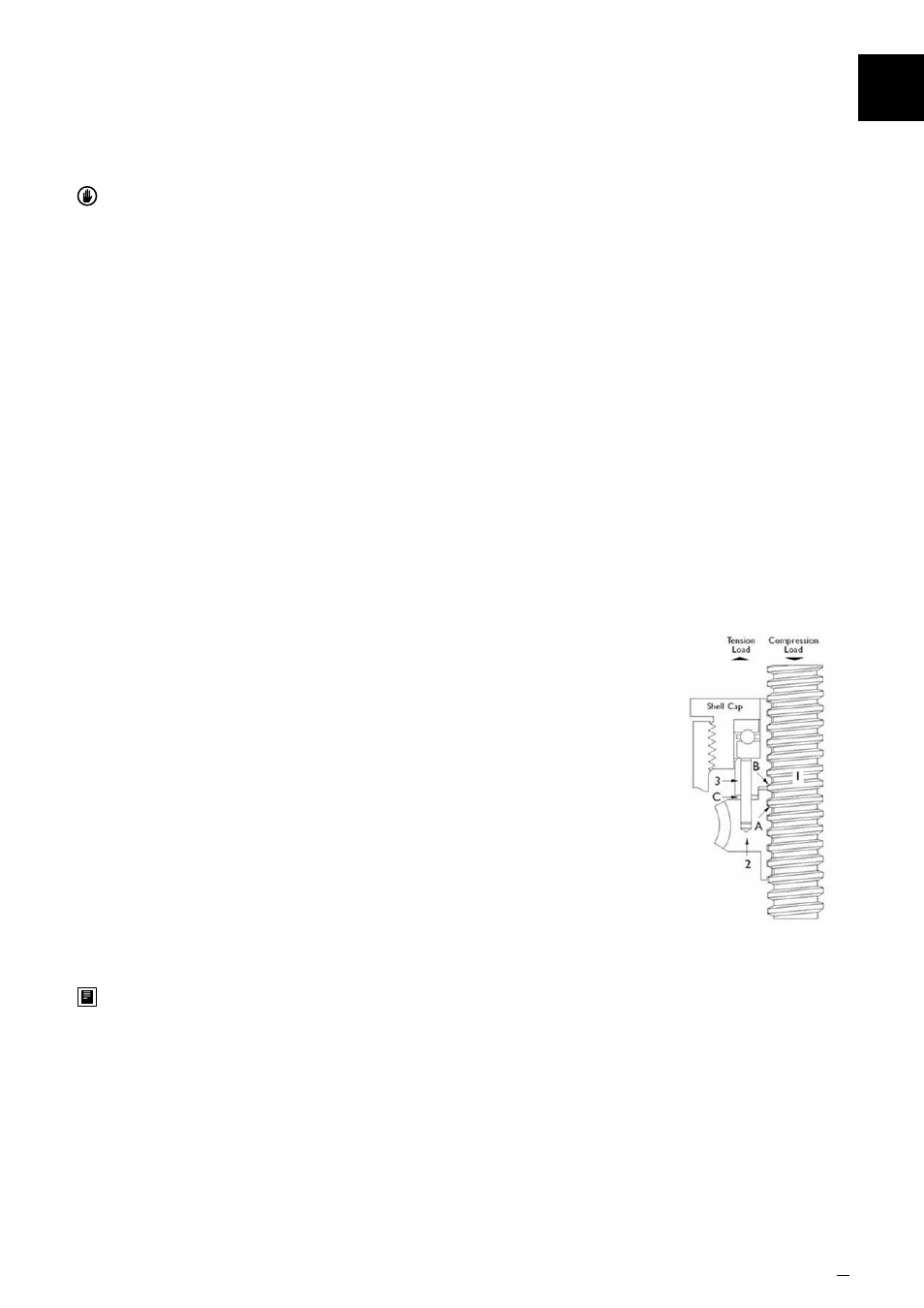
How the Anti-Backlash Device Works
When the screw (1) is under a compression load, the bottom of its
thread surfaces are supported by the top thread surfaces of the worm
gear (2) at point (A). The anti-backlash nut (3), being pinned to the
worm gear and floating on these pins and being adjusted downward
by the shell cap, forces its bottom thread surfaces against the upper
thread surfaces of the lifting screw at point (B). Thus, backlash
between worm gear threads is reduced to a regulated minimum.
When wear occurs in the worm gear threads and on the load carrying
surfaces of the lifting screw thread, the load carrying thickness of the
worm gear thread will be reduced. This wear will create a gap at point
(B) and provide backlash equal to the wear on the threads.
Under compression load, the lifting screw will no longer be in contact
with the lower thread surface of the anti-backlash nut. Under this
condition, backlash will be present when a tension load is applied.
The anti-backlash feature can be maintained simply by adjusting the shell cap until the desired
amount of backlash is achieved.
To avoid binding and excessive wear do not adjust lifting screw backlash to less than 0.025mm
(0.001”). This will reduce the calculated separation (C) between the anti-backlash nut and worm
gear and will reduce the backlash between the worm gear threads and the lifting screw to the
desired minimum value.
When separation (C) has been reduced to zero, wear has taken place. Replace the worm gear
(2) at this point. This feature acts as a built in safety device which can be used to provide wear
indication for critical applications.
5.2.14
Column Strength of the Screw Jack
Column strength of a screw is determined by the relationship between the screw length and its
diameter. For column strength charts consult product literature or Power Jacks.
