Next-generation powerpc architecture – Apple Power Mac G5 User Manual
Page 7
Next-Generation PowerPC Architecture
The design of the PowerPC G5 is based on the execution core of IBM’s 64-bit POWER4
processor—recipient of the Microprocessor Report’s 2001 Analyst’s Choice Award
for Best Workstation/Server Processor, which recognizes excellence in semiconductor
technology innovation, design, and implementation. With two double-precision
floating-point units, advanced branch prediction logic, and support for symmetric
multiprocessing, the POWER4 drives IBM’s top-of-the-line pSeries 690 servers.
Apple and IBM leveraged this industry-leading design to introduce the world’s first
64-bit desktop processor. The development of the PowerPC G5 builds on previous
PowerPC designs, combining an optimized Velocity Engine with a superscalar, super-
pipelined execution core that supports up to 215 simultaneous in-flight instructions.
This high-bandwidth core has over 12 discrete functional units that can process
instructions in parallel.
For more information about the PowerPC G5 architecture, see
www.apple.com/g5processor.
7
Technology and
Performance Overview
Power Mac G5
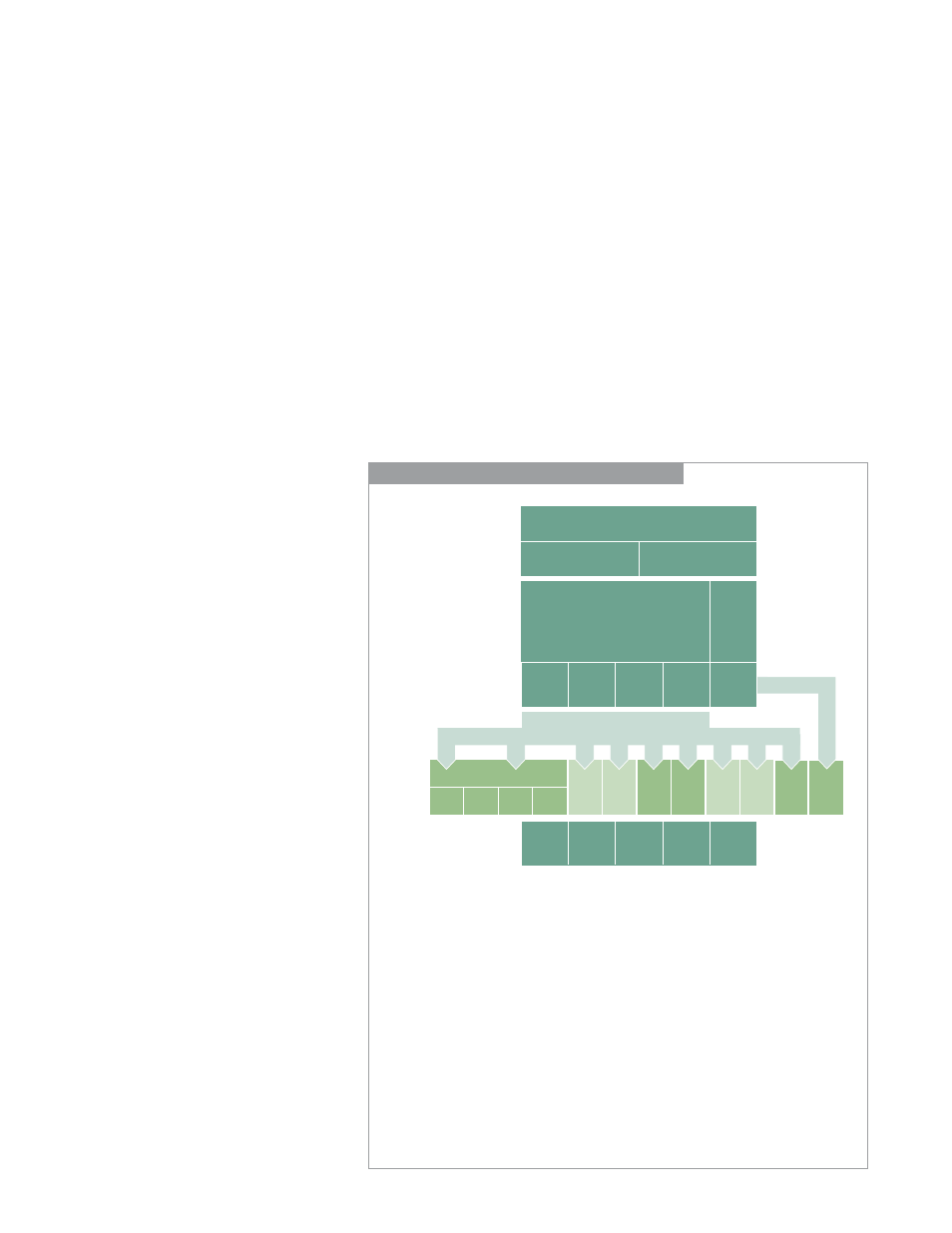
PowerPC G5 Architecture
Execution
Core
Complete
1
2
3
4
5
Velocity Engine
Floating
Point
Permute
Simple
Complex
Floating
Floating
Point
Integer
Integer
Load
Store
Load
Store
Condition
Register
Branch
Instruction Queues
Dispatch
Fetch and Decode
L2 Cache
L1 Instruction Cache
1
2
3
4
5
L1 Data Cache
Branch
12 Functional
Units
The execution core contains 12 discrete functional units:
• A dual-pipelined Velocity Engine uses two very large queues and dedicated 128-bit
registers to perform single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) processing.
• Two 64-bit double-precision floating-point units provide the speed and accuracy
required for highly complex scientific computations.
• Two 64-bit integer units perform calculations for a broad range of simple and complex
computing tasks.
• Two load/store units manage data as it is processed, keeping the processor’s registers
filled for faster operations.
• The condition register stores the results of branch predictions to improve the accuracy
of future predictions.
• The branch prediction unit uses innovative three-component logic that increases the
accuracy of speculative operation and maximizes processor efficiency.
