Electrical connections – KROHNE OPTIFLUX 4040 C Ex EN User Manual
Page 14
3
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
14
OPTIFLUX 4040 C
www.krohne.com
09/2010 - 7312232100 - AD EX OPTIFLUX 4040 C R01 en
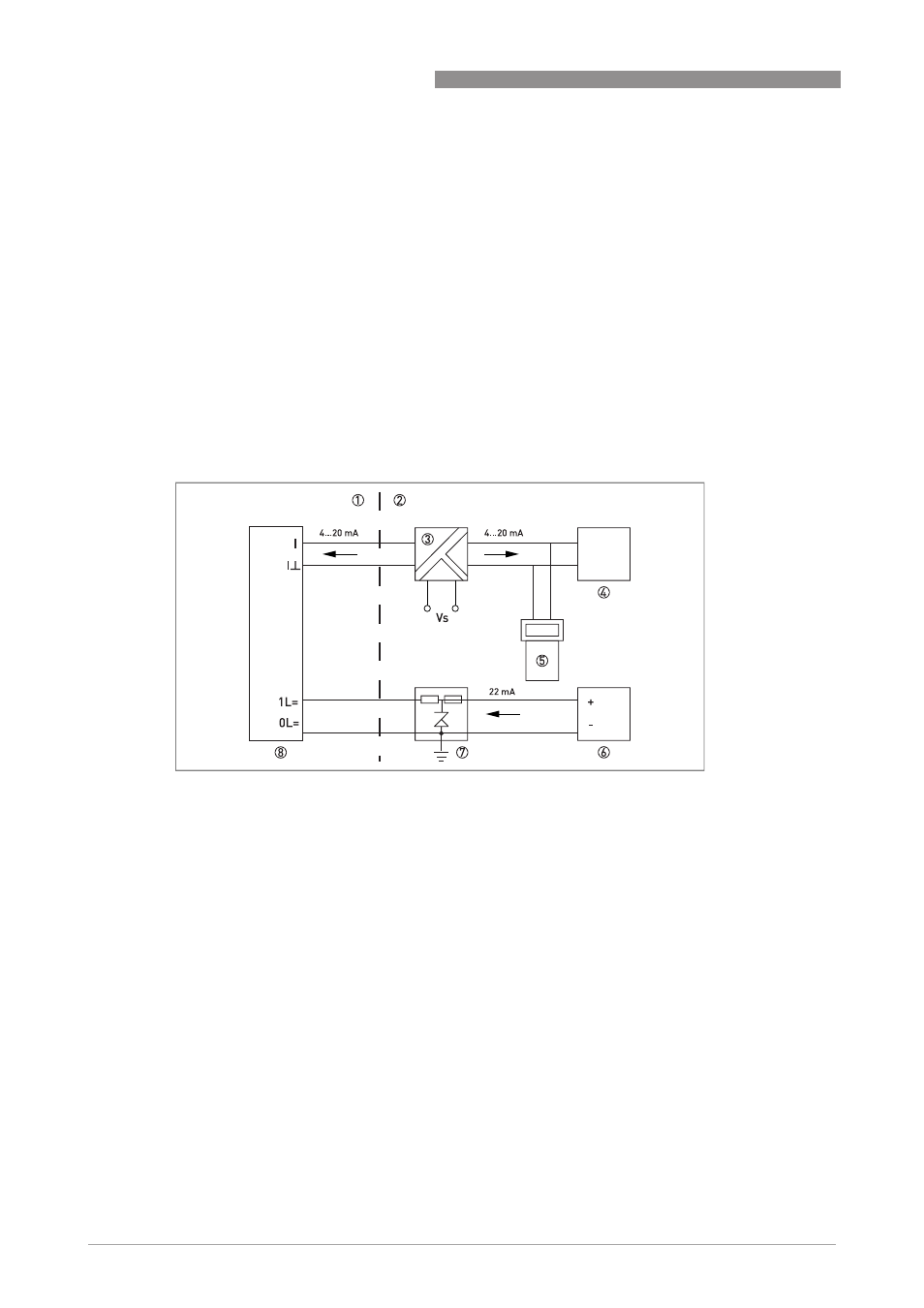
3.5.2 Example of OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx in 2x2-wire mode (4-wire)
The diagram shows an example of the connection of the OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx in 2x2-wire
mode. As in the previous example, the terminal compartment is again version A.
The additional power supply (terminals 1L=, 0L=) of the OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx is supplied by an
external power supply unit through an "EEx i" zener barrier with a linear output load.
The connection of the current output (terminals I, I
gnd
) and the additional power supply
(terminals 1L=, 0L=) is insensitive for polarity reversal.
Important notes
• Only one of the two connected circuits of the OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx, namely the "currrent
output" or the "additional power supply" may be earthed to maintain the required galvanic
separation between the two circuits!
• It is strictly interdicted to use the IMoCOM adapter with the IFC 040-EEx unit!
The voltage of the external power supply unit must be carefully chosen to keep it within the
allowed limits. The upper limit is determined by the maximum working voltage of the zener
barrier, which in general lies a few volts below the maximum open voltage value U
o
of the used
zener barrier. The lower limit is determined by the sum of the minimum working voltage of the
additional power supply of the OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx flowmeter of 14 V and the voltage drop over
the zenerbarrier caused by the end-to-end resistance of the barrier and (if not neglectable) the
serie cable resistance. This voltage drop can be significant. The above described determination
of the external power supply voltage is explained by the following example.
Figure 3-3: Connection example in 4-wire mode
1 Hazardous area
2 Safe area
3 Transmitter power supply (EEx i)
4 Process / display unit
5 Hand held terminal
6 External power supply
7 Zener barrier
8 OPTIFLUX 4040 C-EEx
