3 wireless advanced, 1 beacon interval, Wireless advanced – Advantech EKI-1351 User Manual
Page 40
EKI-1351/1352 User Manual
34
3.3.3
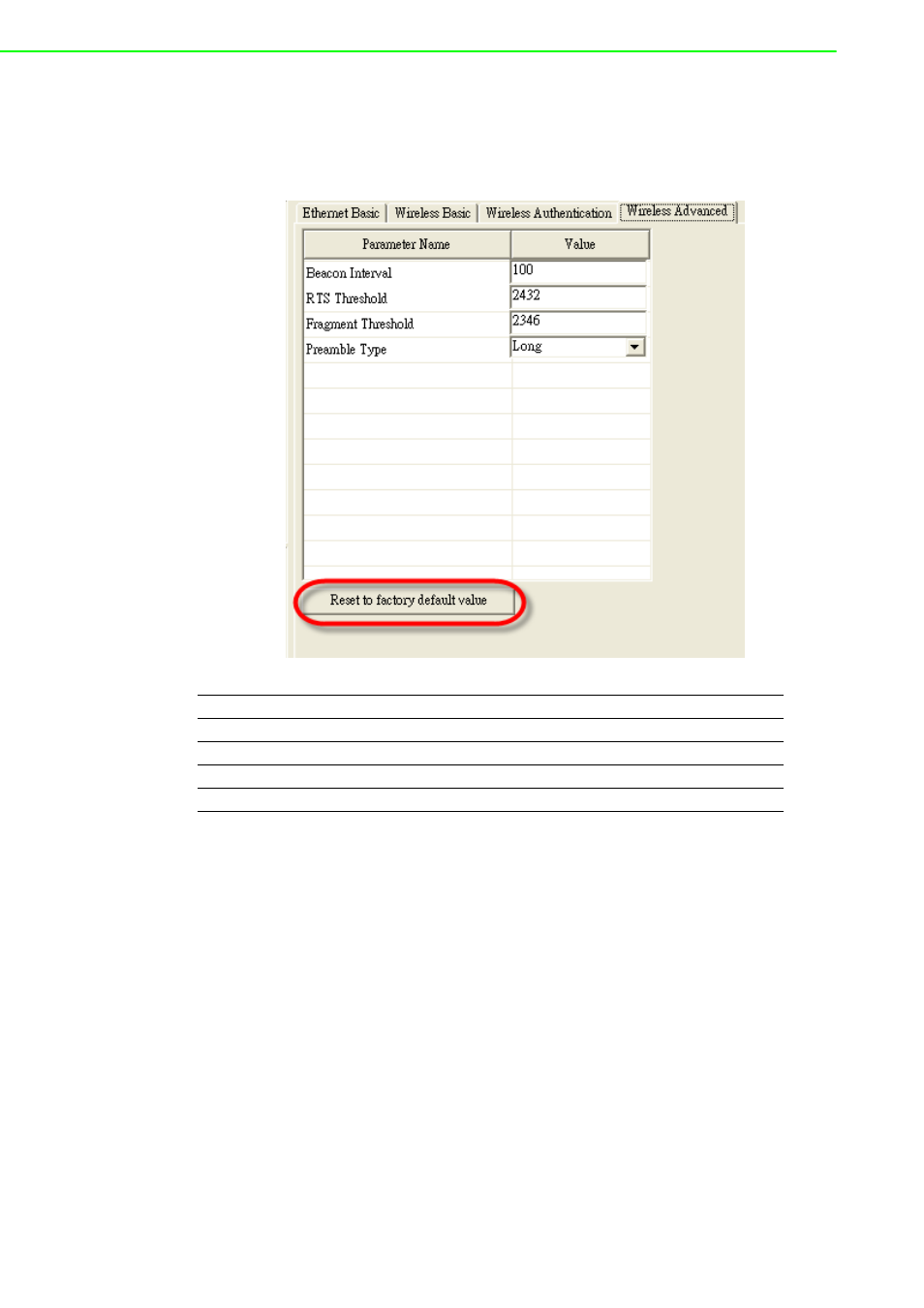
Wireless Advanced
The tab identifies several parameters that are related to the 802.11b/g wireless net-
work. We strongly suggested the default settings are not changed unless necessary.
If you want to recovery to factory value, you click the “Reset to factory default value”.
3.3.3.1
Beacon Interval
In infrastructure networks, the access point periodically sends beacons. You can set
the beacon interval with the access point configuration screen. In general, the bea-
con interval is set to 100 ms, which provides good performance for most applications.
In ad hoc networks, there are no access points. As a result, one of the peer stations
assumes the responsibility for sending the beacon. After receiving a beacon frame,
each station waits for the beacon interval and then sends a beacon if no other station
does so after a random time delay. This ensures that at least one station will send a
beacon, and the random delay rotates the responsibility for sending beacons.
By increasing the beacon interval, you can reduce the number of beacons and asso-
ciated overhead, but that will likely delay the association and roaming process
because stations scanning for available access points may miss the beacons. You
can decrease the beacon interval, which increases the rate of beacons. This will
make the association and roaming process very responsive; however, the network
will incur additional overhead and throughput will go down. In addition, stations using
power save mode will need to consume more power because they’ll need to awaken
more often, which reduces power saving mode benefits.
Parameters
Default Value
Range
Beacon Interval
100
0~65535
RTS Threshold
2347
0~2347
Fragment Threshold
2346
256~2346
Preamble
Long
Long/Short
