Helmet care and maintenance, Shade guide settings – Lincoln Electric IM10086 SHADE 11 AUTO-DARKENING HELMET User Manual
Page 5
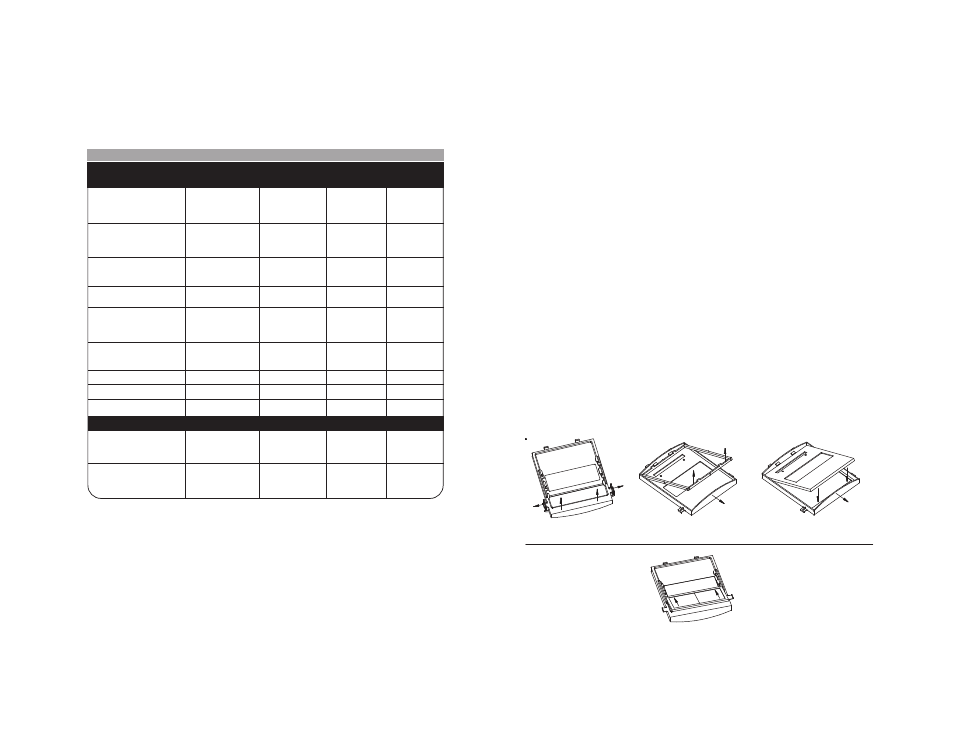
HELMET CARE AND MAINTENANCE
Replacing Front Clear Cover Lens: Replace the front cover lens if it is
damaged. Remove ADF holder assembly per Figure 1. Remove front cover
lens from helmet assembly. Carefully remove gasket from cover lens. Install
new cover lens into gasket and assemble to helmet shell. Make sure to
assemble cover lens and gasket to helmet shell in the same way as it was
removed.
Change the Shade Cartridge: Remove ADF holder assembly from helmet
shell. See figure 1 for removal. Flex one end of the ADF holder to allow for
Adapter and ADF cartridge to be removed from frame per figure 2. Install
new ADF cartridge into frame per figure 3 below. Make sure that the ADF
cartridge is inserted in ADF holder correctly as shown. Install Adapter into the
ADF holder in the same way as it was removed. Install ADF holder into hel-
met shell.
Cleaning: Clean the helmet by wiping with a soft cloth. Clean cartridge sur-
faces regularly. Do not use strong cleaning solutions. Clean sensors and
solar cells with soapy water solution and a clean cloth and wipe dry with a
lint-free cloth. Do NOT submerge shade cartridge in water or other solution.
Storage: Store in a clean, dry location.
INSTALLING AN AFTERMARKET MAGNIFYING LENS:
Simply slide the magnifying lens into the short rail located on the sides of ADF
holder per Figure 4.
5
FFiigure
gure 22
FFiigure
gure 11
FFiigure
gure 33
FFiigure
gure 44
FFiigure
gure 22
FFiigure
gure 11
FFiigure
gure 33
FFiigure
gure 44
ALWAYS TEST TO BE SURE THE ADF CARTRIDGE IS CHARGED
BEFORE WELDING. The helmet needs to be charged prior to first use and
after extended storage. Face the solar cell on the helmet toward sun light or
light bulb for at least 1 hour before use.
SHADE GUIDE SETTINGS
If your helmet does not include any one of the shades referenced above, it is
recommended you use the next darker shade.
4
NT 1
GUIDE FOR SHADE NUMBERS
OPERATION
ELECTRODE SIZE
ARC
MINIMUM
SUGGESTED(1)
1/32 in. (mm)
CURRENT (A)
PROTECTIVE
SHADE NO.
SHADE
(COMFORT)
Shielded metal arc
Less than 3 (2.5)
Less than 60
7
–
welding
3-5 (2.5–4)
60-160
8
10
5-8 (4–6.4)
160-250
10
12
More than 8 (6.4)
250-550
11
14
Gas metal arc
Less than 60
7
–
welding and flux
60-160
10
11
cored arc welding
160-250
10
12
250-500
10
14
Gas tungsten arc
Less than 50
8
10
welding
50-150
8
12
150-500
10
14
Air carbon
(Light)
Less than 500
10
12
Arc cutting
(Heavy)
500-1000
11
14
Plasma arc welding
Less than 20
6
6 to 8
20-100
8
10
100-400
10
12
400-800
11
14
Plasma arc cutting
(Light)
(2)
(2)
(2)
Less than 300
8
9
(Medium)
300-400
9
12
(Heavy)
400-800
10
14
Torch brazing
–
–
3 or 4
Torch soldering
–
–
2
Carbon arc welding
–
–
14
PLATE THICKNESS
in.
mm
Gas welding
Light
Under 1/8
Under 3.2
4 or 5
Medium
1/8 to 1/2
3.2 to 12.7
5 or 6
Heavy
Over 1/2
Over 12.7
6 or 8
Oxygen cutting
Light
Under 1
Under 25
3 or 4
Medium
1 to 6
25 to 150
4 or 5
Heavy
Over 6
Over 150
5 or 6
(1) As a rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark, then go to a lighter shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going
below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas welding or cutting where the torch produces a high yellow light, it is desirable to use a filter lens that absorbs
the yellow or sodium line the visible light of the (spectrum) operation
(2) These values apply where the actual arc is clearly seen. Experience has shown that lighter filters may be used when the arc is hidden by the
workpiece.
.
Data from ANSI Z49.1-2005
NT 1
GUIDE FOR SHADE NUMBERS
OPERATION
ELECTRODE SIZE
ARC
MINIMUM
SUGGESTED(1)
1/32 in. (mm)
CURRENT (A)
PROTECTIVE
SHADE NO.
SHADE
(COMFORT)
Shielded metal arc
Less than 3 (2.5)
Less than 60
7
–
welding
3-5 (2.5–4)
60-160
8
10
5-8 (4–6.4)
160-250
10
12
More than 8 (6.4)
250-550
11
14
Gas metal arc
Less than 60
7
–
welding and flux
60-160
10
11
cored arc welding
160-250
10
12
250-500
10
14
Gas tungsten arc
Less than 50
8
10
welding
50-150
8
12
150-500
10
14
Air carbon
(Light)
Less than 500
10
12
Arc cutting
(Heavy)
500-1000
11
14
Plasma arc welding
Less than 20
6
6 to 8
20-100
8
10
100-400
10
12
400-800
11
14
Plasma arc cutting
(Light)
(2)
(2)
(2)
Less than 300
8
9
(Medium)
300-400
9
12
(Heavy)
400-800
10
14
Torch brazing
–
–
3 or 4
Torch soldering
–
–
2
Carbon arc welding
–
–
14
PLATE THICKNESS
in.
mm
Gas welding
Light
Under 1/8
Under 3.2
4 or 5
Medium
1/8 to 1/2
3.2 to 12.7
5 or 6
Heavy
Over 1/2
Over 12.7
6 or 8
Oxygen cutting
Light
Under 1
Under 25
3 or 4
Medium
1 to 6
25 to 150
4 or 5
Heavy
Over 6
Over 150
5 or 6
(1)
As a rule of thumb, start with a shade that is too dark, then go to a lighter shade which gives sufficient view of the weld zone without going
below the minimum. In oxyfuel gas welding or cutting where the torch produces a high yellow light, it is desirable to use a filter lens that absorbs
the yellow or sodium line the visible light of the (spectrum) operation
(2)
These values apply where the actual arc is clearly seen. Experience has shown that lighter filters may be used when the arc is hidden by the
workpiece.
.
Data from ANSI Z49.1-2005
