Pin input jack wiring, Microphone rf bypassing, Line level signals – Lectrosonics SMQ User Manual
Page 12: The normal hookup for, Line level signals is, Signal hot to pin 5, Signal gnd to pin 1 and pin 4 jumped to, Pin 1. this allows signal levels up to 6v, Rms to be applied, Without limiting
SM
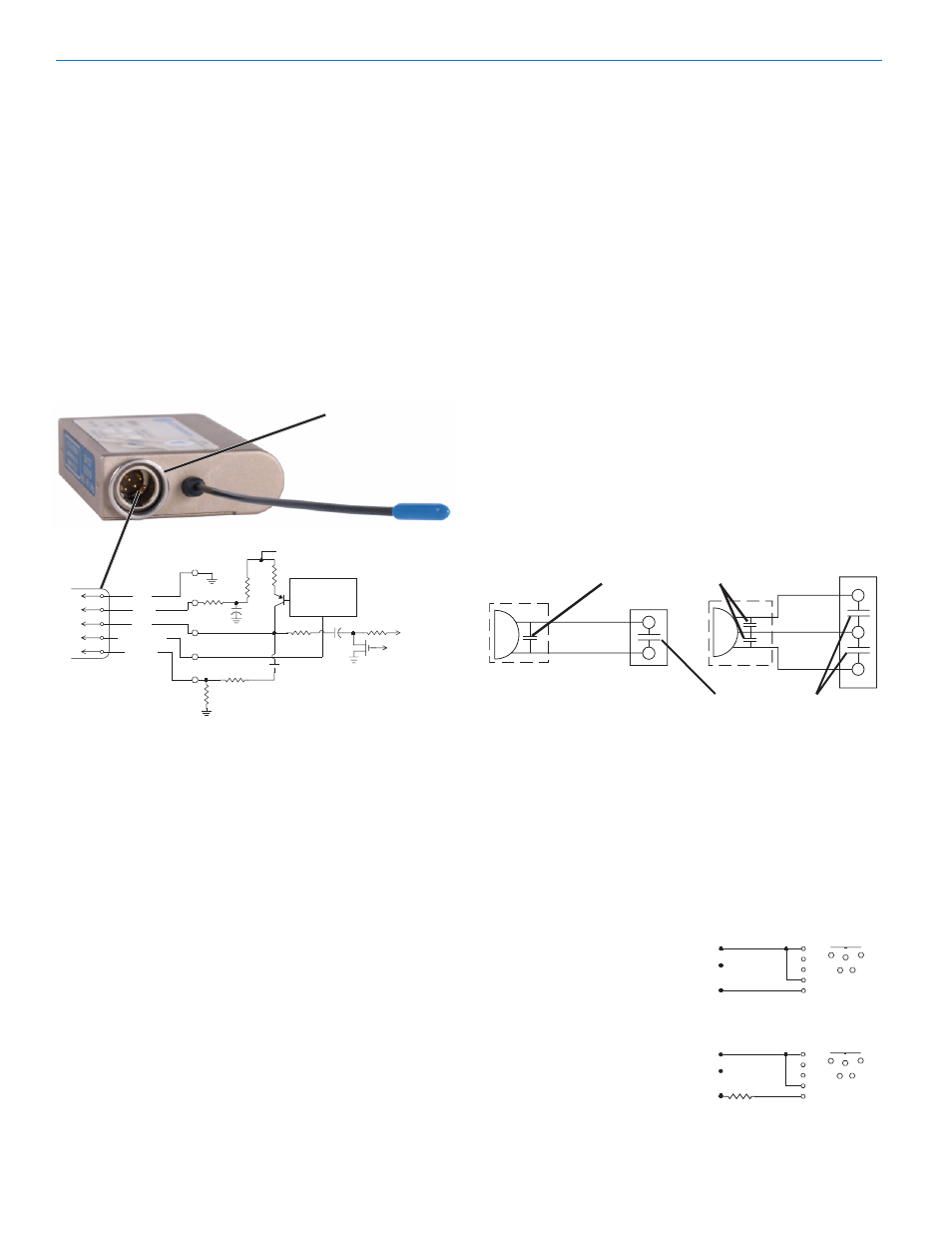
5-Pin Input Jack Wiring
The wiring diagrams included in this section represent
the basic wiring necessary for the most common types
of microphones and other audio inputs. Some micro
phones may require extra jumpers or a slight variation
on the diagrams shown.
It’s virtually impossible to keep completely up to date on
changes that other manufacturers make to their products.
It is possible that you may encounter a microphone that
differs from these instructions. If this occurs please call
our toll-free number listed under Service and Repair in
this manual or visit our web site at:
http://www.lectrosonics.com
The Audio Input Jack for the SM is wired as shown
below:
SM Equivalent Input Circuit Wiring
10k
1k
5
4
3
2
1
To Virtual Ground
Audio Amplifier
BIAS
MIC
BIAS SELECT
LINE IN
GND
+
30uF
+6 VDC
Servo Bias
Pin 4 to Pin 1 = 0 V
Pin 4 Open = 2 V
Pin 4 to Pin 2 = 4 V
+
To Limiter Control
30uF
750 Ohm
100 Ohm
2.7K
200 Ohm
+
3.3uF
100 Ohm
Audio Input Jack
PIN 1 Shield (ground) for positive biased electret
lavaliere microphones. Shield (ground) for
dynamic microphones and line level inputs.
PIN 2 Bias voltage source for positive biased electret
lavaliere microphones.
PIN 3 Low impedance microphone level input for
dynamic microphones. Also accepts hand-held
electret microphones provided the microphone
has its own built-in battery.
PIN 4 Bias voltage selector for Pin 3. Pin 3 voltage (0,
2 or 4 volts) depends on Pin 4 connection.
Pin 4 tied to Pin 1: 0 V
Pin 4 Open:
Pin 4 to Pin 2:
2 V
4 V
PIN 5 High impedance, line level input for tape decks,
mixer outputs, musical instruments, etc.
Microphone RF Bypassing
When used on a wireless transmitter, the microphone
element is in the proximity of the RF coming from the
transmitter. The nature of electret microphones makes
them sensitive to RF, which can cause problems with
the microphone/transmitter compatibility. If the electret
microphone is not designed properly for use with
wireless transmitters, it may be necessary to install a
chip capacitor in the mic capsule or connector to block
the RF from entering the electret capsule.
Some mics require RF protection to keep the radio
signal from affecting the capsule, even though the
transmitter input circuitry is already RF bypassed (see
schematic diagram).
If the mic is wired as directed, and you are having
difficulty with squealing, high noise, or poor frequency
response; RF is likely to be the cause.
The best RF protection is accomplished by installing RF
bypass capacitors at the mic capsule. If this is not
possible, or if you are still having problems, capacitors
can be installed on the mic pins inside the TA5F con
nector housing.
2 WIRE MIC
3 WIRE MIC
CAPSULE
CONNECTOR
TA5F
CONNECTOR
CAPSULE
SHIELD
AUDIO
SHIELD
AUDIO
BIAS
TA5F
Preferred locations for bypass capacitors
Alternate locations for bypass capacitors
Install the capacitors as follows: Use 330 pF capacitors.
Capacitors are available from Lectrosonics. Please
specify the part number for the desired lead style.
Leaded capacitors: P/N 15117
Leadless capacitors: P/N SCC330P
All Lectrosonics lavaliere mics are already bypassed
and do not need any additional capacitors installed for
proper operation.
Line Level Signals
The normal hookup for
PIN
SHIELD (GND)
1
line level signals is:
2
Line Level
Signal Hot to pin 5,
Normal Hookup
3
1
2
3
4
5
4
AUDIO
TA5F
5
Signal Gnd to pin 1
and pin 4 jumped to
PLUG
pin 1. This allows
signal levels up to 6V
PIN
SHIELD (GND)
1
Line Level
RMS to be applied
2
without limiting.
More Headroom
3
(20 dB)
1
2
3
4
5
20k
4
AUDIO
TA5F
If more headroom is
5
PLUG
needed, insert a 20 k
resistor in series with pin 5. Put this resistor inside the
TA5F connector to minimize noise pickup.
LECTROSONICS, INC.
12
