Global Specialties 4005 - Manual User Manual
Page 19
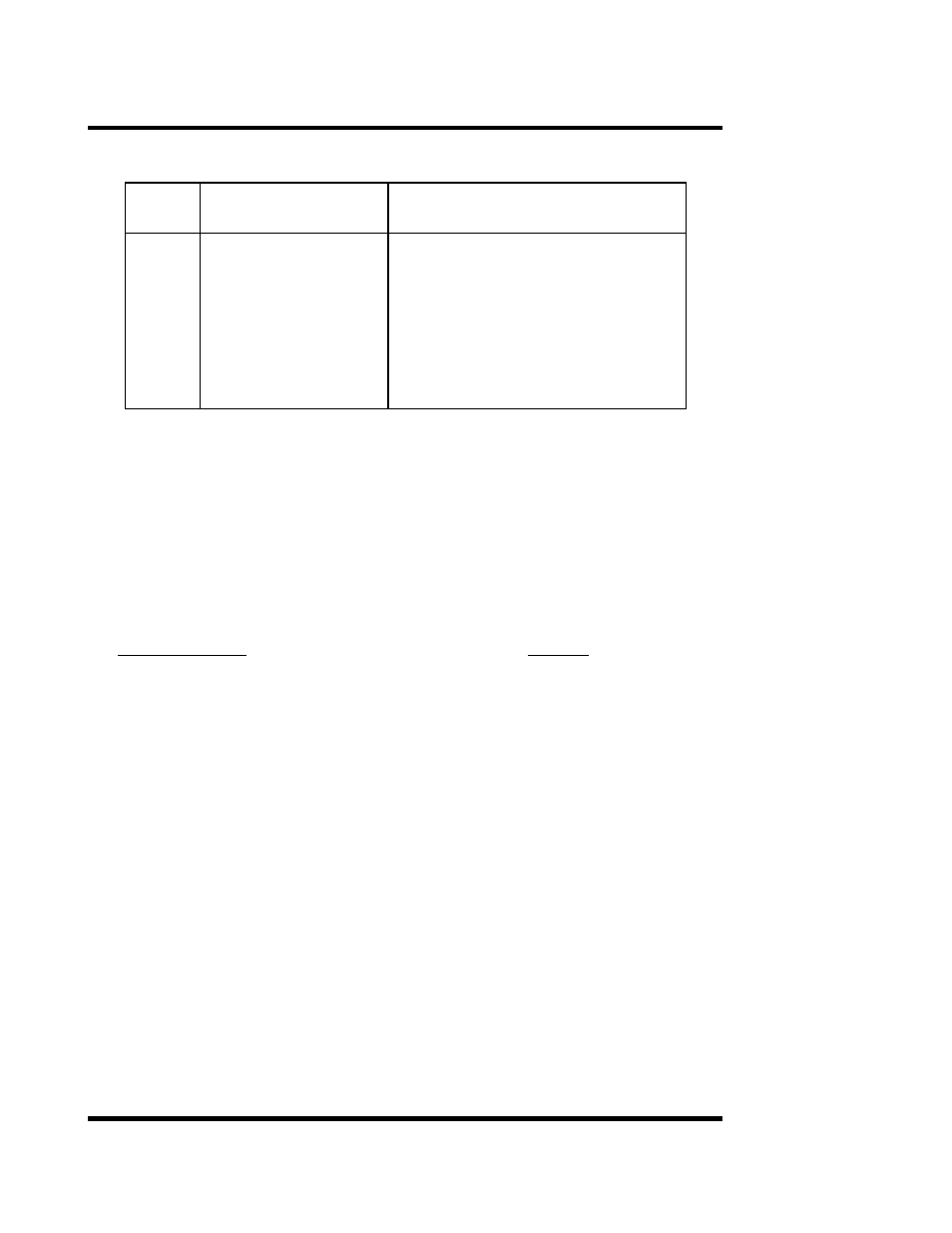
19
HIGHEST FREQ.
FREQ. DEVIATION FOR EACH
RANGE
OBTAINABLE(Hz)
0.1 VOLT VCF IN CHANGE(Hz)
5
5
0.05
50
50
0.5
500
500
5
5K
5K
50
50K
50K
500
500K
500K
5K
5M
5M
50K
Frequency Deviation vs VCF IN Voltage.
B. For an example, it is assumed that we wish to generate a 455 KHz signal with FM deviation of ±15
KHz (30 KHz swing). The 500k range will be used to obtain the 455 KHz carrier with the FREQ. dial
set to 4.55. The highest frequency obtainable in this range is 500kHz. One percent of 500kHz is 5
KHz. Our requirement of 30 KHz deviation is 6 times greater than 5 KHz deviation produced by a
0.1 volt VCF IN swing, thus we will use 6 times as much peak-to-peak voltage swing, or 0.6 V.
For Instance:
desired deviation 30 KHz
1% deviation 5KHz
C. Remember that the value of VCF IN signal is the peak to peak amplitude.
3-7. External Control of VCF
Within a given range, the FREQ dial setting normally controls the output frequency of generator.
However, applying a voltage at the VCF IN BNC on the front panel also may control it. There are three
basic possible modes of external VCF control as detailed below:
A. Applying an AC voltage produces FM modulation (previously described in the
“Use as FM Signal
Generator” paragraph)
B. Applying a specific fixed DC voltage will produce a specific output frequency described in
following “Programmed Frequency Selection”paragraph)
C. Applying a ramp voltage (or other type waveform if desired) provides externally controlled sweep
generator operation (described in the
“Use as Externally Controlled Sweep Generator”
paragraph)
The following considerations apply to all modes of operation involving external control of the VCF
(voltage controlled frequency)
A. The output frequency of the generator is determined by the voltage applied to the VCF.
X 0.1 V = required VCF IN
signal
x 0.1 = 6 x 0.1V = 0.6V
