Carolina Mammal Brain Dissection Guide User Manual
Page 4
4
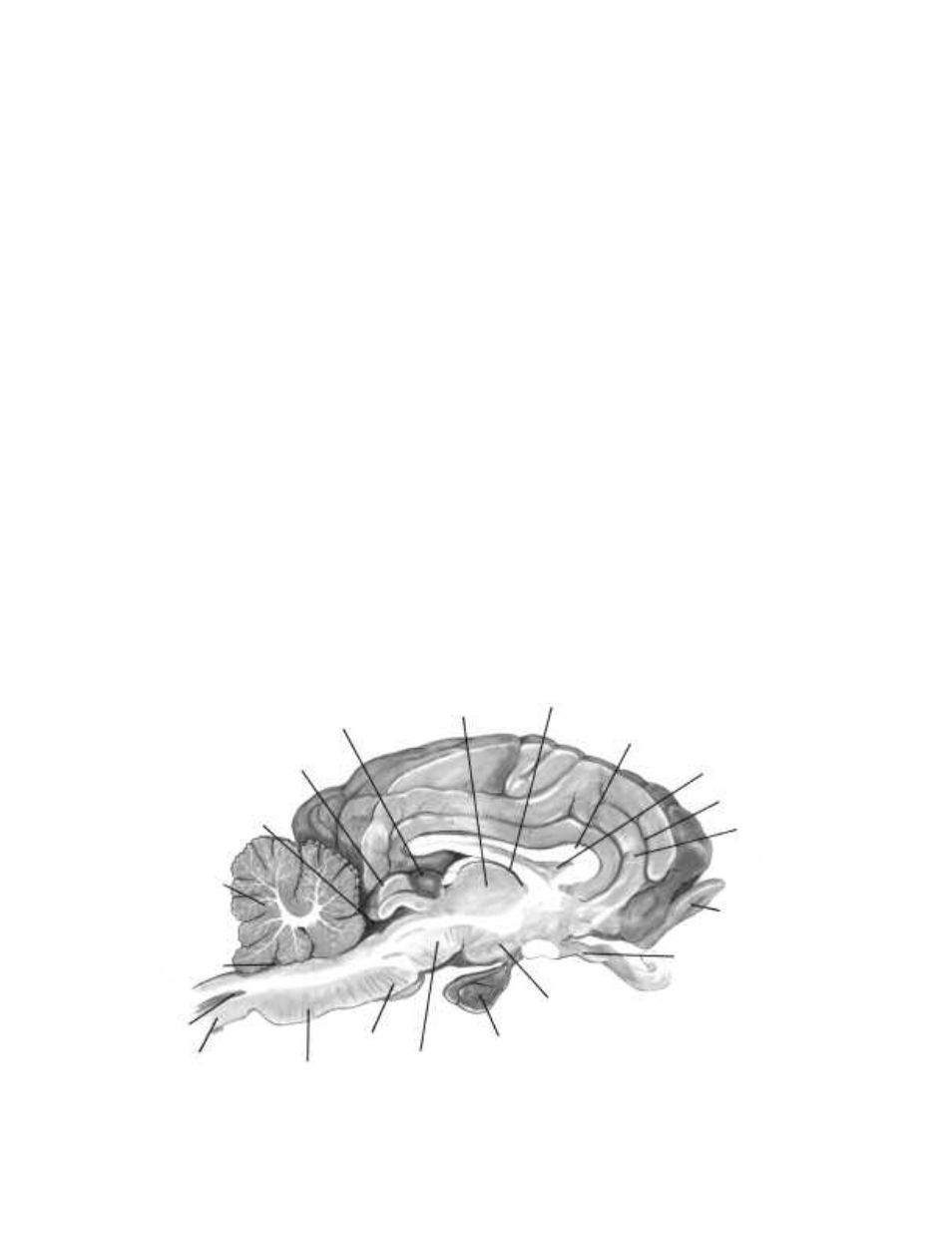
11. Locate the third and fourth ventricles. The fourth ventricle connects to the central canal of the spinal
cord. It is also connected to the third ventricle by a cerebral aqueduct. Examine each ventricle and try to
identify the choriod plexus, which produces cerebrospinal fluid.
12. With the cut side facing up, locate the following parts: thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal body, pons, and
medulla.
13. Observe the cut surface of the cerebellum. In medial section, the white matter of the cerebellum forms a
branched, treelike pattern called the arbor vitae. Try to identify this pattern.
14. Locate the midbrain region, located inferiorly between the thalamus and pons. This area contains
important nerve tracts. Dorsal areas of the midbrain are concerned with responses to visual and auditory
stimuli.
15. Make a cross section through a cerebral hemisphere just anterior to the thalamus. Examine the cross
section and identify the inner white matter and outer gray matter.
16. Remove the cerebellum and the remainder of the cerebral hemisphere by dissecting away everything
dorsal to the floor of the lateral ventricle. This will expose an infolding of the cerebral cortex, called the
hippocampus. The hippocampus is involved with emotions and memory.
17. Remove the hippocampus to locate the remainder of the thalamus.
18. Once you have observed all the structures of the brain, dispose of the specimen in accordance with local
guidelines and your teacher’s instructions.
Mammal Brain Section
Cerebellum
Fourth ventricle
Central canal
Spinal cord
Medulla
Pons
Midbrain
Hypophysis
Hypothalamus
Optic nerve
Olfactory bulb
Gyrus
Sulcus
Septum pellucidum
Corpus callosum
Third ventricle
Thalamus
Pineal body
Superior colliculus
Cerebral aqueduct
