5 electrolyte, 4 positive and negative electrode plate, continued – Alpha Technologies Lomain Ni-Cd Pocket Plate Battery User Manual
Page 15
15
745-680-B10-001 Rev. A
The electrode strips are mechanically linked together to form the electrode plate and are
consecutively cut to the appropriate width based on the cell type and range. The plates then
are welded or mechanically linked to the plate frame (see Fig. 8) to form the electrodes, then
assembled to the plate block.
The extemely long useful lifetime and the very good cycle life features of the Ni-Cd pocket
plate batteries are a direct result of the special plate designs whose structural components
are made of steel.
This prevents the gradual deterioration by corrosion. Because the alkaline electrolyte does
not react with steel, the substructure of the battery remains intact for the total lifetime of the
battery. The integrity of the substructure is maintained by surrounding the electrochemical
active mass in perforated nickel-steel pockets, reducing the risk of shedding or penetration of
material as well as the risk of structural damage. Also, this design allows for the control of soft
short circuits.
1.5 Electrolyte
The electrolyte used in the Ni-Cd batteries is a solution of potassium hydroxide and lithium
hydroxide that is optimized to give the best combination of performance, energy efficiency
and a wide temperature range of use.
It is an important property of the battery, and indeed all nickel-cadmium batteries, that the
electrolyte does not change during charge and discharge. It retains its ability to transfer ions
between the cell plates, irrespective of the charge level.
In most applications the electrolyte will retain its effectiveness for the life of the battery and
will never need replacing. However, under certain conditions, such as extended use in high
temperature situations, the electrolyte can become carbonated. If this occurs the battery
performance can be improved by replacing the electrolyte (see ·Maintenance and Handling
Instructions“).
1.0
Introduction, continued
1.4 Positive and negative electrode plate, continued
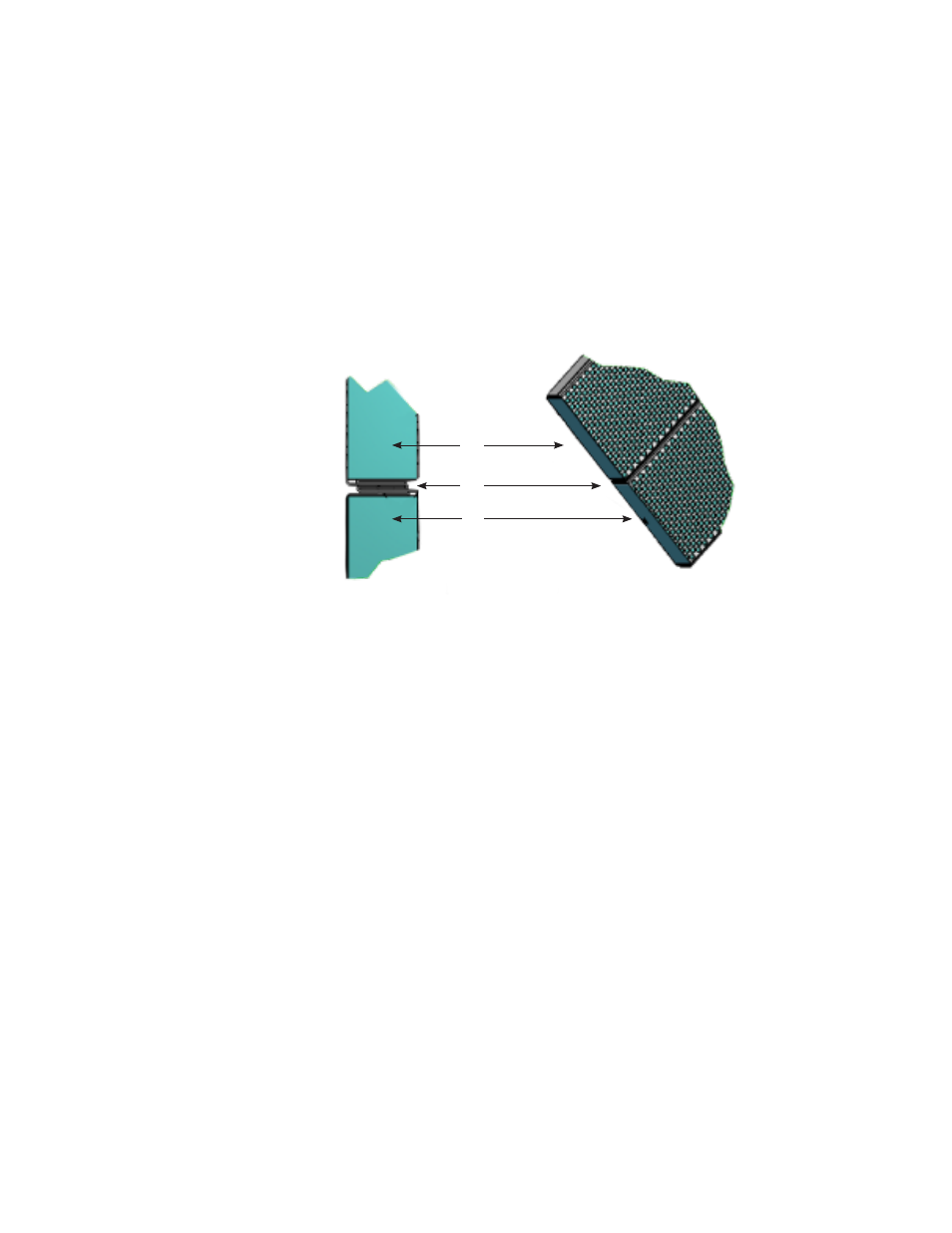
1 Electrode Strips
2 Mechanical Linkage
1
2
1
Fig. 9, Strips connected
