Gorman-Rupp Pumps SF4A 1488019 and up User Manual
Page 43
SF SERIES
OM-06432
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
PAGE E - 18
housing over the opening in the top of the motor
housing.
Check to ensure that the contacts on the ends of
the motor stator leads are firmly installed in their re
spective housings. Check to ensure that any wire
connectors installed on the stator leads are tight
and secured with heat shrink tubing.
The plastic housings on the ends of the power and
control cable leads are color‐coded to match the
housings on the leads coming off the stator. Match
each cable lead housing with its corresponding
stator lead housing and firmly press them together
until they lock in place.
When all of the cable lead housings are securely
locked into the stator lead housings, slide the ter
minal housing assembly down over the studs in the
top of the motor housing. Secure the terminal
housing to the motor housing by tightening the
hardware (10 and 11) in an alternating pattern until
the terminal housing is fully seated in the motor
housing. Torque the hex nuts (10) to 27 ft. lbs. (3,7
m. kg.).
After installing the motor housing, perform the vac
uum check described below to ensure the water‐
tight integrity of the pump.
Reconnect the power and control cable leads to
the control box. Check pump rotation as described
in OPERATION, Section C, before putting the
pump back into service.
Hoisting Bail Installation
(Figure E-1)
If the hoisting bail (19) was removed in order to re
move the terminal housing assembly (15) position
the bail over the motor housing so the holes for the
mounting hardware align. Apply “Never‐Seez” or
equivalent compound to the threads of the caps
crews (18) and secure the bail to the motor hous
ing with the hardware (7 and 18). Torque the caps
crews to 64 ft. lbs. (8,8 m. kg.).
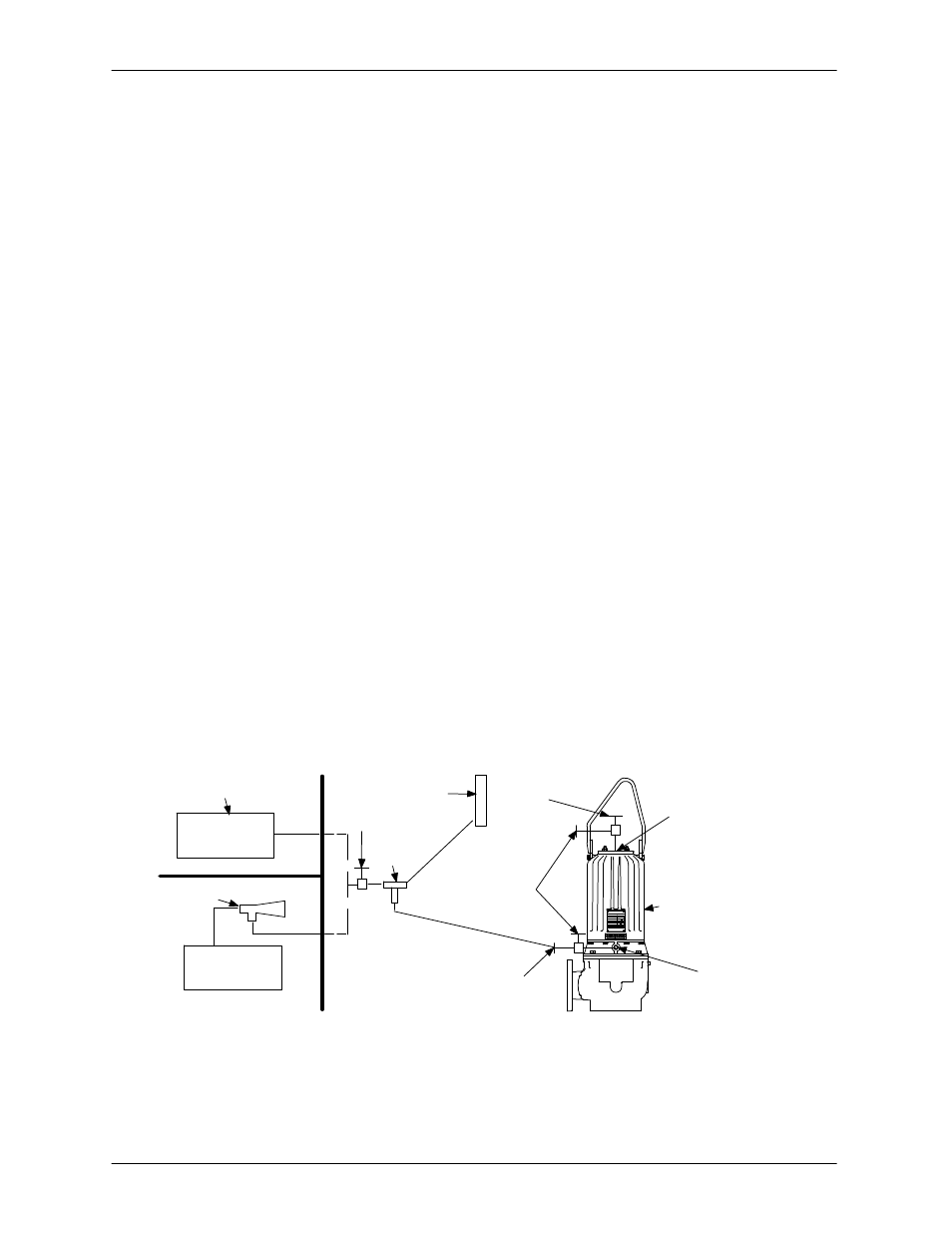
VACUUM TESTING
To ensure the water‐tight integrity of the pump, the
motor and seal cavities must be vacuum tested any
time the seal(s) and/or motor are serviced.
Use a manometer with a range of 30 to 0 to 30 inch
es of mercury to perform the test. Do not use a vac
uum gauge. Vacuum gauges are not sensitive
enough to detect minor leaks.
It is recommended that a vacuum pump be used to
draw the vacuum on the cavities. If a vacuum pump
is not available, a compressor/venturi system may
be used. If the compressor/venturi cannot draw
the higher vacuum level shown in Table E-1, draw
the motor cavity vacuum down as far as the system
will allow, then draw the seal cavity down so the dif
ferential between the two cavities is the same as
the differential between the vacuum readings
shown in the table.
Tee
Manometer
Vacuum Pump
Submersible
Pump
Full-Closing
Ball-Type
Shutoff Valve
Quick Disconnect
Fitting
Quick Disconnect
Fitting
Air Compressor
Venturi
Seal Cavity
Fill/Drain
Motor Vacuum
Test Plate
S.O. Valve
Figure E-4. Vacuum Test System
Seal Cavity Testing
If the water‐tight integrity of the motor was not dis
turbed during disassembly, the seal cavity can be
tested without testing the motor.
Drain all of the oil from the seal cavity before per
forming the test. Oil within the cavity will be drawn
into the system, resulting in damage to the vacuum
pump or manometer.
