Chip information – Rainbow Electronics MAX105 User Manual
Page 19
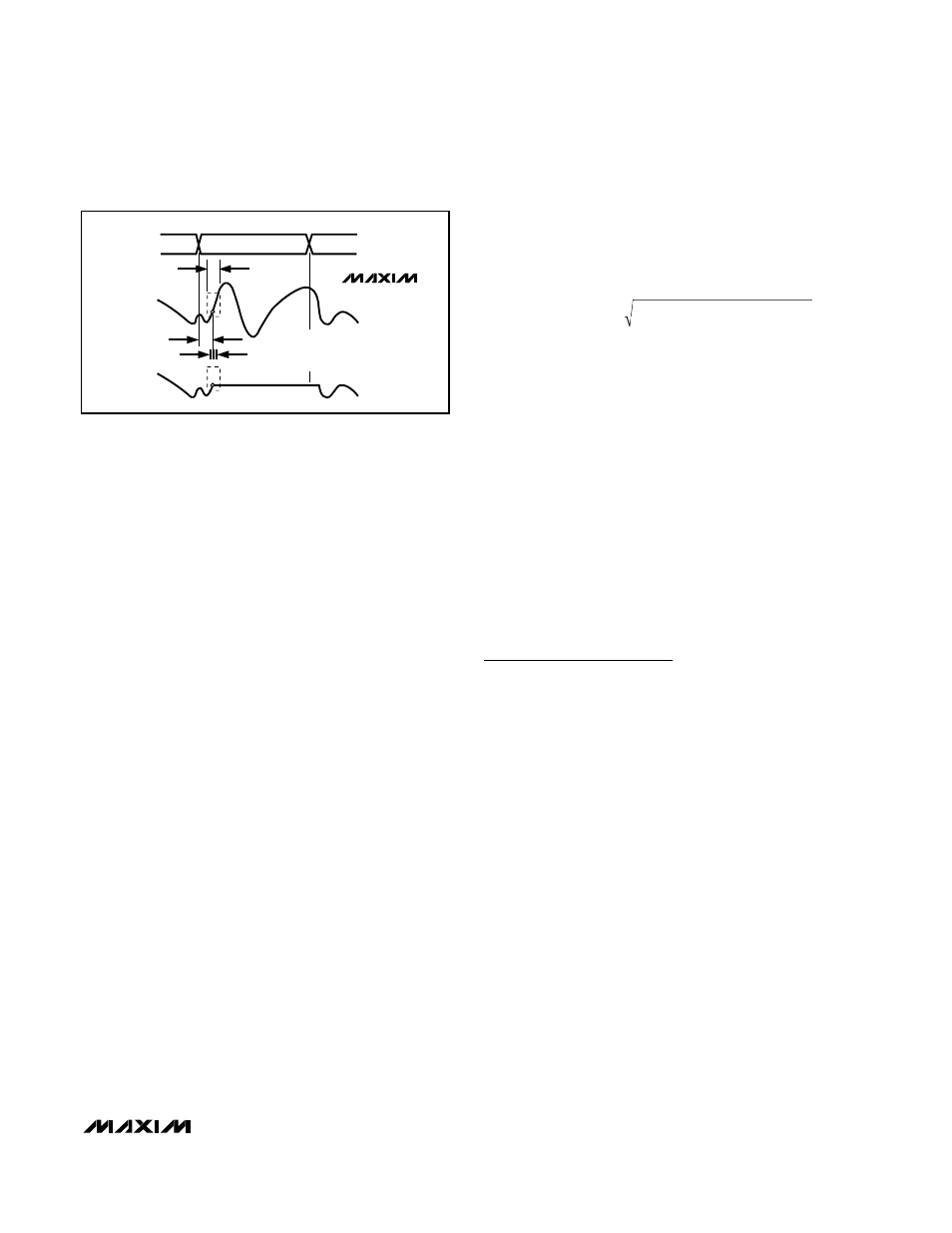
clock design limits aperture jitter to typically 1.5ps
RMS
.
Figure 11 depicts the aperture jitter (t
AJ
), which is the
sample-to-sample variation in the aperture delay.
Aperture delay (t
AD
) is the time defined between the
rising edge of the sampling clock and the instant when
an actual sample is taken (
Figure 11).
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
For a waveform perfectly reconstructed from digital
samples, the theoretical maximum SNR is the ratio of
the full-scale analog input (RMS value) to the RMS
quantization error (residual error). The ideal, theoretical
minimum analog-to-digital noise is caused by quantiza-
tion error only and results directly from the ADC’s reso-
lution (N-Bits):
SNR
MAX[dB]
= 6.02
dB
x N + 1.76
dB
In reality, there are other noise sources besides quanti-
zation noise: thermal noise, reference noise, clock jitter
(see Aperture Uncertainties). SNR is computed by tak-
ing the ratio of the RMS signal to the RMS noise, which
includes all spectral components minus the fundamen-
tal, the first four harmonics, and the DC offset.
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion (SINAD)
SINAD is computed by taking the ratio of the RMS sig-
nal to all spectral components minus the fundamental
and the DC offset.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
ENOB specifies the dynamic performance of an ADC at
a specific input frequency, amplitude, and sampling
rate relative to an ideal ADC’s quantization noise. For a
full-scale input ENOB is computed from:
ENOB = (SINAD - 1.76
dB
) / 6.02
dB
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
THD is typically the ratio of the RMS sum of the first four
harmonics of the input signal to the fundamental itself.
This is expressed as:
where V1 is the fundamental amplitude, and V
2
through
V
5
are the amplitudes of the 2nd- through 5th-order har-
monics.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
SFDR is the ratio expressed in decibels of the RMS
amplitude of the fundamental to the RMS value of the
next largest spurious component, excluding DC offset.
Two-Tone Intermodulation
Distortion (IMD)
The two-tone IMD is the ratio expressed in decibels of
either input tone to the worst 3rd-order (or higher) inter-
modulation products. The individual input tone levels
are at -7dB full-scale and their envelope peaks at -1dB
full-scale.
Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 12,286
THD
x
V
V
V
V
V
=
+
+
+
20
2
2
3
2
4
2
5
2
1
2
log (
) /
)
MAX105
Dual, 6-Bit, 800Msps ADC with On-Chip,
Wideband Input Amplifier
______________________________________________________________________________________
19
CLK+
ANALOG
INPUT
SAMPLING
INSTANT
t
AW
t
AD
t
AJ
CLK-
t
AW
: APERTURE WIDTH
t
AJ
: APERTURE JITTER
t
AD
: APERTURE DELAY
MAX105
Figure 11. Aperture Timing
