Table 1. component selection guide – Rainbow Electronics MAX1655 User Manual
Page 10
MAX1649/MAX1651
5V/3.3V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low-Dropout, Step-Down DC-DC Controllers
10
______________________________________________________________________________________
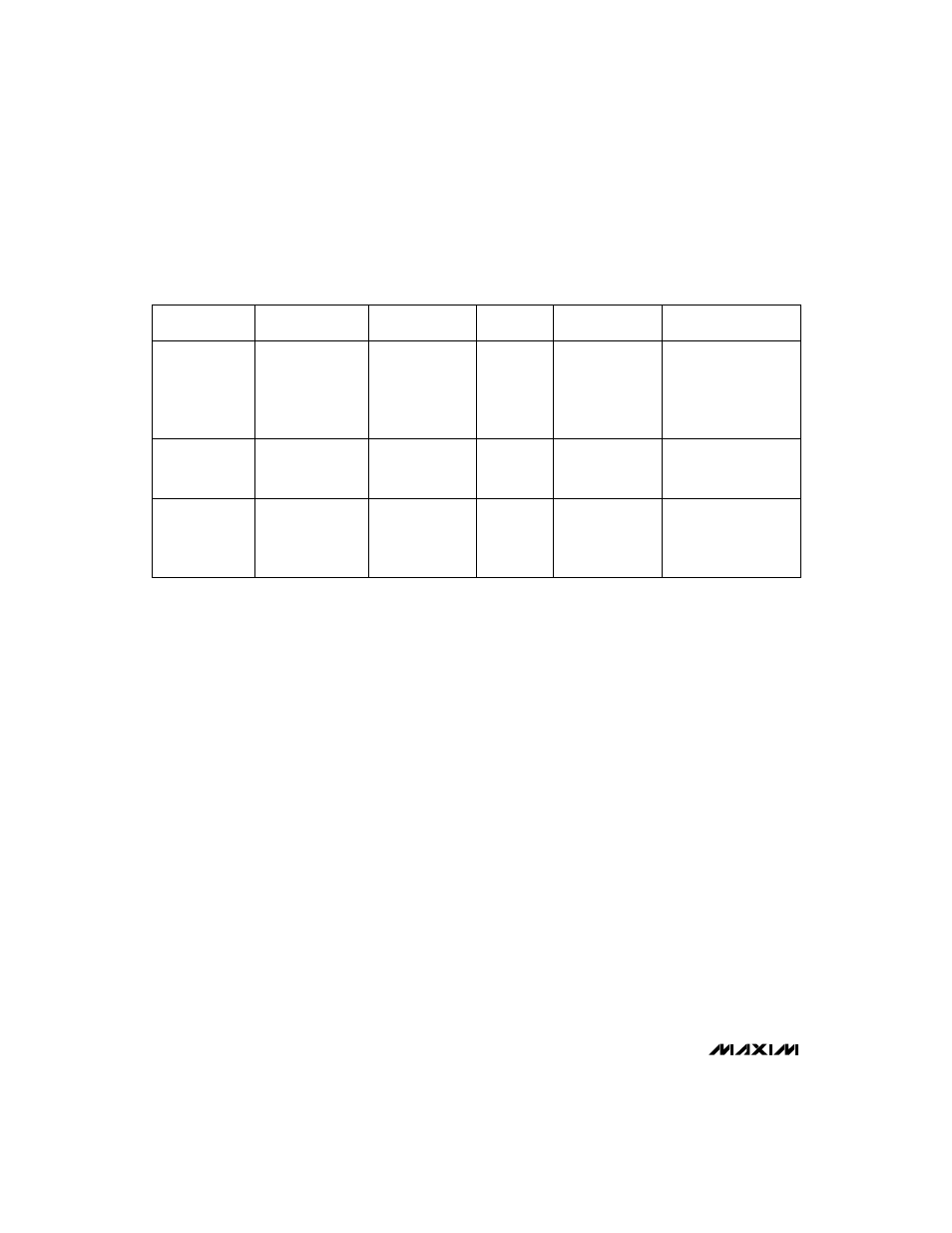
Table 1. Component Selection Guide
The peak current of Figure 1 is 2.35A for a 1.5A output.
The inductor used in this circuit is specified to drop by
10% at 2.2A (worst case); a curve provided by the
manufacturer shows that the inductance typically drops
by 20% at 2.7A. Using a slightly underrated inductor
can sometimes reduce size and cost, with only a minor
impact on efficiency.
Table 1 lists inductor types and suppliers for various
applications. The efficiencies of the listed surface-
mount inductors are nearly equivalent to those of the
larger size through-hole versions.
Diode Selection
The MAX1649/MAX1651’s high switching frequency
demands a high-speed rectifier. Schottky diodes, such
as the 1N5817 through 1N5823 (and their surface-
mount equivalents), are recommended. Choose a
diode with an average current rating equal to or greater
than I
LIM
(max) and a voltage rating higher than
V+(max).
External Switching Transistor
The MAX1649/MAX1651 drive P-channel enhancement-
mode MOSFET transistors only. The choice of power
transistor is primarily dictated by the input voltage and
the peak current. The transistor’s on-resistance, gate-
source threshold, and gate charge must also be appro-
priately chosen. The drain-to-source and gate-to-
source breakdown voltage ratings must be greater than
V+. The total gate-charge specification is normally not
critical, but values should be less than 100nC for best
efficiency. The MOSFET should be capable of handling
the peak current and, for maximum efficiency, have a
very low on-resistance at that current. Also, the on-
resistance must be low for the minimum available V
GS
,
which equals V+(min). Select a transistor with an on-
resistance between 50% and 100% of the current-
sense resistor. The Si9430 transistor chosen for the
Typical Operating Circuit has a drain-to-source rating
of -20V and a typical on-resistance of 0.070
Ω
at 2A with
V
GS
= -4.5V. Tables 1 and 2 list suppliers of switching
transistors suitable for use with these devices.
Capacitor Selection
Output Filter Capacitor
The primary criterion for selecting the output filter
capacitor is low equivalent series resistance (ESR),
rather than high capacitance. An electrolytic capacitor
with low enough ESR will automatically have high
enough capacitance. The product of the inductor-cur-
rent variation and the output filter capacitor’s ESR
determines the amplitude of the high-frequency ripple
seen on the output voltage. When a 330µF, 10V
Sprague surface-mount capacitor (595D series) with
ESR = 0.15
Ω
is used, 40mV of output ripple is typically
observed when stepping down from 10V to 5V at 1A.
The output filter capacitor's ESR also affects efficiency.
Again, low-ESR capacitors perform best. Table 1 lists
some suppliers of low-ESR capacitors.
PRODUCTION
METHOD
INDUCTORS
CAPACITORS
DIODES
CURRENT-SENSE
RESISTORS
MOSFETS
Surface Mount
AVX
TPS series
Sprague
595D series
Motorola
MBRS340T3
Nihon
NSQ series
Dale
WSL Series
IRC
LRC series
Miniature
Through-Hole
Sumida
RCH875-470M (1.3A)
Sanyo
OS-CON series
low-ESR organic
semiconductor
IRC
OAR series
Motorola
Low-Cost
Through-Hole
CoilCraft
PCH-45-473 (3.4A)
Motorola
1N5817 to
1N5823
Motorola
TMOS power MOSFETs
Sumida
CDRH125-470 (1.8A)
CDRH125-220 (2.2A)
CoilCraft
DO3316-473 (1.6A)
DO3340-473 (3.8A)
Siliconix
Little Foot series
Motorola
medium-power
surface-mount products
Nichicon
PL series
low-ESR electrolytics
United Chemi-Con
LXF series
