Pin description – Rainbow Electronics DS1511 User Manual
Page 9
DS1501/DS1511 Y2KC Watchdog Real-Time Clocks
9 of 20
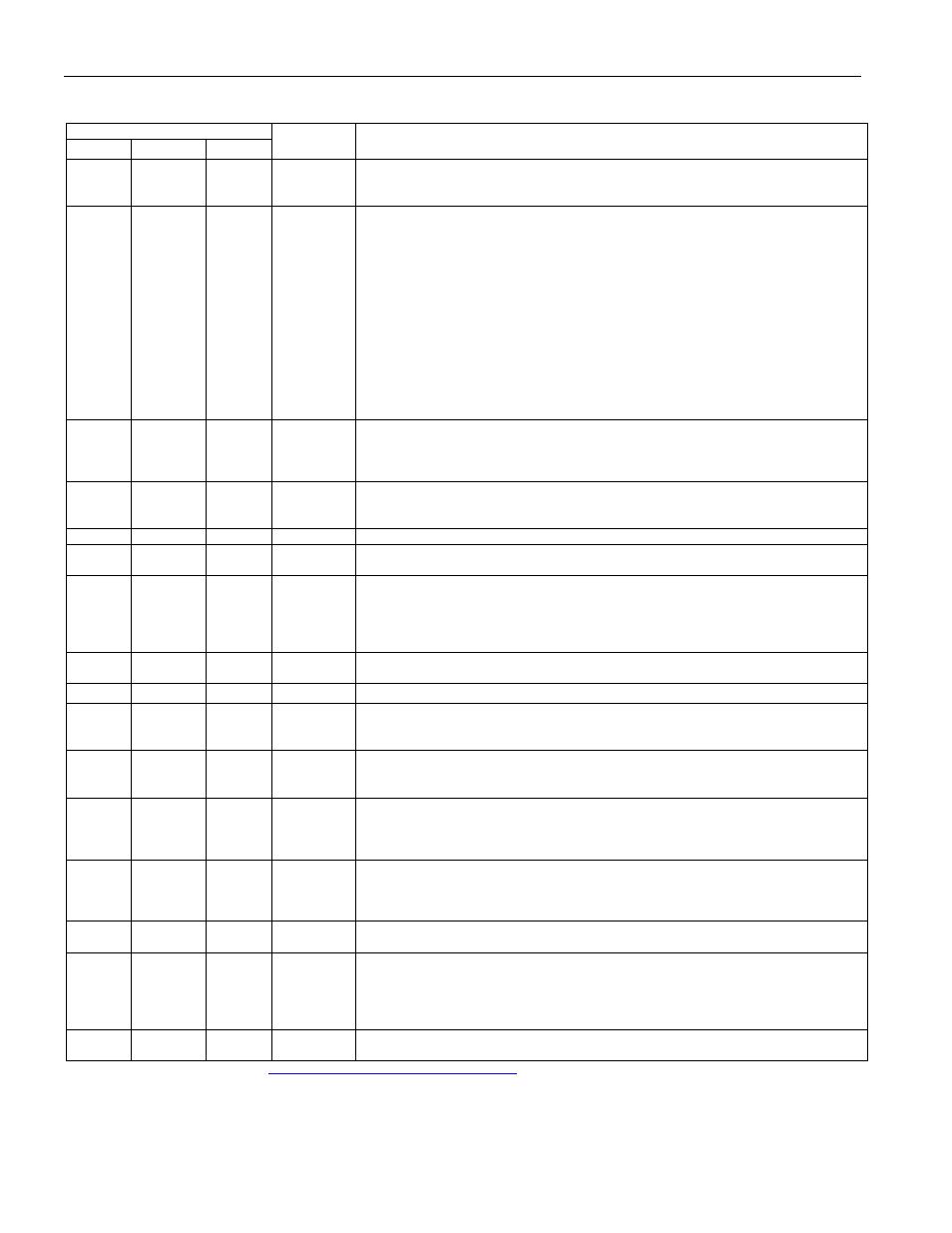
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN
DIP, SO MODULE
TSOP
NAME FUNCTION
1 1 8
PWR
Power-On Output (Open Drain). This output, if used, is normally connected to
power-supply control circuitry. This pin requires a pullup resistor connected to a
positive supply to operate correctly.
2, 3
—
9, 10
X1, X2
Connections for a standard 32.768kHz quartz crystal. For greatest accuracy, the
DS1501 must be used with a crystal that has a specified load capacitance of either
6pF or 12.5pF. The crystal select (CS) bit in control register B is used to select
operation with a 6pF or 12.5pF crystal. The crystal is attached directly to the X1 and
X2 pins. There is no need for external capacitors or resistors. An external 32.768kHz
oscillator can also drive the DS1501. In this configuration, the X1 pin is connected to
the external oscillator signal and the X2 pin is floated. For more information about
crystal selection and crystal layout considerations, refer to Application Note 58:
Crystal Considerations with Dallas Real-Time Clocks. See Figure 9. An enable bit in
the month register controls the oscillator. Oscillator startup time is highly dependent
upon crystal characteristics, PC board leakage, and layout. High ESR and excessive
capacitive loads are the major contributors to long startup times. A circuit using a
crystal with the recommended characteristics and proper layout usually starts within
one second.
4 4 11
RST
Reset Output (Open Drain). This output, if used, is normally connected to a
microprocessor-reset input. This pin requires a pull up resistor connected to a
positive supply to operate correctly. When
RST is active, the device is not
accessible.
5 5 12
IRQ
Interrupt Output (Open Drain). This output, if used, is normally connected to a
microprocessor interrupt input. This pin requires a pullup resistor connected to a
positive supply to operate correctly.
6–10
6–10
13–17
A4–A0
Address Inputs. Selects one of 17 register locations.
11–13,
15–19
11–13,
15–19
18–20,
22–26
DQ0–DQ7
Data I/O pins for 8-bit parallel data transfer.
14,
21 14 21,
28 GND
DC power is applied to the device on these pins. V
CC
is the positive terminal. When
power is applied within the normal limits, the device is fully accessible and data can
be written and read. When V
CC
drops below the normal limits, reads and writes are
inhibited. As V
CC
drops below the battery voltage, the RAM and timekeeping circuits
are switched over to the battery.
22 22 1
OE
Output-Enable Input. Active-low input that enables DQ0–DQ7 for data output from
the device.
20 20 27
CE
Chip-Enable Input. Active-low input to enable the device.
23 23 2 SQW
Square-Wave Output. When enabled, the SQW pin outputs a 32.768kHz square
wave. If the square wave (
E32K) and battery backup 32kHz (BB32) bits are enabled,
power is provided by V
BAUX
when V
CC
is absent.
24 24 3
KS
Kickstart Input. This pin is used to wake up a system from an external event, such
as a key closure. The
KS pin is normally connected using a pullup resistor to V
BAUX
.
If the
KS function is not used, connect to ground.
25 — 4 V
BAT
Battery input for any standard 3V lithium cell or other energy source. Battery voltage
must be held between 2.5V and 3.7V for proper operation. UL recognized to ensure
against reverse charging current when used with a lithium battery. If not used,
connect to ground.*
26 26 5 V
BAUX
Auxiliary battery input for any standard 3V lithium cell or other energy source.
Battery voltage must be held between 2.5V and 3.7V for proper operation. UL
recognized to ensure against reverse charging current when used with a lithium
battery. If not used, connect to ground.*
27 27 6
WE
Write-Enable Input. Active-low input that enables DQ0–DQ7 for data input to the
device.
28 28 7 V
CC
DC power is applied to the device on these pins. V
CC
is the positive terminal. When
power is applied within the normal limits, the device is fully accessible and data can
be written and read. When V
CC
drops below the normal limits, reads and writes are
inhibited. As V
CC
drops below the battery voltage, the RAM and timekeeping circuits
are switched over to the battery.
—
2, 3, 21,
25
— N.C.
No
Connect
*See “Conditions of Acceptability” at
