Table 1. i, C slave addresses – Rainbow Electronics MAX7502 User Manual
Page 5
MAX7500/MAX7501/MAX7502
Digital Temperature Sensors and Thermal
Watchdog with Bus Lockup Protection
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5
I
2
C-Compatible Bus Interface
From a software perspective, the MAX7500/MAX7501/
MAX7502 appear as a set of byte-wide registers that
contain temperature data, alarm threshold values, and
control bits. A standard I
2
C-compatible 2-wire serial
interface reads temperature data and writes control bits
and alarm threshold data. Each device responds to its
own I
2
C slave address, which is selected using A0, A1,
and A2. See
Table
1.
The MAX7500/MAX7501/MAX7502 employ four stan-
dard I
2
C protocols: write byte, read byte, send byte,
and receive byte (Figures 1, 2, and 3). The shorter
receive byte protocol allows quicker transfers, provided
that the correct data register was previously selected
by a read-byte instruction. Use caution when using the
shorter protocols in multimaster systems, as a second
master could overwrite the command byte without
informing the first master. The MAX7500 has eight dif-
ferent slave addresses available; therefore, a maximum
of eight MAX7500 devices can share the same bus.
The MAX7501/MAX7502 each have four different slave
addresses available.
DEVICE
BIT 7
BIT 6
BIT 5
BIT 4
BIT 3
BIT 2
BIT 1
BIT 0
MAX7500
1
0
0
1
A2
A1
A0
RD/W
MAX7501
1
0
0
1
1
A1
A0
RD/W
MAX7502
1
0
0
1
0
A1
A0
RD/W
Table
1. I
2
C Slave Addresses
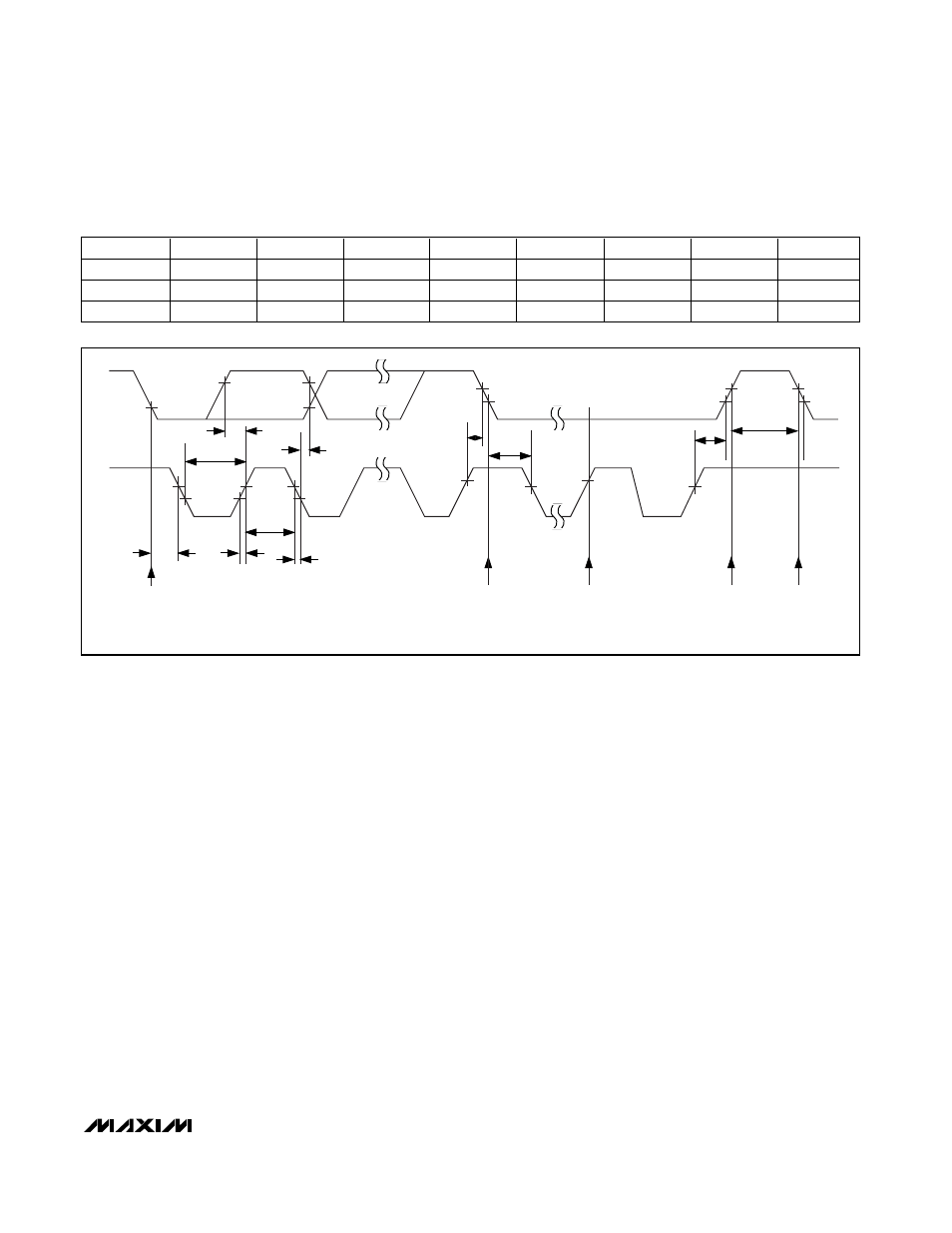
t
BUF
t
SU:STO
t
HD:STA
t
SU:STA
t
HD:DAT
t
HIGH
t
LOW
t
SU:DAT
t
HD:STA
SCL
SDA
t
F
t
R
ACKNOWLEDGE
(A)
STOP
CONDITION
(P)
START
CONDITION
(S)
START
CONDITION
(S)
REPEATED START
CONDITION
(SR)
PARAMETERS ARE MEASURED FROM 10% TO 90%.
Figure 1. Serial Bus Timing
