Table 3. fault queue register bit definition (22h), Table 4. fault queue length bit definition – Rainbow Electronics MAX6692 User Manual
Page 9
MAX6648/MAX6692
Precision SMBus-Compatible Remote/Local
Temperature Sensors with Overtemperature Alarms
_______________________________________________________________________________________
9
rules apply, and the device with the lower address
code wins. The losing device does not generate an
acknowledge and continues to hold the ALERT line low
until cleared. (The conditions for clearing an ALERT
vary, depending on the type of slave device).
Successful completion of the read alert response proto-
col clears the interrupt latch, provided the condition
that caused the alert no longer exists.
OVERT
Overtemperature Alarm/Warning
Outputs
OVERT asserts when the temperature rises to a value
stored in one of the OVERT limit registers (19h, 20h). It
deasserts when the temperature drops below the
stored limit, minus hysteresis. OVERT can be used to
activate a cooling fan, send a warning, invoke clock
throttling, or trigger a system shutdown to prevent com-
ponent damage.
Command Byte Functions
The 8-bit command byte register (Table 5) is the master
index that points to the various other registers within the
MAX6648/MAX6692. The register’s POR state is 0000
0000, so a receive byte transmission (a protocol that
lacks the command byte) that occurs immediately after
POR, returns the current local temperature data.
The MAX6648/MAX6692 incorporate collision avoid-
ance so that completely asynchronous operation is
allowed between SMBus operations and temperature
conversions.
One-Shot
The one-shot command immediately forces a new con-
version cycle to begin. If the one-shot command is
received while the MAX6648/MAX6692 are in standby
mode (RUN bit = 1), a new conversion begins, after
which the device returns to standby mode. If a one-shot
conversion is in progress when a one-shot command is
received, the command is ignored. If a one-shot com-
mand is received in autonomous mode (RUN bit = 0)
between conversions, a new conversion begins, the
conversion rate timer is reset, and the next automatic
conversion takes place after a full delay elapses.
Configuration Byte Functions
The configuration byte register (Table 6) is a read-write
register with several functions. Bit 7 is used to mask (dis-
able) interrupts. Bit 6 puts the MAX6648/MAX6692 into
standby mode (STOP) or autonomous (RUN) mode.
Status Byte Functions
The status byte register (Table 7) indicates which (if
any) temperature thresholds have been exceeded. This
byte also indicates whether the ADC is converting and
whether there is an open-circuit fault detected in the
external sense junction. After POR, the normal state of
all flag bits is zero, assuming no alarm conditions are
present. The status byte is cleared by any successful
read of the status byte, after a conversion is complete
and the fault no longer exists. Note that the ALERT
interrupt latch is not automatically cleared when the
status flag bit indicating the ALERT is cleared. The fault
condition must be eliminated before the ALERT output
can be cleared.
When autoconverting, if the T
HIGH
and T
LOW
limits are
close together, it is possible for both high-temp and
low-temp status bits to be set, depending on the
amount of time between status read operations (espe-
cially when converting at the fastest rate). In these cir-
cumstances, it is best not to rely on the status bits to
indicate reversals in long-term temperature changes.
Instead use a current temperature reading to establish
the trend direction.
Conversion Rate Byte
The conversion rate register (Table 8) programs the
time interval between conversions in free-running
autonomous mode (RUN = 0). This variable rate control
can be used to reduce the supply current in portable-
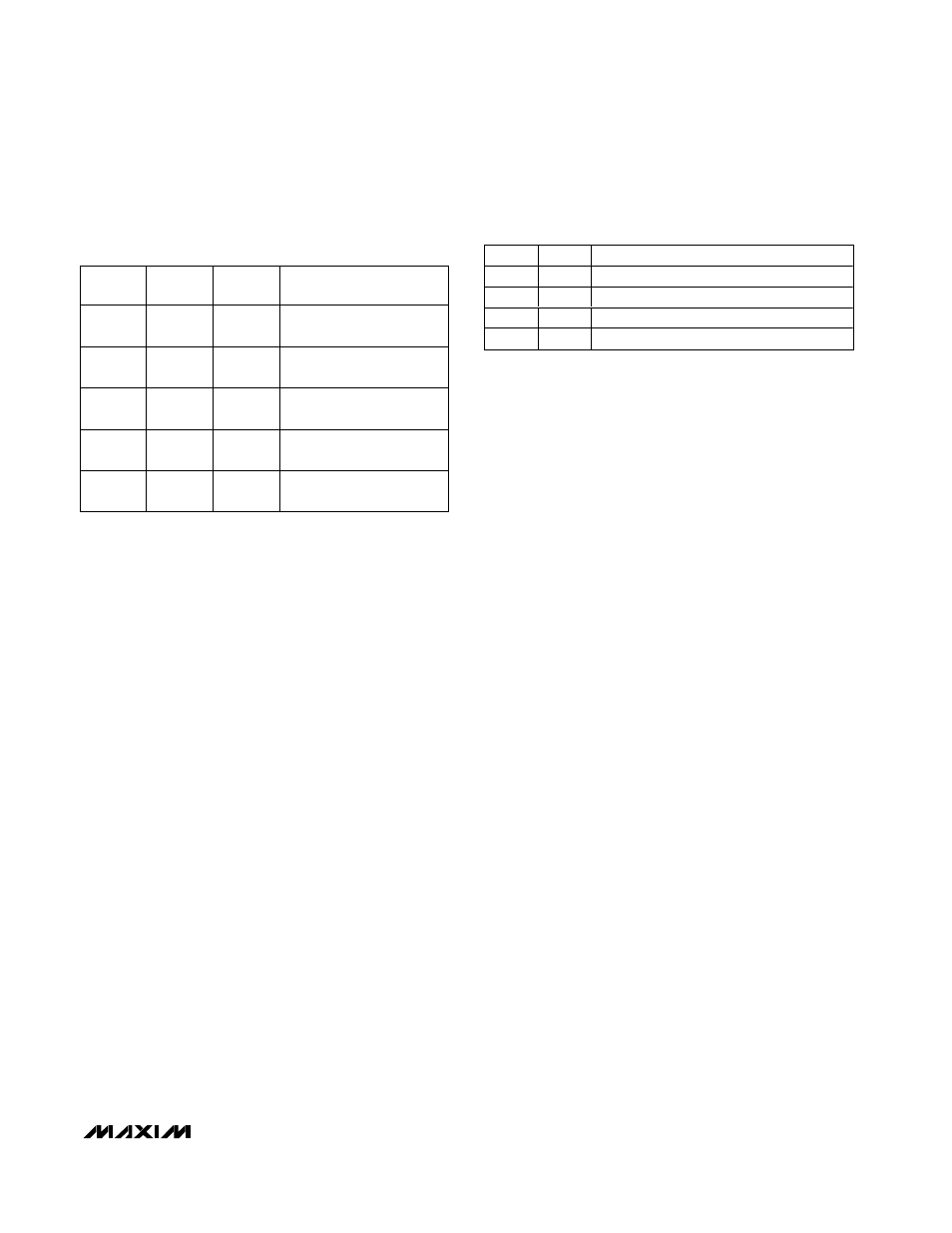
BIT
NAME
POR
STATE
FUNCTION
7
RFU
1
Reserved. Always write 1 to
this bit.
6 to 3
RFU
0
Reserved. Always write
zero to this bit.
2
FQ1
0
Fault queue-length control
bit (see Table 4).
1
FQ0
0
Fault queue-length control
bit (see Table 4).
0
RFU
0
Reserved. Always write
zero to this bit.
Table 3. Fault Queue Register Bit Definition
(22h)
FQ1
FQ0
FAULT QUEUE LENGTH (SAMPLES)
0
0
1
0
1
2
1
1
3
1
0
—
Table 4. Fault Queue Length Bit Definition
