Max6691, Chip information, Functional diagram – Rainbow Electronics MAX6691 User Manual
Page 6: Table 1. standard thermistors
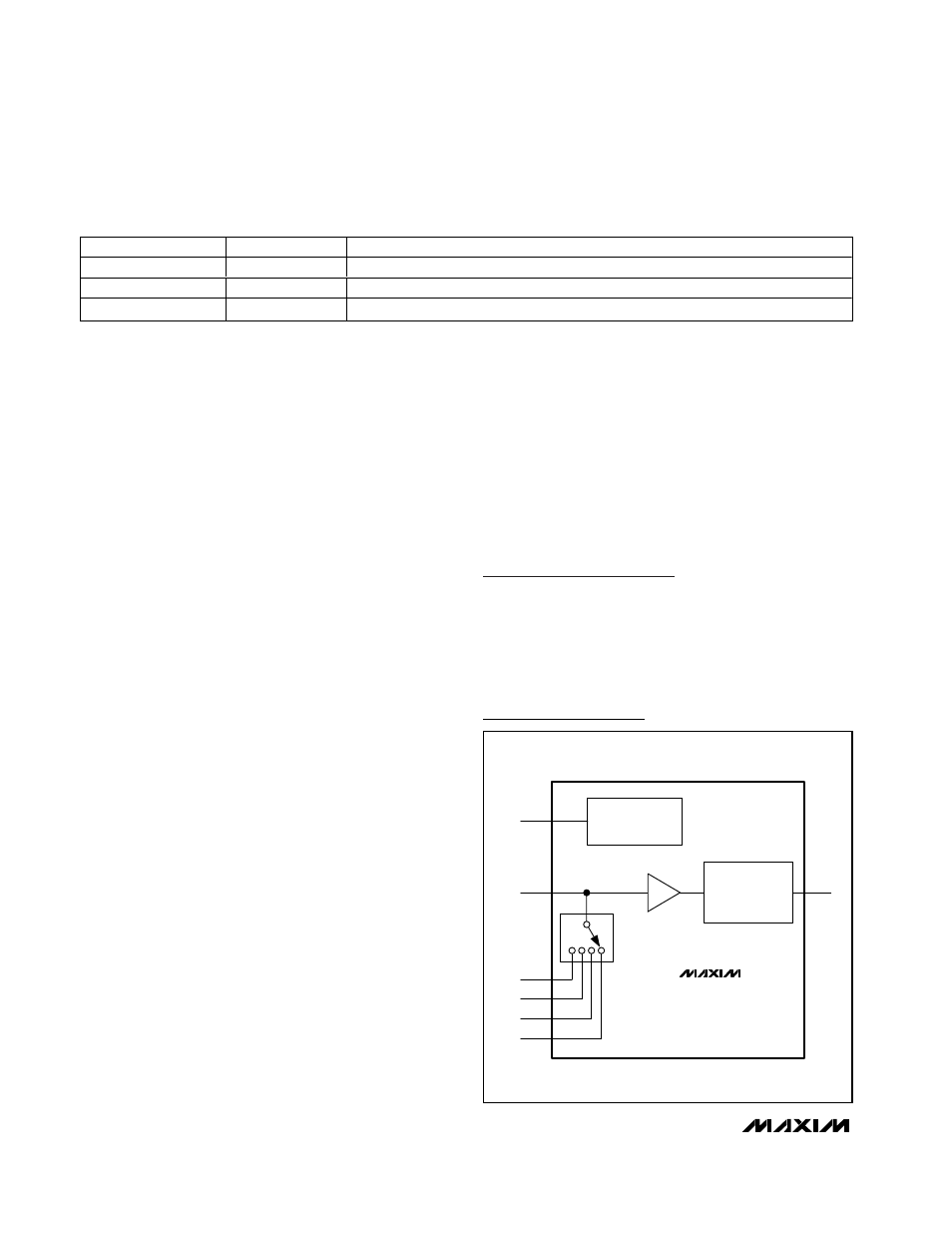
MAX6691
bypass V
CC
to GND by placing a 0.1µF to 1.0µF
ceramic bypass capacitor close to the supply pin of the
devices.
Thermal Considerations
Self-heating degrades the temperature measurement
accuracy of thermistors. The amount of self-heating
depends on the power dissipated and the dissipation
constant of the thermistor. Dissipation constants
depend on the thermistor’s package and can vary con-
siderably.
A typical thermistor might have a dissipation constant
equal to 1mW/°C. For every milliwatt the thermistor dis-
sipates, its temperature rises by 1°C. For example, con-
sider a 10k
Ω (at +25°C) NTC thermistor in series with a
5110
Ω resistor operating +40°C with a constant 5V
bias. If it is one of the standard thermistors previously
mentioned, its resistance is 5325
Ω at this temperature.
The power dissipated in the thermistor is:
(5V)
2
(5325
Ω) / (5325Ω + 5110Ω)
2
= 1.22mW
This thermistor therefore has a self-heating error at
+40°C of 1.22°C. Because the MAX6691 uses a small
reference voltage and energizes each thermistor for
only about 25ms per conversion cycle, the self-heating
of the thermistor under the same conditions when used
with the MAX6691 is far less. Assuming one conversion
cycle every 5s, each thermistor is energized only 0.5%
of the time:
(1.22)
2
(5325)(0.005) / (5325 + 5110)
2
= 0.364µW, or
only about 0.00036°C self-heating error.
Chip Information
TRANSISTOR COUNT: 7621
PROCESS: BiCMOS
Four-Channel Thermistor Temperature-to-Pulse-
Width Converter
6
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Table 1. Standard Thermistors
MANUFACTURER
PART
WEBSITE
Betatherm
10K3A1
www.betatherm.com/indexna.htm
Dale
1M1002
www.vishay.com/brands/dale/main.html
Thermometrics
C100Y103J
www.thermometrics.com
T1
T2
T3
T4
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE-TO-PWM
CONVERTER
R-
R+
I/O
MAX6691
Functional Diagram
