Max6691, Detailed description, Applications information – Rainbow Electronics MAX6691 User Manual
Page 4
MAX6691
Detailed Description
The MAX6691 is an interface circuit that energizes up to
four thermistors and converts their temperatures to a
series of output pulses. The MAX6691 powers the ther-
mistors only when a measurement is being made. This
minimizes the power dissipation in the thermistors, virtu-
ally eliminating self-heating, a major component of ther-
mistor error. The simple I/O allows the initiation of
conversion and delivery of output pulses or a single pin.
Temperature Measurement
When it is not performing conversions or transmitting
output pulses, the MAX6691 is in a low-power sleep
mode and the I/O pin is held at V
CC
by the external
pullup resistor (typically 10k
Ω). To initiate measurement
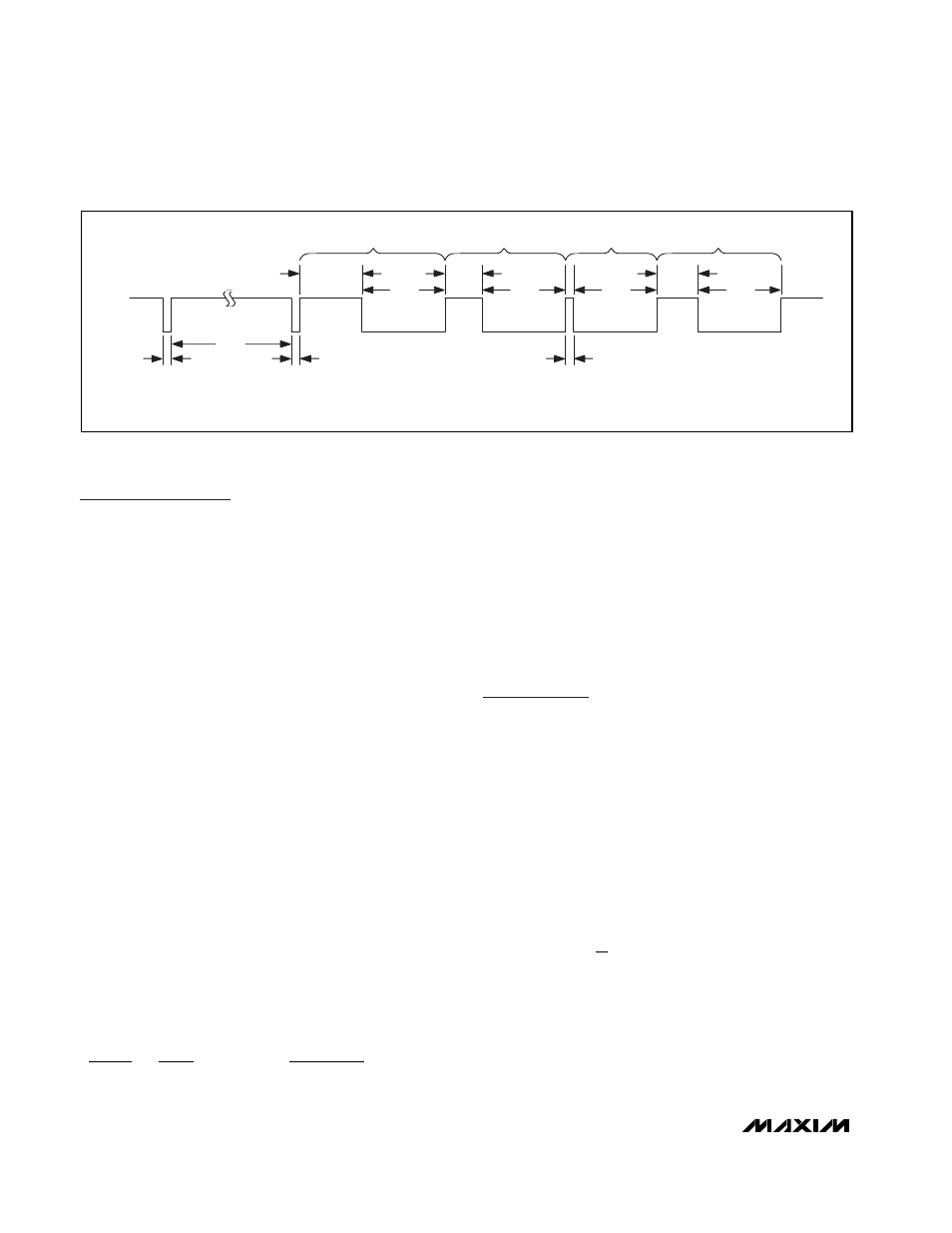
of up to four thermistor temperatures, the external
microcontroller pulls the I/O pin low for at least 5µs
(Figure 1). When the microcontroller releases the I/O
pin, the MAX6691 applies the reference voltage (V
REF
)
to the external resistor (R
EXT
), which is connected
sequentially to each of the four external thermistors (T1
through T4).
When the measurements are complete (after a period
equal to T
CONV
), the MAX6691 pulls the I/O pin low for
125µs. The I/O pin remains high for a period proportion-
al to the first V
EXT
measurement (corresponding to the
first thermistor). The MAX6691 then pulls the I/O pin low
for a period proportional to V
REF
. Three more high/low
pulse pairs follow, corresponding to T2 through T4,
after which the I/O pin is released.
The relationship between pulse width, R
EXT
, and ther-
mistor resistance (R
TH
) can be described as:
The relationship between V
EXT
and the temperature of
a thermistor is determined by the values of R
EXT
and
the thermistor’s characteristics. If the relationship
between R
TH
and the temperature is known, a micro-
controller with no on-chip ADC can measure T
HIGH
and
T
LOW
and accurately determine the temperature at the
corresponding thermistor.
For each operation, the MAX6691 generates four puls-
es on the I/O pin. In the case of an open or short con-
nection on the thermistor, the corresponding pulse
(T
HIGH
) is a short pulse of less than 5% of T
LOW
.
Applications Information
Thermistors and Thermistor Selection
Either NTC or PTC thermistors can be used with the
MAX6691, but NTC thermistors are more commonly
used. NTC thermistors are resistive temperature sen-
sors whose resistance decreases with increasing tem-
perature. They are available in a wide variety of
packages that are useful in difficult applications such
as measurement of air or liquid temperature. Some can
operate over temperature ranges beyond that of most
ICs. The relationship between temperature and resis-
tance in an NTC thermistor is very nonlinear and can be
described by the following approximation:
Where T is absolute temperature, R is the thermistor’s
resistance, and A, B, C are coefficients that vary with
manufacturer and material characteristics. The general
shape of the curve is shown in Figure 2.
1
3
T
C InR
= +
A
B(InR) +
(
)
T
T
V
V
.0002
=
R
R
+R
HIGH
LOW
EXT
REF
EXT
EXT
TH
=
−
−
0
0 0002
.
Four-Channel Thermistor Temperature-to-Pulse-
Width Converter
4
_______________________________________________________________________________________
t
START
CONV REQUEST,
PULLED LOW BY
µC
t
READY
DATA READY,
PULLED LOW BY
MAX6691
t
ERROR
THERMISTOR IS
EITHER OPEN OR
SHORT
t
CONV
T
HIGH1
T
HIGH2
T
HIGH4
THERMISTOR 1
DATA
T
LOW
T
LOW
T
LOW
T
LOW
THERMISTOR 2
DATA
THERMISTOR 3
DATA
THERMISTOR 4
DATA
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
