1 equipment, Figure 2–1. load test board – Texas Instruments bq24013 User Manual
Page 11
Test Procedure
2-3
Test Summary
Another way to briefly see each mode on a scope is to connect a 1-mF
capacitor and a 10-k
Ω
resistor on the output in place of a battery to observe
the power-up and cycling between voltage regulation and fast charge via the
refresh threshold.
Note:
Because of the battery-detection circuit, it is not possible to switch-in static
load resistors to jump between regulation and constant-current modes. An
alternate procedure described below uses a dynamic load to replace the
battery circuit. That procedure allows testing of each mode.
This is an alternative way of testing the EVM using a dynamic load board in
place of a battery. The circuit is adjusted to work with the displayed parts and
their inherent thresholds. The sequence of the test procedure is important
because of the active battery-detection circuit, refresh feature, and precharge
and fast-charge current levels (switching load in or out has different results in
different modes). No damage should occur, but results might be different than
anticipated if the procedure is altered.
2.2.1
Equipment
1) Power source: current-limited 5-V lab supply with its current limit set to
1.0 A
±
0.1 A
2) Two Fluke 75, equivalent or better
3) Oscilloscope – TDS220 or better
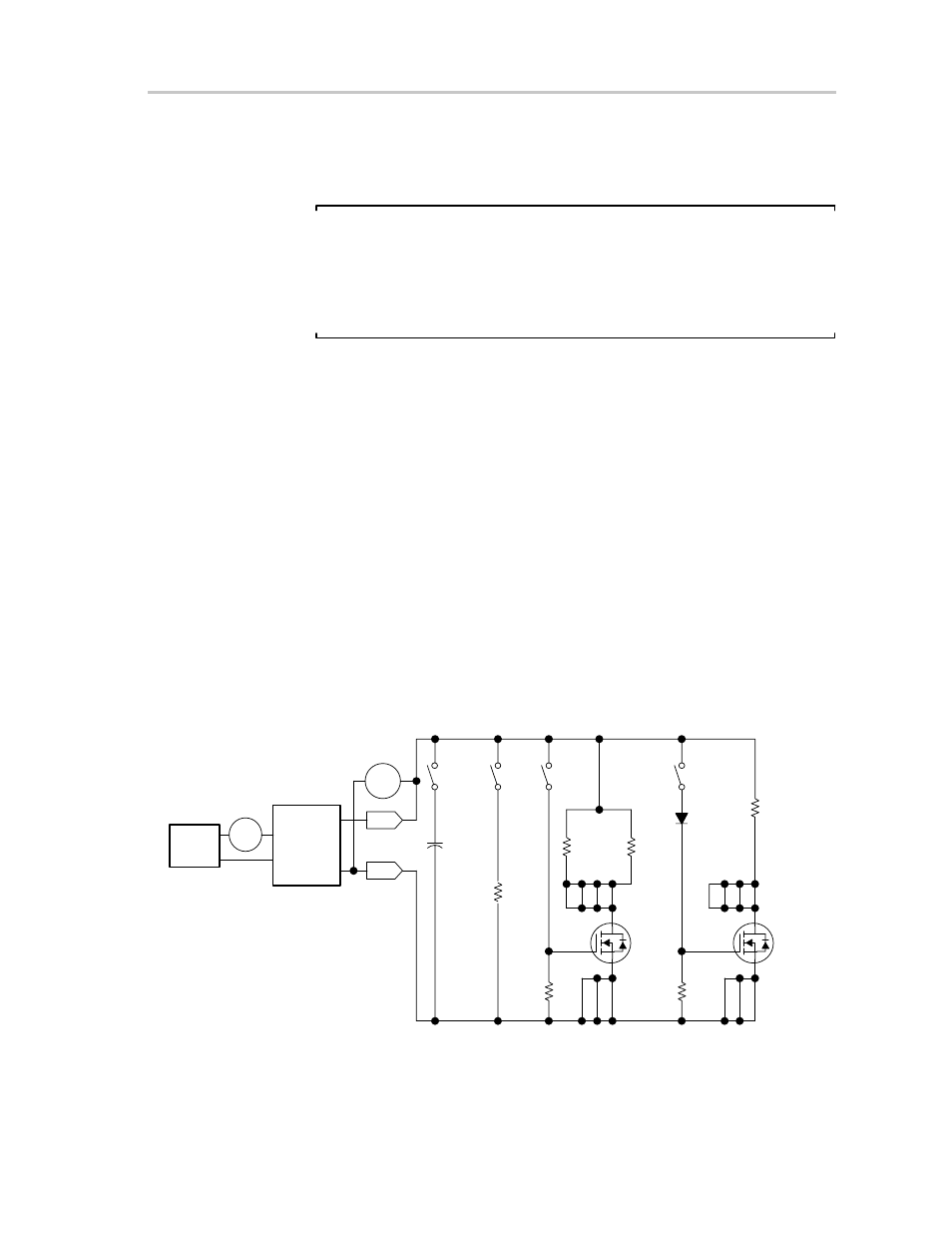
4) Load test board (Figure 2–1)
Figure 2–1. Load Test Board
C1
2000
µ
F
25 V
8
Power Supply
5.1 V
±
0.1 V
Current Limit
1 A
±
0.1 A
+
–
DMM
DC+
DC–
UUT
bq24013 EVM
BAT+
BAT–
BAT+
BAT–
DMM
Volts
S4
R3
3 k
Ω
0.25 W
S1
R6
10 k
Ω
0.25 W
S2
R4
66.5
Ω
0.25 W
7 6 5
R5
66.5
Ω
0.25 W
Q1
Si4410DY
3 2 1
D1
1N4148
S3
R7
10 k
Ω
0.25 W
8 7 6 5
Q2
Si4410DY
3 2 1
4
4
R1
5
Ω
5 W
