Memory operations, Ptn3501 maintenance and control device – Philips PTN3501 User Manual
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
PTN3501
Maintenance and control device
2001 Jan 17
8
MEMORY OPERATIONS
Write operations
Write operations require an additional address field to indicate the
memory address location to be written. The address field is eight
bits long providing access to any one of the 256 words of memory.
There are two types of write operations, byte write and page write.
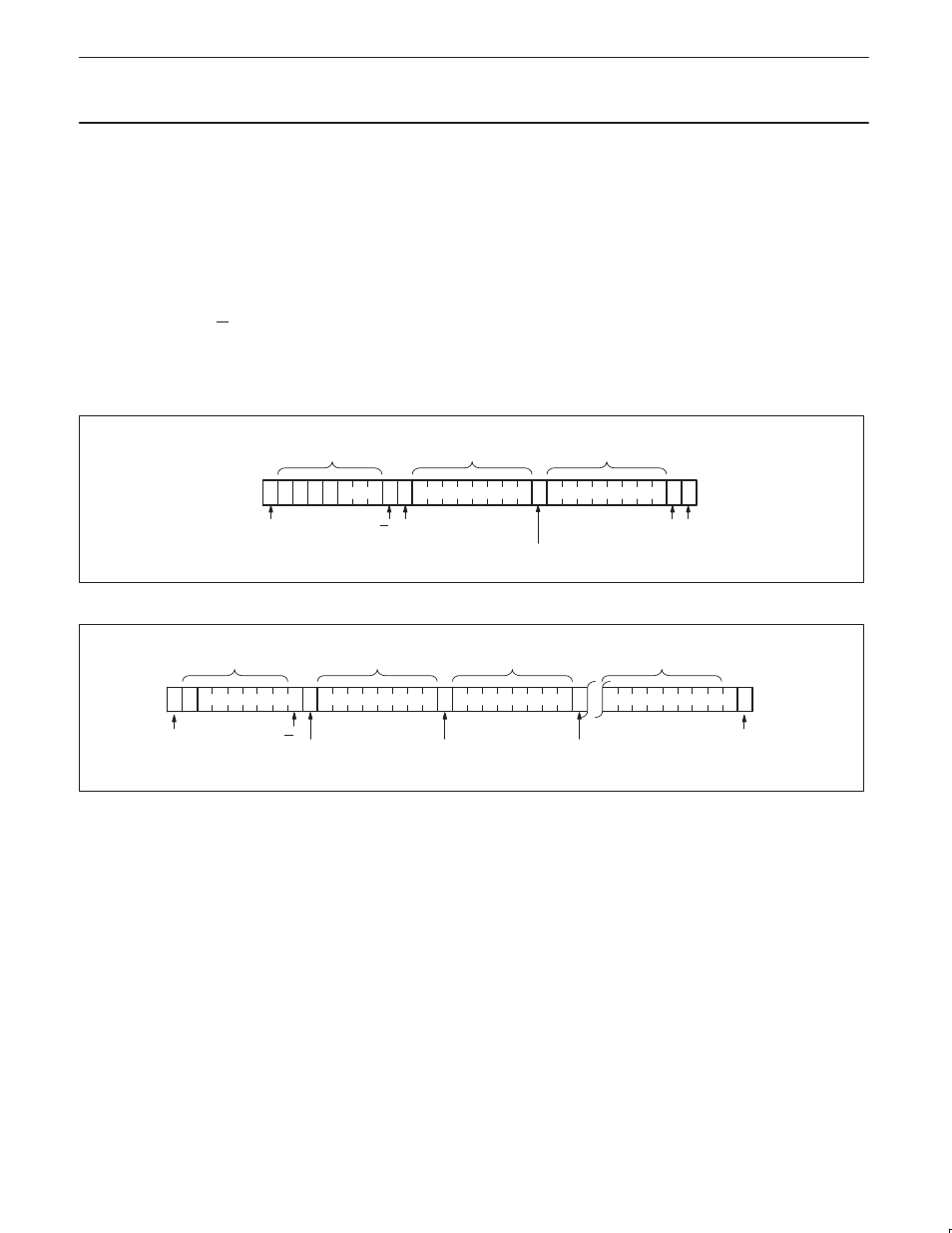
Byte Write (see Figure 14)
To perform a byte write the start condition is followed by the memory
slave address and the R/W bit set to 0. The PTN3501 will respond
with an acknowledge and then consider the next eight bits sent as
the word address and the eight bits after the word address as the
data. The PTN3501 will issue an acknowledge after the receipt of
both the word address and the data. To terminate the data transfer
the master issues the stop condition, initiating the internal write cycle
to the non–volatile memory. Only write and read operations to the
quasi–bidirectional I/Os are allowed during the internal write cycle.
Page Write (see Figure 15)
A page write is initiated in the same way as the byte write, if after
sending the first word of data, the stop condition is not received the
PTN3501 considers subsequent words as data. After each data
word the PTN3501 responds with an acknowledge and the four least
significant bits of the memory address field are incremented. Should
the master not send a stop condition after 16 data words the
address counter will return to its initial value and overwrite the data
previously written. After the receipt of the stop condition the inputs
will behave as with the byte write during the internal write cycle.
P
SW00651
SDA
SLAVE
ADDRESS
(MEMORY)
WORD
ADDRESS
DATA
S
1 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
A
A
R/W
START CONDITION
STOP
CONDITION
0
A
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
Figure 14. Byte write
S
P
SDA
SW00652
SLAVE ADDRESS
(MEMORY)
WORD ADDRESS
DATA TO MEMORY
1 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
A
A
0
START
CONDITION
R/W
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
DATA n
A
ACKNOWLEDGE
FROM SLAVE
DATA +3n
DATA TO MEMORY
STOP
CONDITION
A
Figure 15. Page Write
