Kawasaki 840641 User Manual
Page 10
17
W
WE
EL
LD
DIIN
NG
G P
PO
OS
SIIT
TIIO
ON
NS
S
Welding positions can be categorized into four basic types: flat, horizontal, vertical,
and overhead. Welding in the flat position is the easiest of all the different types
because welding speed can be increased and the molten metal has a less tendency
to run, better penetration can be achieved and the work is less fatiguing. Welding is
performed with wire at a 45° travel angle and a 45° work angle. Other positions
require different welding techniques such as weaving pass, circular pass, or jogging
pass. These techniques should only be attempted as the welder’s skills improve over
time. Overhead welding is least desirable position as it is the most dangerous and
most difficult. Heat setting and wire selections are more critical in this type. The
same special requirements are true for horizontal and vertical welding. For specific
applications, consult an arc welding technical manual.
A
AD
DD
DIIT
TIIO
ON
NA
AL
L S
SA
AFFE
ET
TY
Y S
ST
TA
AN
ND
DA
AR
RD
DS
S
• A
AN
NS
SII S
Sttaan
nd
daarrd
d Z
Z4
49
9..1
1:: From the American Welding Society.
• S
Saaffeettyy aan
nd
d H
Heeaalltth
h S
Sttaan
nd
daarrd
dss:: OSHA 29 CFR 1910.
• N
Naattiio
on
naall E
Elleeccttrriiccaall C
Co
od
dee:: NPFA Standards 51B and 70 from the National fire
Protection Association.
• C
Co
od
dee FFo
orr S
Saaffeettyy iin
n W
Weelld
diin
ng
g aan
nd
d C
Cu
uttttiin
ng
g:: CSA Standard W117.2, from
Canadian Standards Association.
• S
Saaffee P
Prraaccttiicceess ffo
orr O
Occccu
up
paattiio
on
naall aan
nd
d E
Ed
du
uccaattiio
on
naall E
Eyyee aan
nd
d FFaaccee P
Prro
otteeccttiio
on
n::
ANSI Standard Z87.1 from American National Standards Institute.
T
TR
RO
OU
UB
BL
LE
ES
SH
HO
OO
OT
TIIN
NG
G C
CH
HA
AR
RT
T –
– W
WE
EL
LD
DS
S
S
SY
YM
MP
PT
TO
OM
M
P
PO
OS
SS
SIIB
BL
LE
E C
CA
AU
US
SE
ES
S((S
S))
C
CO
OR
RR
RE
EC
CT
TIIV
VE
E A
AC
CT
TIIO
ON
N
T
TR
RO
OU
UB
BL
LE
ES
SH
HO
OO
OT
TIIN
NG
G C
CH
HA
AR
RT
T –
– W
WE
EL
LD
DS
S
S
SY
YM
MP
PT
TO
OM
M
P
PO
OS
SS
SIIB
BL
LE
E C
CA
AU
US
SE
ES
S((S
S))
C
CO
OR
RR
RE
EC
CT
TIIV
VE
E A
AC
CT
TIIO
ON
N
B
BE
EL
LO
OW
W A
AR
RE
E S
SE
EV
VE
ER
RA
AL
L D
DIIFFFFE
ER
RE
EN
NT
T T
TY
YP
PE
ES
S O
OFF W
WE
EL
LD
D A
AP
PP
PE
EA
AR
RA
AN
NC
CE
ES
S..
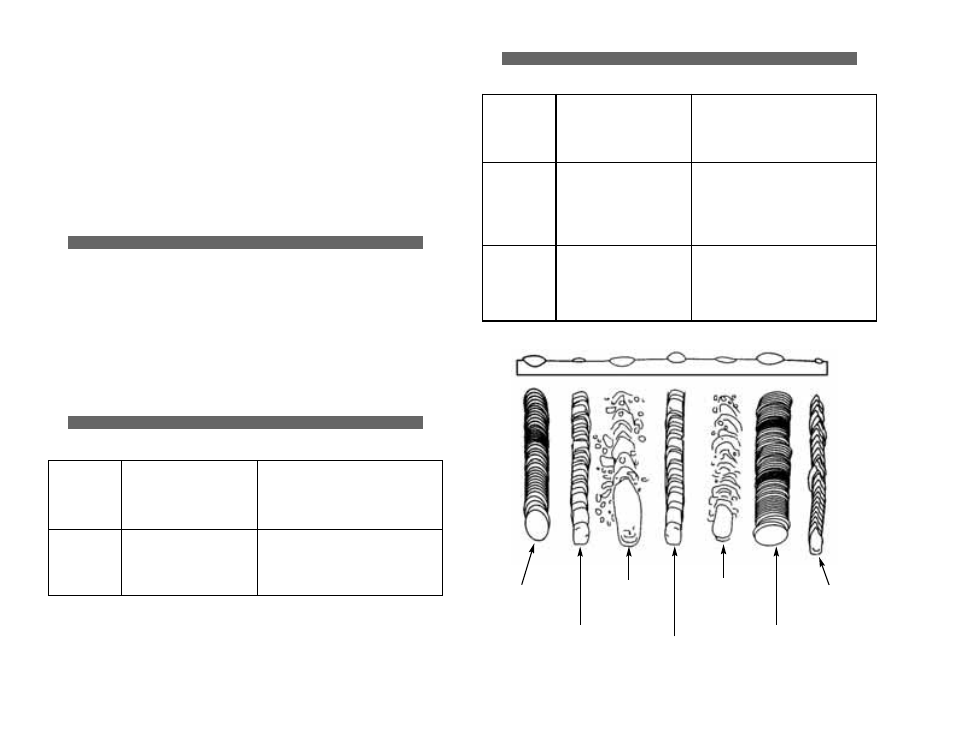
Ragged
depressions
at edge of
weld
1. Travel Speed too fast
2. Wire speed too fast
3. Output heat setting too high
1. Decrease travel speed
2. Decrease wire speed
3. Reduce output heat setting
Weld bead
does not
penetrate
base metal
1. Inconsistent ravel speed
2. Output heat setting too low
3. Extension cord too long
1. Decrease and maintain constant
travel speed
2. Increase output heat setting
3. Use an extension cord no longer
than 20 feet
Wire
sputters
and sticks
1. Damp wire
2. Wire speed too fast
3. Wrong type of wire
1. Use dry wire and store in dry place
2. Reduce wire speed
3. Use FLUX CORE wire only - do not
use MIG or copper color wire
Bead is
intermittently
too thin
1. Inconsistent travel
speed
2. Output heat setting too low
1. Decrease and maintain constant
travel speed
2. Increase output heat setting
Bead is
intermittently
too thick
1. Slow and/or inconsistent
travel speed
2. Output heat setting too high
1. Increase and maintain travel
speed
2. Reduce output heat setting
N
No
orrm
maall h
heeaatt,,
w
wiirree ssp
peeeed
d,,
ttrraavveell ssp
peeeed
d
HEAT TOO
LOW
HEAT TOO
HIGH
WIRE SPEED
TOO FAST
WIRE SPEED
TOO SLOW
TRAVEL SPEED
TOO SLOW
TRAVEL SPEED
TOO FAST
18
