System grounding, Setup – Woodstock W1685 User Manual
Page 17
-17-
SETUP
W1666, W1685 Dust Collectors
Under some circumstances, static electricity can be
generated in dust collection systems and can collect on
the plastic ducting surfaces. If this static electricity is
discharged through a spark, there is a potential for the
dust and oxygen in the ducting to ignite.
Therefore, your dust collection system must be grounded
one of three ways.
•
First, the ground is achieved by means of using
metal ducting throughout the system. All static
electricity buildup is carried through the continu
ous metal ducting and dissipated through the dust
collector impeller housing.
•
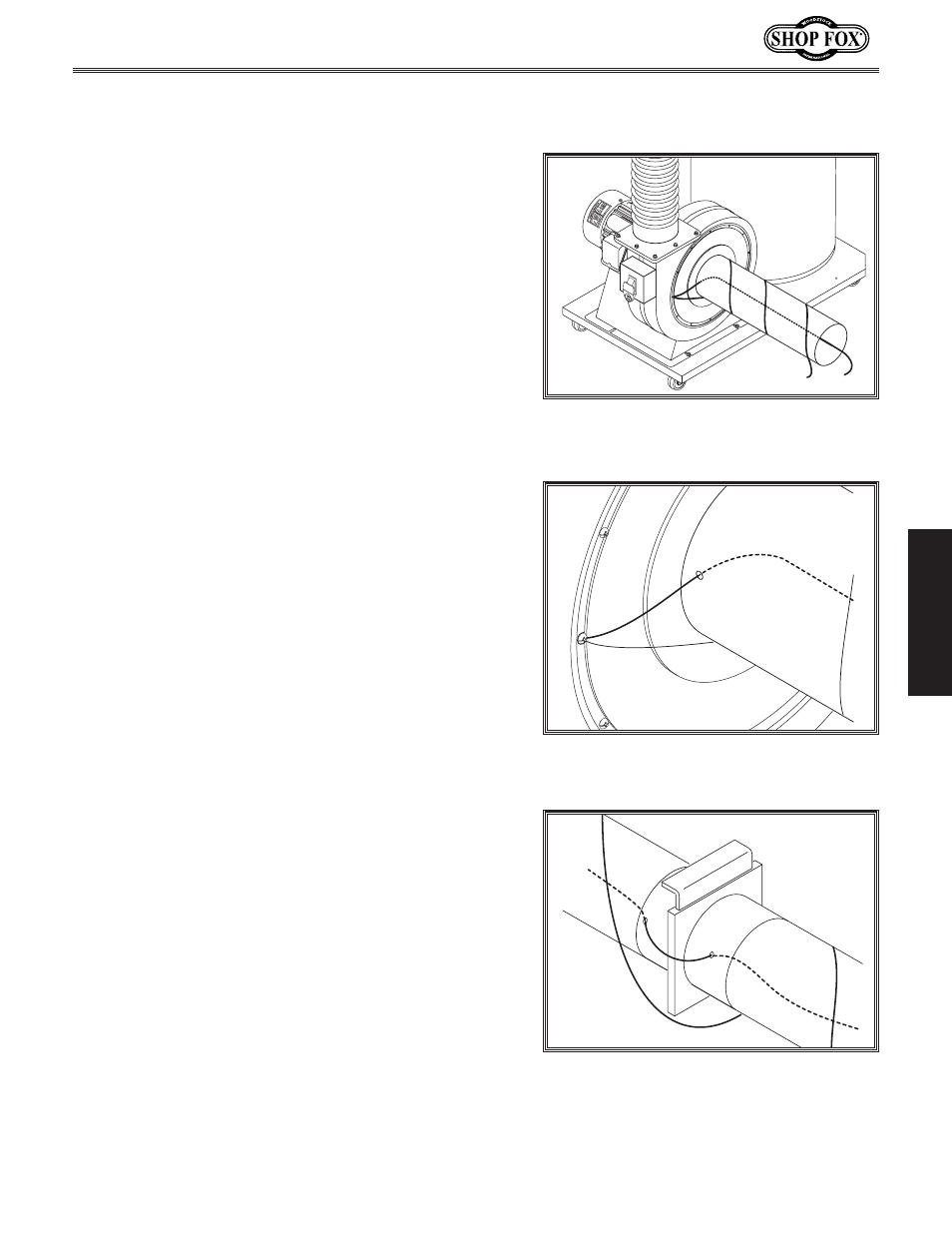
Second, for plastic pipe or hose ducting systems,
install an uncoated bare copper wire inside
the entire length of all ducting. An additional
wire must be spiral-wrapped on the outside of
all the ducting (see
Figure 21). Both wires must
be connected to the dust collector impeller hous-
ing (see
Figure 22) so all static electricity inside
and out of the ducting is carried through the
wires and dissipated through the dust collector
ground.
If the system has branches, place wires in the
same fashion and connect to the wires on the
main pipe/hose with wire nuts. If blast gates
are to be used, drill exit and entrance holes on
either side of the blast gate to allow wire to be
fed out of and into the system (see
Figure 23).
•
Third, if you use a combination of metal and
plastic ducting, make sure that you use a copper
grounding wire to ground all plastic connections
with the metal ducting so no part of the ducting
is insulated by the plastic.
Note: For more in-depth information on Dust Collection
System design, refer to refer to The Dust Collection
Handbook (ISBN 0-9635821-2-7), which is available for
purchase through any Woodstock/SHOP FOX
®
Dealer.
System Grounding
Figure 21. Typical dust collector with
ground wire installed inside and around
pipe.
Figure 22. Typical dust collector impeller
housing with ground wires secured to
the housing.
Figure 23. Ground wires bypassing a blast
gate.
