2 conducted noise, 3 voltage tolerance, 4 power-management modes – Seagate BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3640330AS User Manual
Page 20
14
Barracuda 7200.11 Serial ATA Product Manual, Rev. G
2.7.2
Conducted noise
Input noise ripple is measured at the host system power supply across an equivalent 80-ohm resistive load on
the +12 volt line or an equivalent 15-ohm resistive load on the +5 volt line.
• Using 12-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of 120 mV peak-to-peak square-wave
injected noise at up to 10 MHz.
• Using 5-volt power, the drive is expected to operate with a maximum of
100 mV peak-to-peak square-wave
injected noise at up to 10 MHz.
Note. Equivalent resistance is calculated by dividing the nominal voltage by the typical RMS read/write
current.
2.7.3
Voltage tolerance
Voltage tolerance (including noise):
5V +10% / -7.5%
12V +10% / -7.5%
2.7.4
Power-management modes
The drive provides programmable power management to provide greater energy efficiency. In most systems,
you can control power management through the system setup program. The drive features the following
power-management modes:
• Active mode
The drive is in Active mode during the read/write and seek operations.
• Idle mode
The buffer remains enabled, and the drive accepts all commands and returns to Active mode any time disc
access is necessary.
• Standby mode
The drive enters Standby mode when the host sends a Standby Immediate command. If the host has set
the standby timer, the drive can also enter Standby mode automatically after the drive has been inactive for
a specifiable length of time. The standby timer delay is established using a Standby or Idle command. In
Standby mode, the
drive buffer is enabled, the heads are parked and the spindle is at rest. The drive
accepts all commands and returns to Active mode any time disc access is necessary.
• Sleep mode
The drive enters Sleep mode after receiving a Sleep command from the host. In Sleep mode, the drive buf-
fer is disabled, the heads are parked and the spindle is at rest. The drive leaves Sleep mode after it
receives a Hard Reset or Soft Reset from the host. After receiving a reset, the drive exits Sleep mode and
enters Standby mode with all current translation parameters intact.
• Idle and Standby timers
Each time the drive performs an Active function (read, write or seek), the standby timer is reinitialized and
begins counting down from its specified delay times to zero. If the standby timer reaches zero before any
drive activity is required, the drive makes a transition to Standby mode. In both Idle and Standby mode, the
drive accepts all commands and returns to Active mode when disc access is necessary.
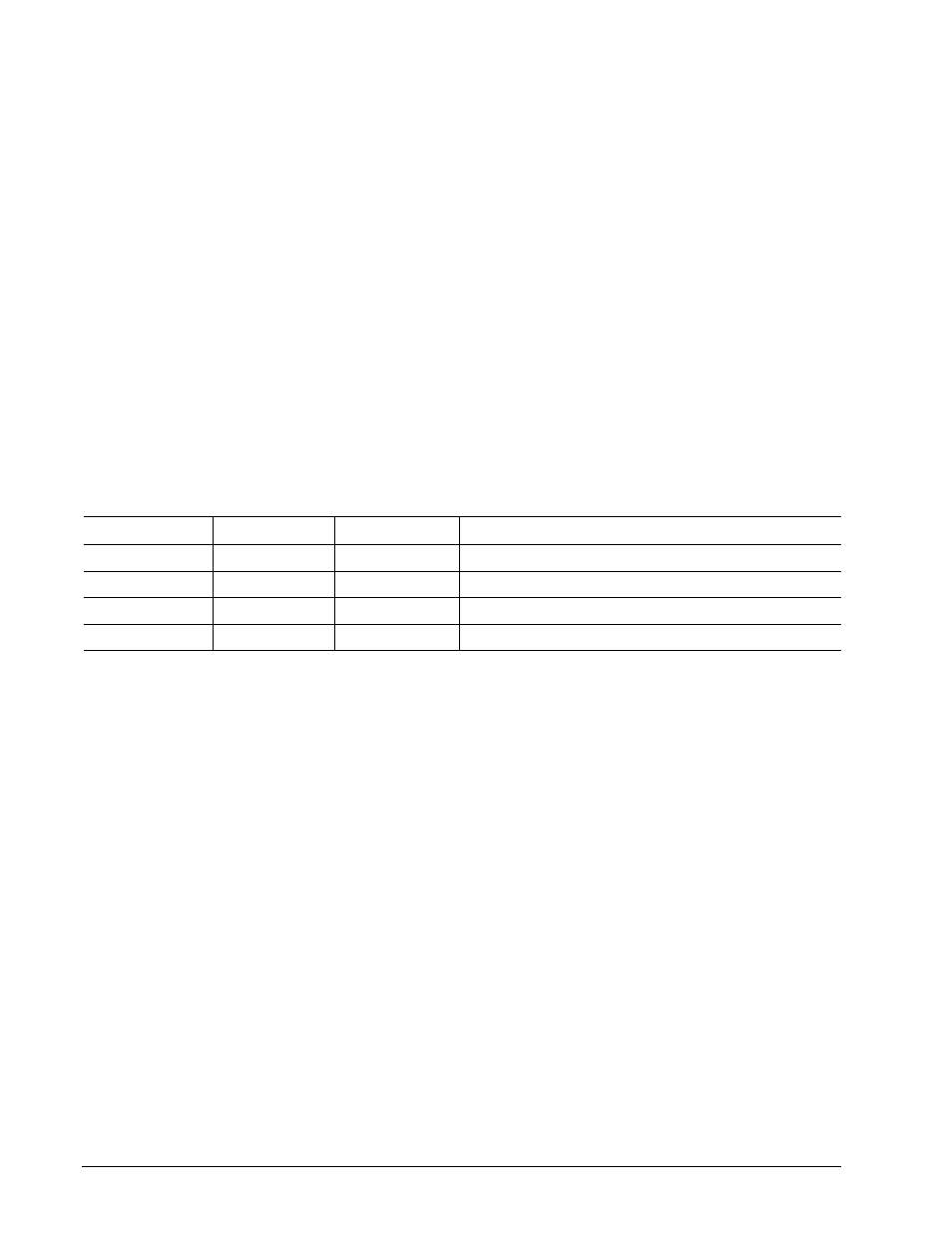
Power modes
Heads
Spindle
Buffer
Active
Tracking
Rotating
Enabled
Idle
Tracking
Rotating
Enabled
Standby
Parked Stopped
Enabled
Sleep
Parked
Stopped
Disabled
- BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3750630AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3640630AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST31000640AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST31000340AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3750330AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3500320AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3500820AS BARRACUDA 7200.11 SERIAL ATA ST3500620AS
