Schumacher 85-716 User Manual
Page 10
•
8
•
9.
ELECTRICAL CONDITION OF BATTERY
9.1 The state of charge of refillable-top batteries can be checked by using a
hydrometer. A hydrometer is a bulb-type syringe which is used to extract a
small quantity of the electrolyte from each battery cell. Types are calibrated
in terms of specific gravity (a common scale being 1.120 to 1.265) or the
type which uses four colored balls to indicate the state of charge. A float in
the hydrometer barrel indicates the specific gravity of the electrolyte. This
specific gravity reading indicates the battery’s state of charge at a given
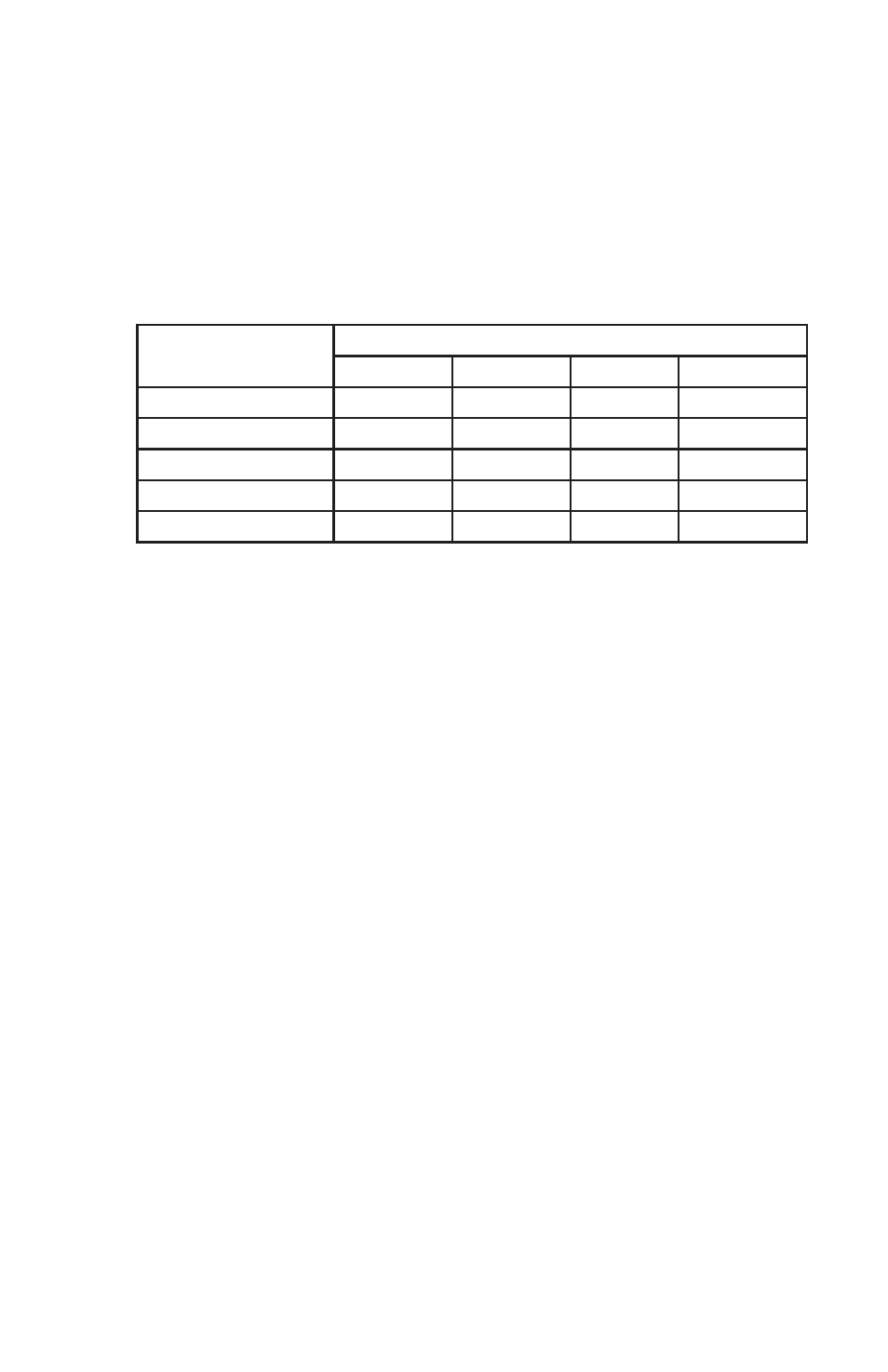
temperature, as shown in the table below:
State of Charge of
Battery at 80°F (27°C)
** Initial Specific Gravity Reading
.280
.265
.225
Floating Balls
00%
.280
.265
.225
4
75%
.240
.225
.85
3
50%
.200
.90
.50
2
25%
.70
.55
.5
Discharged
.40
.20
.080
*
** Initial specific gravity readings vary, depending on battery type and manufacturer.
Contact the seller or manufacturer of the battery for this specification.
* No balls float in the barrel of the hydrometer.
9.2 The state of charge of sealed-top (maintenance-free and recombination-
type) batteries must be checked with a high resolution voltage tester.
9.3 If uncertain about type of battery you will be charging, or the correct
procedure for checking the battery’s state of charge, contact the seller or
manufacturer of the battery.
9.4 The temperature of the battery and the equipment the battery is used
with has a dramatic effect on battery efficiency and system power
requirements. For example, at 0°F (–18°C ), a battery is operating at 40%
of its rated efficiency, while the engine it is attempting to start requires over
twice as much power as would be necessary at 80°F (27°C).
