Df250ss product information, Vvt (variable valve timing), Diagram of vvt mechanism – Suzuki DF250SS User Manual
Page 5
4
Diagram of VVT Mechanism
D
Suzuki Technologies Deliver Outstanding Performance
Camshaft Position Sensor
Rotation Direction
VVT Actuator
Throttle Opening Angle
Water Temp
Feed
back
Cam Position
Crank
Position
Manifold Pressure
Water Temp Sensor
Throttle Sensor
Map Sensor*
Intk Camshaft
Ex Camshaft
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Duty Control
Crankshaft
ECM
Target
Advance
Actual Valve
Timing
Intk Camshaft
Retard
Advance
Drain
Oil
Filter
Oil
Pump
Oil Pan
Engine Oil Flow
Oil Control Valve (OCV)
Signal
*Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
DF250SS PRODUCT INFORMATION
T
O
R
Q
U
E
LOW
MID
ENGINE SPEED
HIGH
without VVT
with VVT
Valve Overlap
V
a
lv
e
L
if
t
Ex Valve
Advance
40° Movable Angle
Intk Valve
Retard
Crank Angle
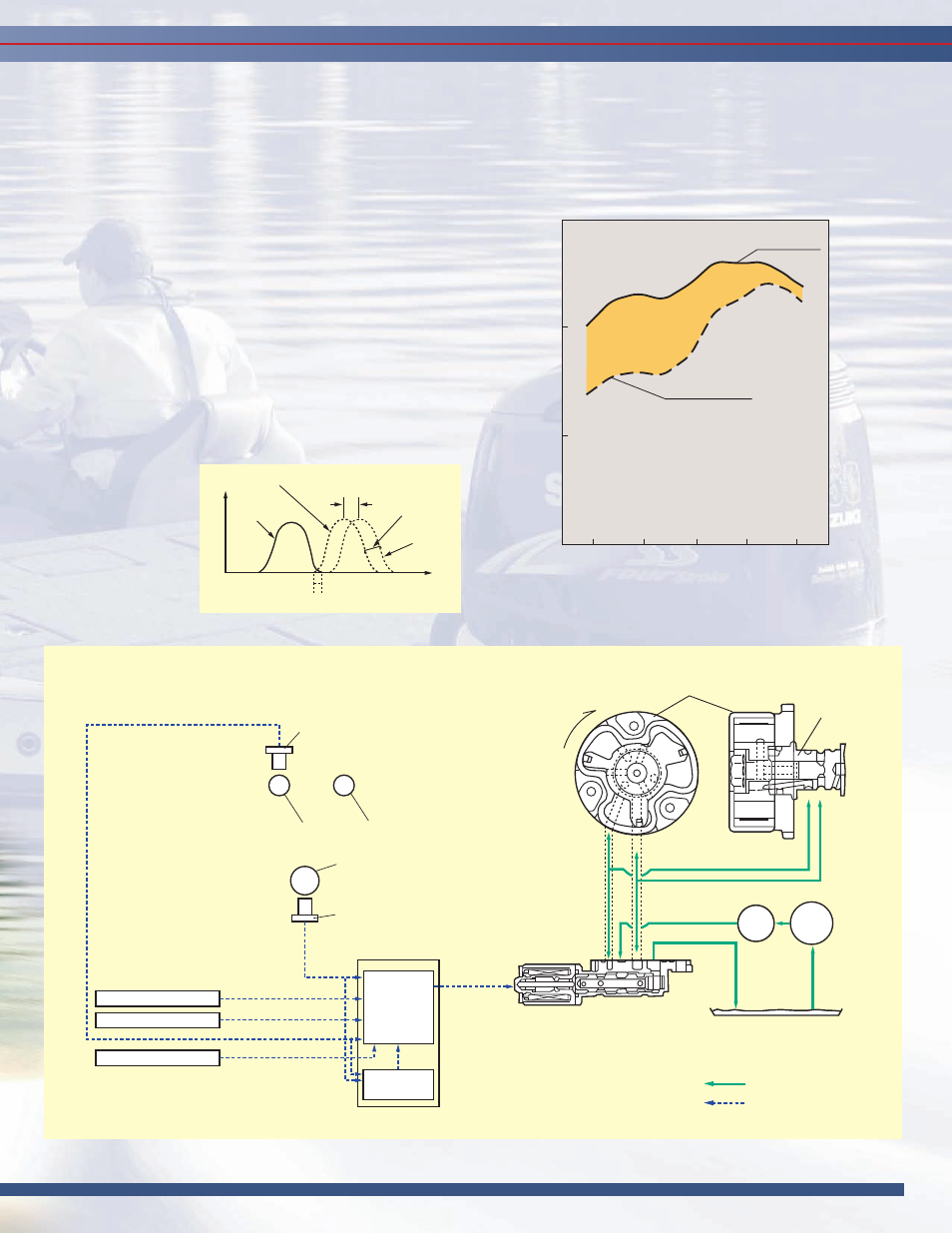
VVT (Variable Valve Timing)
Suzuki engineers started off in a big way by designing the
DF250SS based on a big block 4.0-liter engine, the largest displace-
ment found in this class. This V6 engine features an aggressive cam
profile, delivering maximum output and performance at high rpm,
and Suzuki’s advanced Variable Valve Timing (VVT), provides the
DF250SS with the torque needed to boost low- to mid-range
acceleration. VVT provides this boost by adjusting the intake valve
timing, allowing intake valves to open before the exhaust valves are
fully closed. This process creates a momentary overlap in the
timing where both sets of valves are open. With VVT, this overlap
can be increased or
decreased by altering
intake timing with the
camshafts to optimize
timing for low- and
mid-range operation.
■
