Migration support, Alps – IBM BC-201 User Manual
Page 29
Overview of IBM Networking
ALPS
BC-229
Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide
78-11737-02
Migration Support
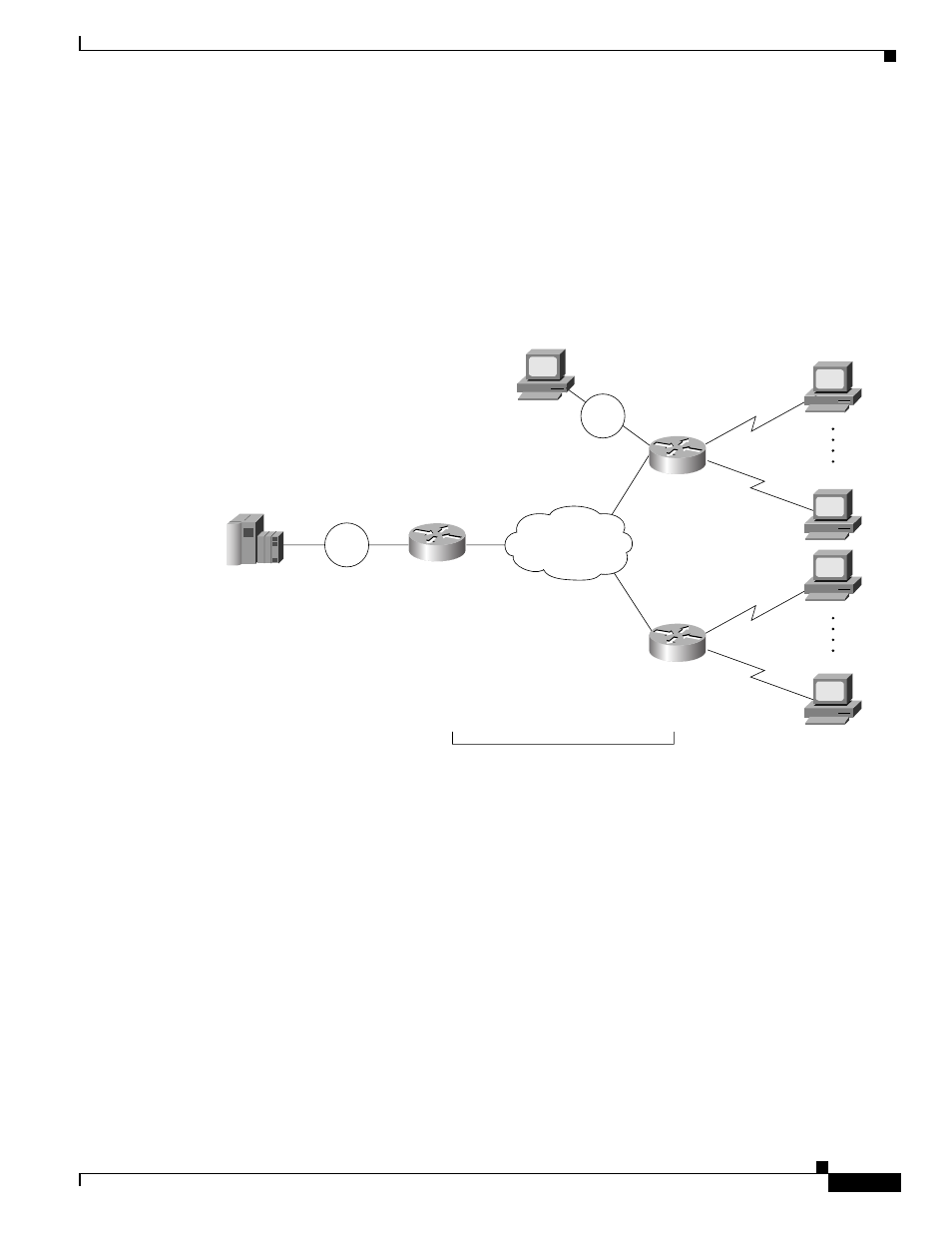
Using a client/server model allows the NCIA Server feature to be independent of the upstream
implementation, allowing it to be implemented in a network that is still using RSRB and in a DLSw+
network. It also greatly simplifies migration from RSRB to DLSw+, because it requires no changes at
the client. A single NCIA server can support either approach (but not both). As
illustrates, a
central site router can support RSRB and DLSw+ concurrently, allowing a portion of the NCIA servers
to communicate using RSRB and another portion to communicate using DLSw+.
Figure 103
NCIA Server Provides Independence from the Upstream Network Implementation
ALPS
The Airline Product Set (ALPS) is a tunneling mechanism that transports airline protocol data across a
TCP/IP network to a mainframe. ALPS provides connectivity between agent set control units (ASCUs)
and a mainframe host that runs the airline reservation system.
shows the basic ALPS topology and the protocols implemented in the feature. Three major
components provide the end-to-end transportation of airline protocol traffic across the network: the
P1024B Airline Control (ALC) or P1024C (UTS) protocol, the TCP/IP-based MATIP protocol
conversion, and the TCP/IP access to the mainframe.
Mainframe
with FEP
Cisco
RSRB/DLSw+
DLSw+
NCIA server
NCIA server
51915
IP
backbone
RSRB
Client
workstation
Token
Ring
Token
Ring
Router peers
Computing center
