5 battery terminology, 5 battery terminology -3 – Motorola 68P64114B12B User Manual
Page 43
Batteries
3-3
1.5
Battery Terminology
Memory Effect
Continually not fully discharging a battery causes an accumulation of very tiny gas bubbles and the
formation of irregular shaped crystals which adhere to the cell plates. These irregular shaped
crystals prevent the battery attaining its full capacity.
The result is the battery will only charge to the level at which it was last discharged.
For example, a person over many months routinely uses only 70% of the battery capacity before
recharging. In a Nickel Cadmium battery that originally had a battery life of 8 hours, this would
reduce to only 5.6 hours once memory effect had occurred.
To avoid the memory effect, ensure the battery is fully discharged before starting a charge cycle.
This can most effectively be achieved by purchasing a battery maintenance/optimising system.
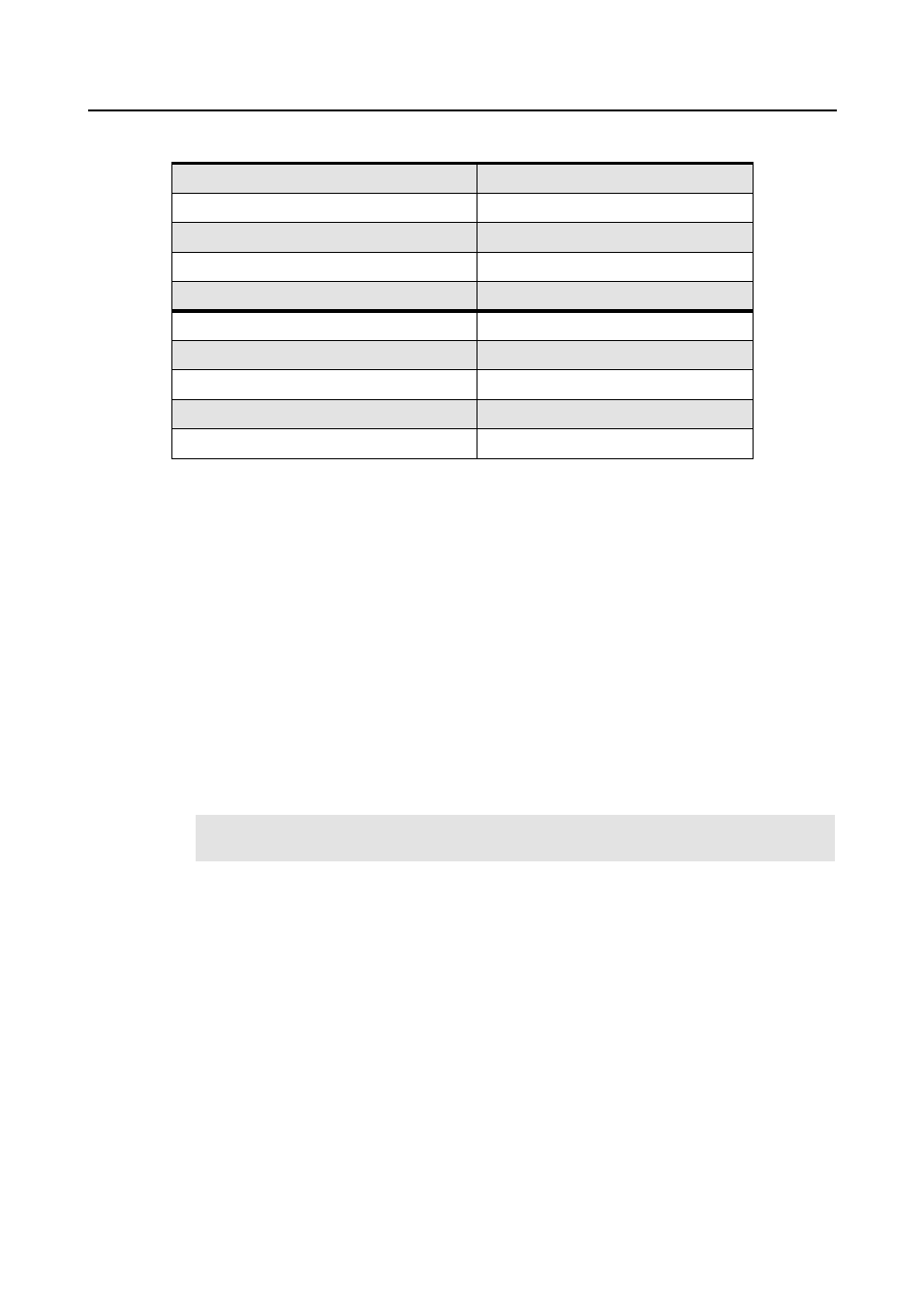
Table 3-1 Battery Specifications
Weight: (gm)
Standard High capacity NiMH battery
202
Ultra high capacity NiMH battery
275
High capacity NiCd battery
225
High Capacity Lilon battery
125
Average Battery Life @5/5/90 Cycle:
Low Power
High Power
With Standard high capacity NiMH battery
11 hours
8 hours
With Ultra high capacity NiMH battery
14 hours
11 hours
With NiCD battery
12 hours
9 hours
With Lilon battery
11 hours
8 hours
NOTE
Nickel Metal Hydride batteries are less prone to memory effect and Lithium Ion batteries do
not exhibit this effect at all.
