Adjusting the headgear, Shade filter – Grizzly h7787 User Manual
Page 2
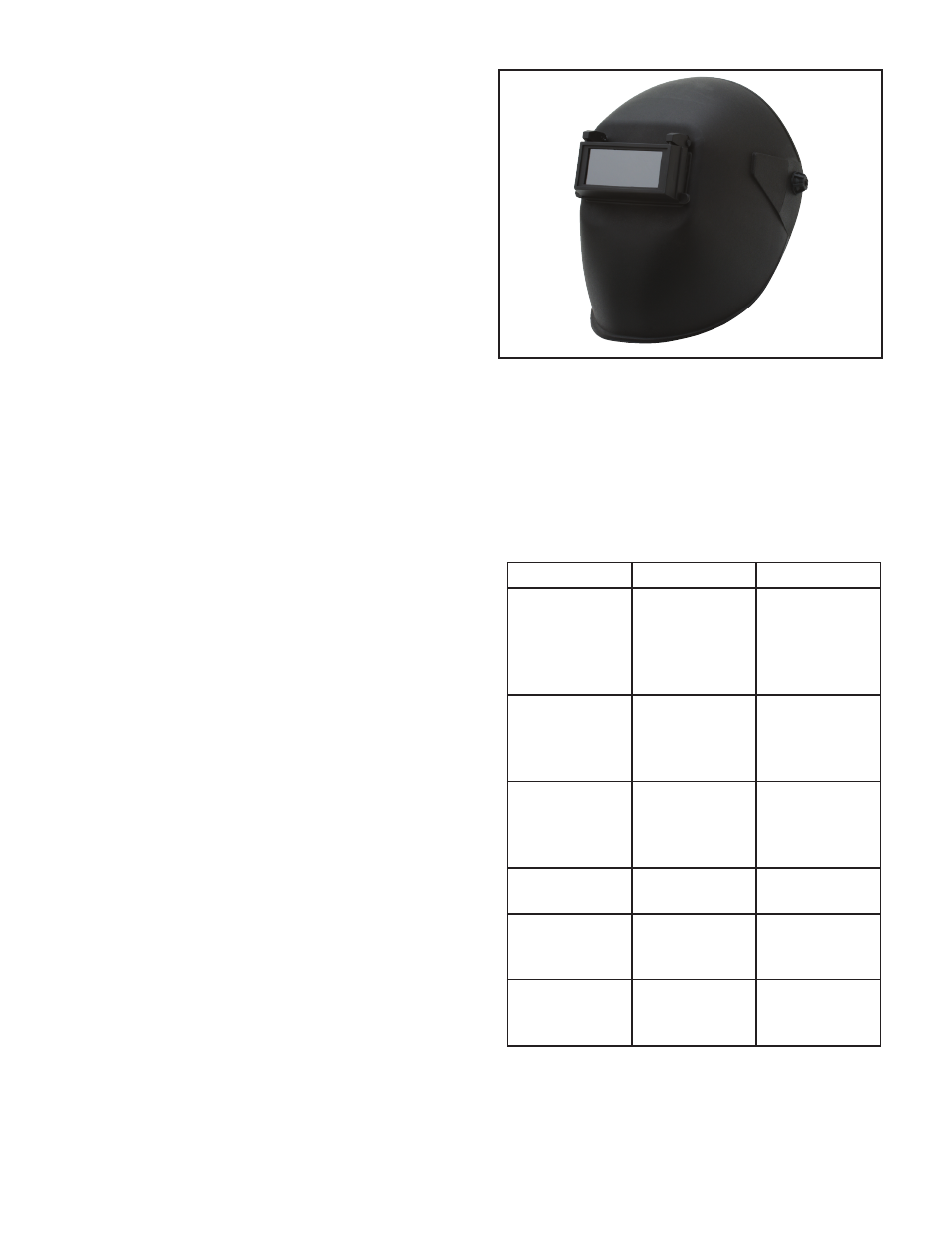
Adjusting the Headgear
The headgear supplied with your welding helmet
can be adjusted for height, diameter, angle and
friction during flip-down.
Height
1. Bend middle strap inward and press the bead
out of the hole.
2. Adjust the strap length until the sweat band is
positioned just above your eye brows.
3. Snap the bead into the closest hole in the
strap.
Diameter
1. Locate the hand knob on the back of the
headband. Rotate it clockwise to tighten and
counterclockwise to loosen.
2. Place the helmet on your head and make
adjustments to the headband until it is com-
fortably snug.
Angle
1. Looking at the back of the helmet, locate the
friction knob on the right hand side and loos-
en it 4 or 5 complete turns. It is not necessary
to remove it completely.
2. On the side of the helmet and just below the
friction knob are 3 holes. One of these holes
will be occupied by a plastic pin. Push the pin
in toward the inside of the helmet and posi-
tion it over the desired hole.
3. Insert the pin and tighten the friction knob.
Choosing the hole furthest from the front of the
helmet will allow the helmet to tilt further forward.
Choosing the hole closest to the front will allow
the helmet to tilt less.
Flip-down Friction
1. Tighten or loosen the friction knobs located
on either side of the helmet to increase or
decrease the amount of effort needed to raise
and lower the helmet.
The headband and middle strap must be properly
adjusted before flipping the helmet down by nod-
ding your head. If the headband is too loose, the
helmet may tumble off after being flipped down
and the lenses could be damaged.
Figure 1.
Model H7787.
Shade Filter
The shade chart below shows recommended
shade filters needed for various welding process-
es. We recommend that you start ANY welding
process at #13 and reduce the shade as needed
for safety.
Welding App. Current Amp.
Shade No.
Stick Welding
<40
40-80
80-175
175-300
300-500
#9
#10
#11
#12
#13
MIG
(metal inert
gas)
<100
100-175
175-300
300-500
#10
#11
#12
#13
TIG
(tungsten inert
gas)
<50
50-100
100-200
200-400
#10
#11
#12
#13
Air Carbon
Arc
<500
500-700
#12
#13
Plasma
Cutting
60-150
150-250
250-400
#11
#12
#13
Plasma
Welding
<50
50-200
200-400
#9
#10
#11
