Danger – Guardian Technologies 004270-3 User Manual
Page 26
24 Generac
®
Power Systems, Inc.
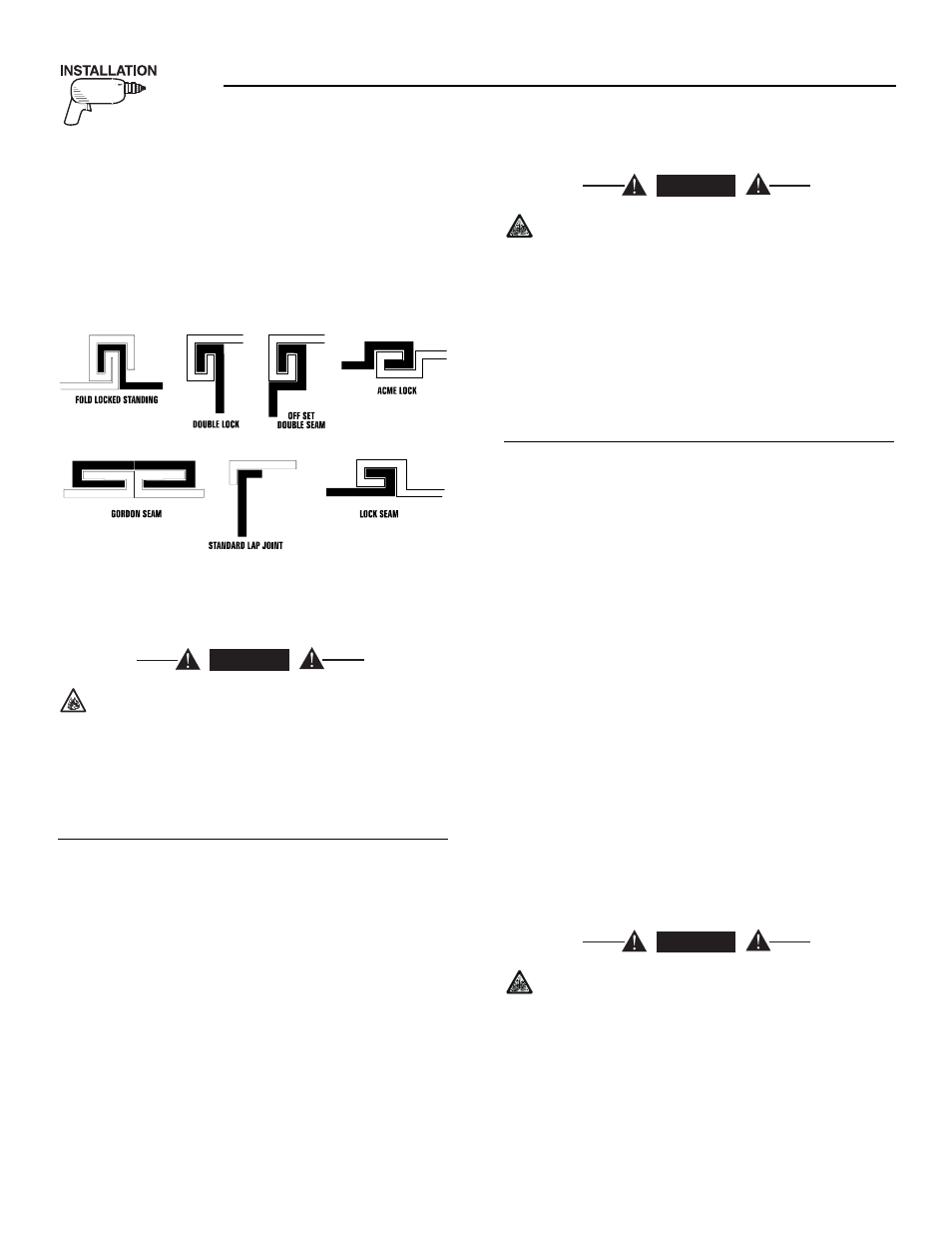
• Seams and joints of the galvanized steel (whether
used as a liner or for the compartment itself) must
be lapped and mechanically secured. Such seams
may be manufactured, welded, bolted, riveted, or
screwed. Manufactured lock seams are shown in
Figure 2.4. Installer-constructed compartments
typically utilize a standard lap joint.
Figure 2.4 – Types of Lock Seams
• After the compartment has been metal -lined and
vapor-sealed, line the compartment interior walls
and ceiling with an approved, nonflammable
sound-insulating material. See Section 2.2.2.
Do not install any flammable material directly
above or around the compartment. Heat, trans-
ferred through the compartment structure, may
be sufficient to ignite, char, or discolor seat
cushions, fiberboard, and other flammable
materials. Use approved, nonflammable insulat-
ing materials in high temperature areas.
2.2.2 SOUND INSULATING MATERIALS
Once installers have determined that a compartment
is properly constructed and metal-lined, they can add
acoustical material. This may include additional
sealant or insulating material, to reflect noise away
from the vehicle interior.
Sound insulating materials should be of a nonflam-
mable type. One excellent insulating material is a 1-
inch (25 mm) thick fiberglass having a 2-pound den-
sity. When fiberglass is used, its coated side should
face toward the compartment interior.
Do not install sound insulation or any
absorbent material on the compartment floor
interior. Such materials will become soaked
with combustible or explosive vapors and
liquids and will become a fire hazard.
Using a combination of sound-insulating materials
can often reduce noise more effectively than a single
material. For example, a sheet of lead or visco-elastic
material, along with a layer of other acoustical mate-
rial, is more effective than when a single material is
used.
2.2.3 ACOUSTICS
For additional noise abatement, the installer may
wish to consider the following:
• Using special sound-insulating materials.
• Construction of a special noise abatement
compartment.
NOTE:
Any method used to reduce noise must not
adversely affect the flow of cooling and ventilating
air into, or out of, the compartment.
In addition to the effective use of sound insulating
materials, construction of a special noise abatement
compartment might be considered to reduce noise
levels. Such a compartment might be constructed as
follows (Figure 2.5):
• Use 5/8-inch thick or 3/4-inch thick plywood in the
compartment.
• Construct the compartment floor of a double thick-
ness of 5/8-inch or 3/4-inch plywood.
• Line the compartment’s interior walls and floor, as
well as the underside of the floor, with 26-gauge
galvanized steel.
• Vapor-seal all compartment seams and joints.
• Over the galvanized steel lining, install a combina-
tion of acoustical materials, as mentioned in
Section 2.2.2.
To prevent fire or explosion, do not install any
insulation, or other absorbent materials, on the
interior or underside of the compartment floor.
• Seal all compartment door edges to prevent noise
leakage around the door perimeter.
• Line the compartment door interior (except for air
openings) with suitable, fireproof sound insulation
(such as, 1-inch (25 mm) thick fiberglass with a 2-
pound density).
DANGER
◆
DANGER
◆
DANGER
Section 2 – Installation
QUIETPACT™ 75D Recreational Vehicle Generator
