Testing diodes, 21 testing diodes, Making measurements – Fluke 87 III User Manual
Page 29: Cat ii, Min max range hold h hz rel, 4 1/2 digits 1 seconds, True rms multimeter, Figure 6. testing a diode, Typical reading, Forward bias reverse bias
Making Measurements
21
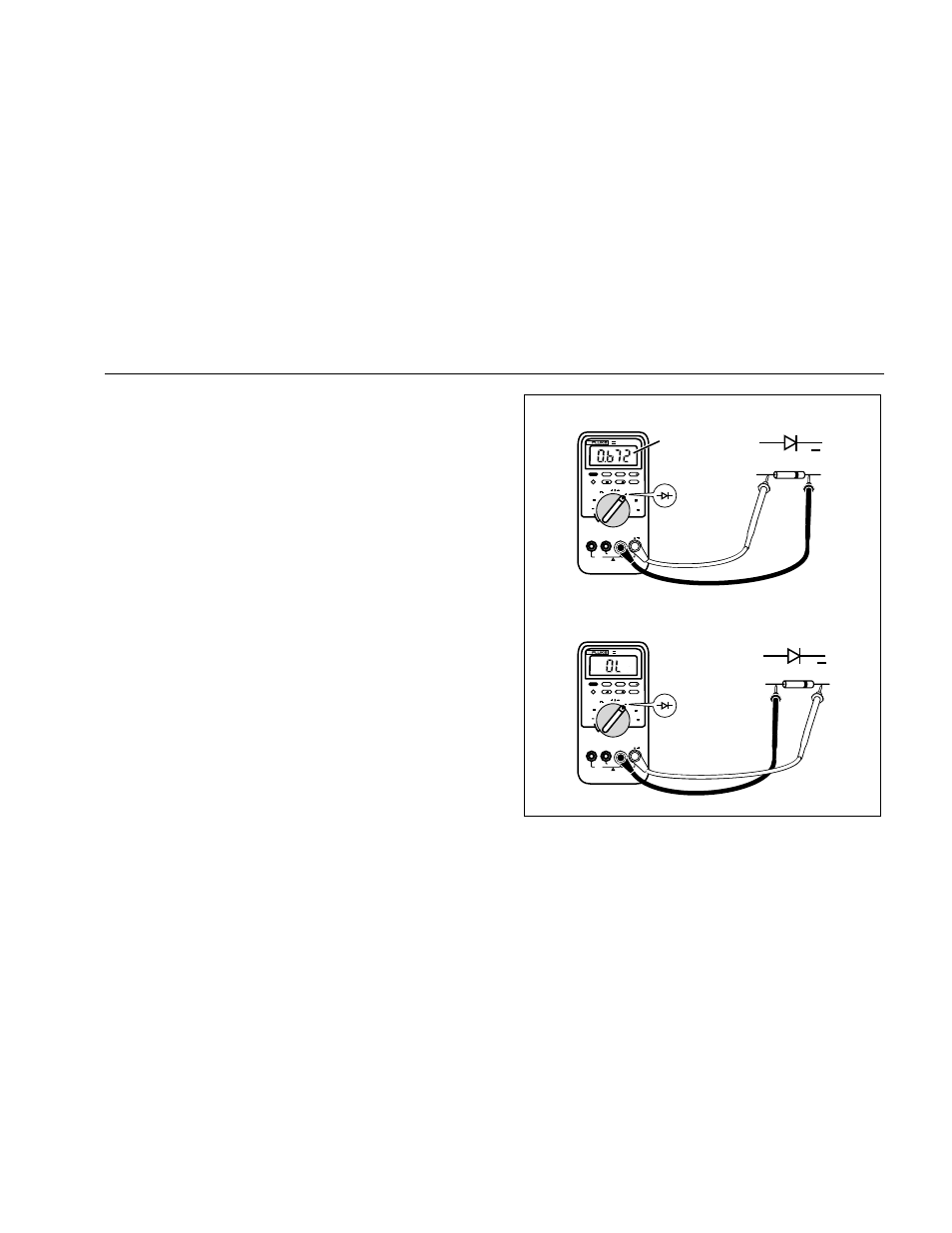
Testing Diodes
Caution
To avoid possible damage to the meter or to
the equipment under test, disconnect circuit
power and discharge all high-voltage
capacitors before testing diodes.
Use the diode test to check diodes, transistors, silicon
controlled rectifiers (SCRs), and other semiconductor
devices. This function tests a semiconductor junction by
sending a current through the junction, then measuring
the junction’s voltage drop. A good silicon junction drops
between 0.5 V and 0.8 V.
To test a diode out of a circuit, set up the meter as shown
in Figure 6. For forward-bias readings on any
semiconductor component, place the red test lead on the
component’s positive terminal and place the black lead
on the component’s negative terminal.
In a circuit, a good diode should still produce a forward-
bias reading of 0.5 V to 0.8 V; however, the reverse-bias
reading can vary depending on the resistance of other
pathways between the probe tips.
MIN MAX
RANGE
HOLD
H
Hz
REL
mA
A
mV
V
V
OFF
!
!
A
COM
V
mA
µ
A
1000V MAX
400mA MAX
FUSED
10A MAX
FUSED
PEAK MIN MAX
µ
A
CAT II
+
Typical
Reading
MIN MAX
RANGE
HOLD
H
Hz
REL
mA
A
mV
V
V
OFF
!
!
A
COM
V
mA
µ
A
1000V MAX
400mA MAX
FUSED
10A MAX
FUSED
PEAK MIN MAX
µ
A
CAT II
+
Forward Bias
Reverse Bias
4 1/2 DIGITS
1 Seconds
87
TRUE RMS MULTIMETER
III
4 1/2 DIGITS
1 Seconds
87
TRUE RMS MULTIMETER
III
iy9f.eps
Figure 6. Testing a Diode
