Switch definitions and terminology – Honeywell Switches User Manual
Page 10
Pressure/Vacuum Switch - A device
that senses a change in pressure/
vacuum and opens or closes an
electrical circuit when the set point is
reached.
Set Point - The pre-determined
pressure/vacuum value that is required
to open or close the electrical contacts
in the switch.
Electrical Contacts - The elements
in the switch that electrically respond
to the media applied to the actuator.
Snap action contacts with a
“self-cleaning” wiping effect are used
in Series III and Series V switches.
Direct action blade contacts are used
in the 5000 Series.
Pressure Switch Actuator - The
member in the switch which receives
the media and ultimately strokes the
electrical contacts to open or close at
the designated set point. The actuator
in the Series III is a beryllium copper
or silicone rubber diaphragm. An
elastomeric diaphragm or piston
actuator is used in the Series V.
The 5000 Series uses a polyimide
film diaphragm.
Normally Open (SPST-N.O.) - A
normally open switch does not conduct
an electrical signal until the actuator
is moved by the media causing the
contacts to close.
Normally Closed (SPST-N.C.)
- A normally closed switch conducts
electricity until the actuator is moved
by the media causing the contacts to
open.
Dual Circuit (SPDT) - A normally
open and normally closed circuit are
contained in a switch.
Dual Circuit (N.O./N.O.) - Switch
contains two normally open circuits.
Dual Circuit (N.C./N.C.) - Switch
contains two normally closed circuits.
System Pressure/Vacuum - This is
the normal pressure/vacuum that would
be present at the switch actuator. This
value is important in order to apply
the proper switch configuration. Even
though the set point may be relatively
low, the system pressure would continue
to be applied to the switch actuator in
most cases.
Proof Pressure - This specification is
the maximum over-pressure condition
that the switch can have for a specified
period of time and still maintain set
point integrity.
Burst Pressure - This specification is
the maximum over pressure condition
that the switch can withstand without
experiencing leakage.
Dry Circuit Load - Typically this would
be a very low electrical load associated
with microprocessors when the open
circuit voltage is .03V or less and the
current is 40mA or less.
Resistive Load - A load in which the
voltage is in phase with the current.
Inductive Load - A load in which the
voltage leads the current.
Motor Load - The load of a motor at
rated horsepower and speed.
Capacitive Load - A load which the
current leads the voltage.
Differential - The difference between
opening (actuation) pressure and the
closing (de-actuation) set points. This
is also referred to as “dead band”. For
example, a switch set at 150 PSI to
open on increasing pressure and close
at 95 PSI on decreasing pressure
would have a differential of 55 PSI
(150-95=55).
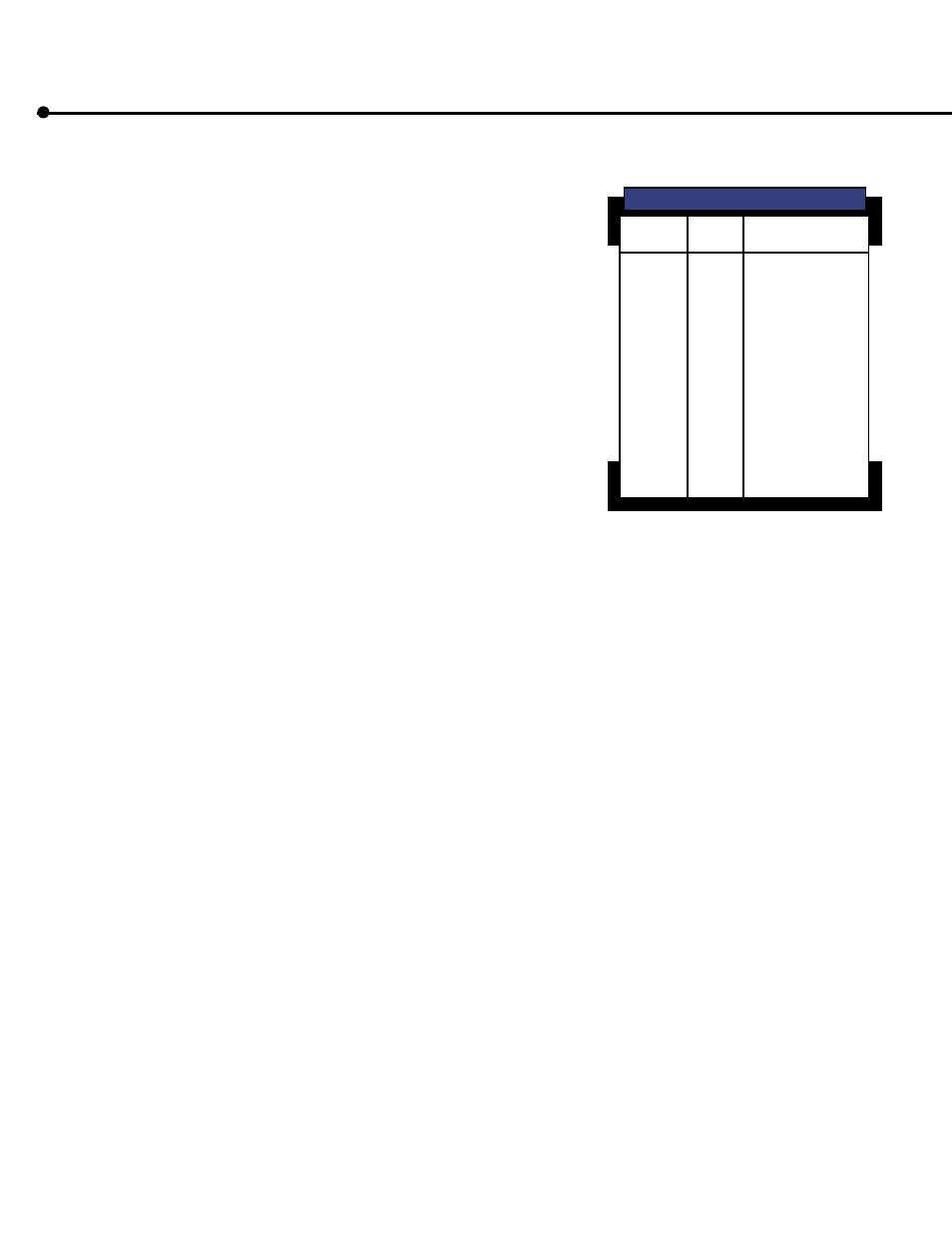
Convert
kPa
PSI
BARS
PSI
Hg”
PSI
H
2
O”
PSI
H
2
O”
Hg”
C°
F°
Conversion Factors
To
PSI
kPa
PSI
BARS
PSI
Hg”
PSI
H
2
O”
Hg”
H
2
O”
F°
C°
Multiply By
.145
6.8948
14.5
.069
.4912
2.036
.03613
27.6778
.07355
13.5962
1.8(C° +17.78)
F-32÷1.8
10
Switch Definitions and Terminology
