Frequency hopping – Linx Technologies HUM-xxx-RC User Manual
Page 19
– –
– –
32
33
Frequency Hopping
The module incorporates a Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)
algorithm. This provides immunity from narrow-band interference and
complies with FCC and IC guidelines.
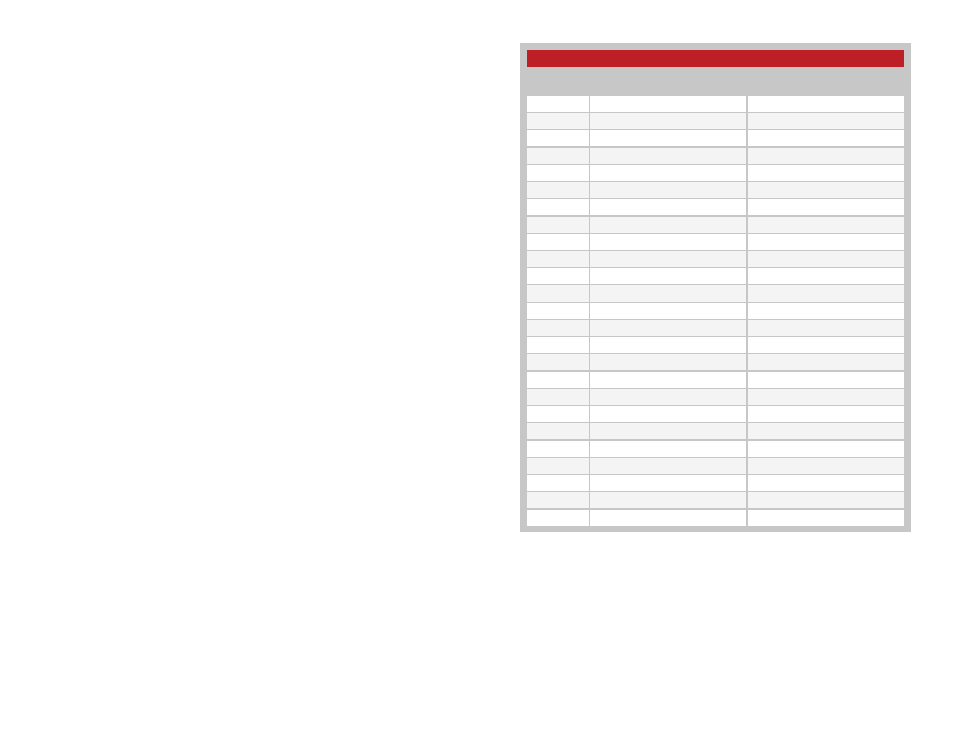
The module uses 25 RF channels as shown in Figure 35. Each channel has
a time slot of 13.33ms before the module hops to the next channel. This
equal spacing allows a receiver to hop to the next channel at the correct
time even if a packet is missed. Up to seven consecutive packets can be
missed without losing synchronization.
The hopping pattern (sequence of transmit channels) is determined from
the transmitter’s address. Each sequence uses all 25 channels, but in
different orders. Once a transmission starts, the module continues through
a complete cycle. If the input line is taken low in the middle of a cycle,
the module continues transmitting through the end of the cycle to ensure
balanced use of all channels.
Frequency hopping has several advantages over single channel operation.
Hopping systems are allowed a higher transmitter output power, which
results in longer range and better performance within that range. Since
the transmission is moving among multiple channels, interference on one
channel causes loss on that channel but does not corrupt the entire link.
This improves the reliability of the system.
Channel Frequencies
Channel
Number
HUM-2.4-RC
Frequency (MHz)
HUM-900-RC
Frequency (MHz)
1
2,420.25
902.750
2
2,422.25
903.250
3
2,424.25
903.750
4
2,426.25
904.250
5
2,428.25
904.750
6
2,430.25
905.249
7
2,432.25
905.749
8
2,434.25
906.249
9
2,436.25
906.749
10
2,438.25
907.249
11
2,440.25
907.749
12
2,442.25
908.249
13
2,444.25
908.749
14
2,446.25
909.248
15
2,448.25
909.748
16
2,450.25
910.248
17
2,452.25
910.748
18
2,454.25
911.248
19
2,456.25
911.748
20
2,458.25
912.248
21
2,460.25
912.748
22
2,462.25
913.247
23
2,464.25
913.747
24
2,466.25
914.247
25
2,468.25
914.747
Figure 35: HumRC
TM
Series Transceiver RF Channel Frequencies
