8 change over functionality – Nevion ADP-3GHD User Manual
Page 13
ADP-3GHD
Rev. A
nevion.com | 13
8 Change over functionality
The change over functionality is only used when the card is set up for a redundant ring.
The card has a number of signal integrity analyzers and something called "triggers". A trigger
is another way of controlling the change-over functionality. The regular change-over
configuration is used for setting latch on/off, EQ or RCL control etc. In addition, the signal
integrity analyzers can be used to control the decision of which signal to use on the DROP
output. Thus, the trigger is a link from the analyzer to the change-over.
ADP-3GHD has four video analyzers.
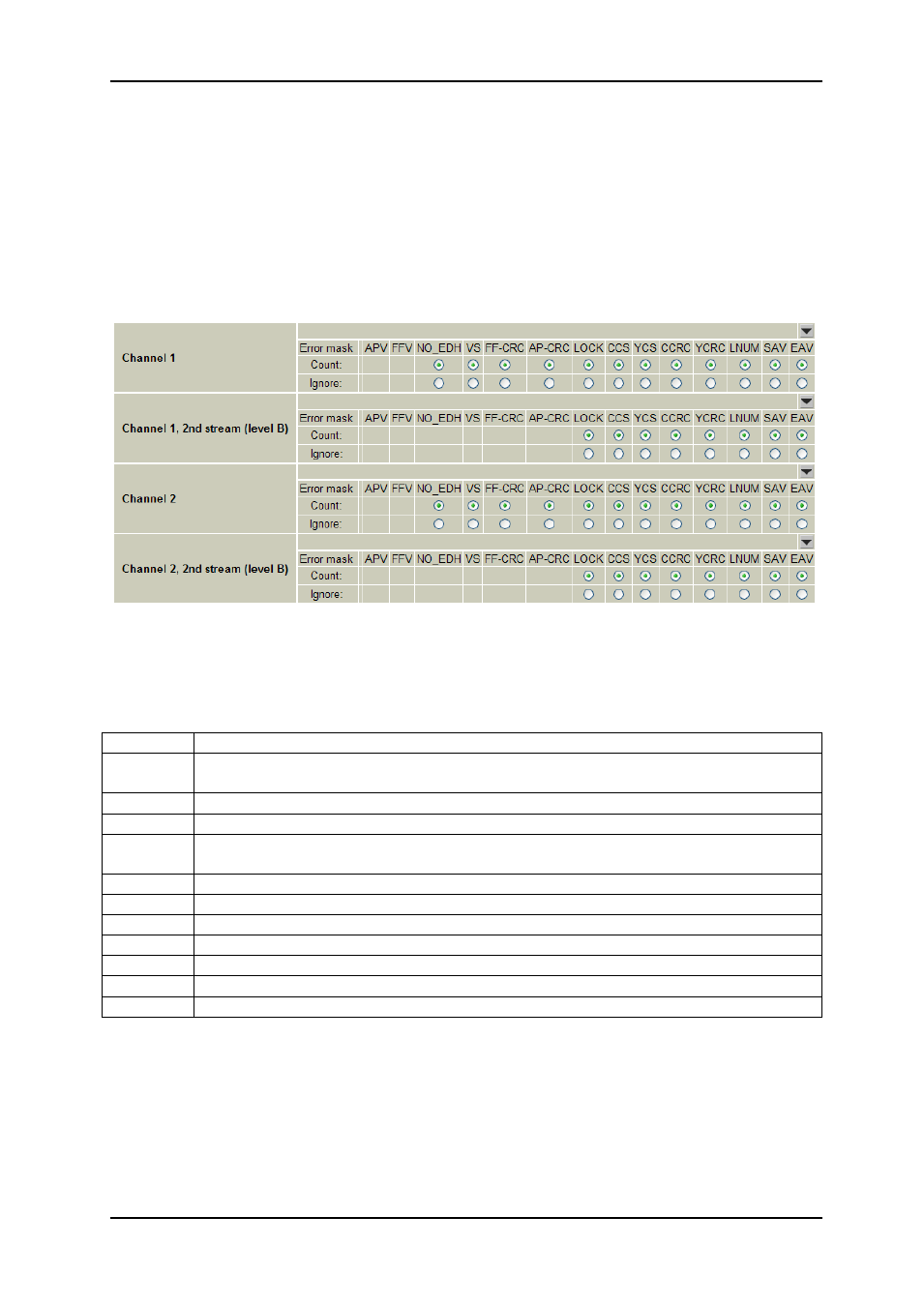
Figure 11 - Video analyzer settings
Figure 9 shows the controls for these. The two inputs each have their analyzers, plus an
extra "Stream 2" analyzer that is used when SMPTE 425M Level B mapping is used.
These errors can be counted (or ignored) based on the settings in the configuration view:
EDH
No EDH packets (SD only)
VSTD
SMPTE 352 packets do not correspond to detected video standard (SD/HD only)
Not supported for 3G.
FFCRC
Full Field CRC (SD only)
APCRC
Active Picture CRC (SD only)
LOCK
Analyzer chip is not locked to a bit stream (or stream 2 not present, for "Stream
2" analyzer)
CCS
Chroma channel ancillary data check sum error
YCS
Luma channel ancillary data check sum error
CCRC
Chroma channel video data check sum error
YCRC
Luma channel video data check sum error
LNUM
Line number error
SAV
Start of active video flags missing or misplaced
EAV
End of active video flags missing or misplaced
Errors are checked once per video field (LOCK errors are counted every 20ms when no
video is present). If an error occurs, it is checked against the bit mask, and if selected for
counting increments the error counter. An SNMP tool is recommended for tracking error
counts over time, with selectable limits on error rate and max count before generating a
warning.
The triggers are using the same information (and therefore have the same bit names as the
analyzers), but have separate bit masks. This means that it is possible to count one set of
error types, while using a different error type to control the change-over.
