Evaluating results – Beurer BM 65 User Manual
Page 24
24
6. Evaluating results
Cardiac arrhythmia:
This instrument can identify possible cardiac arrhythmia dis-
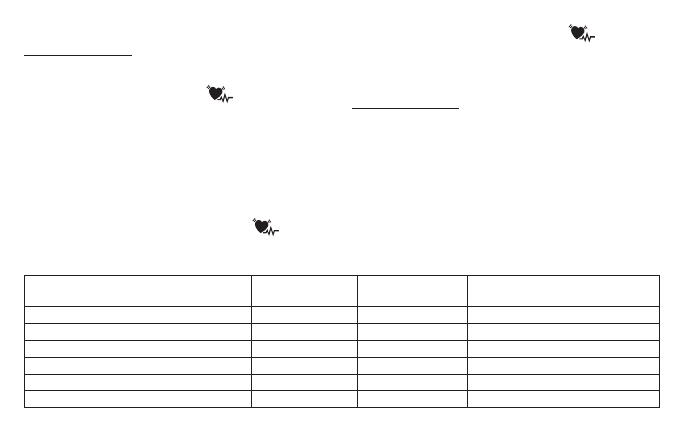
orders during measurement and if necessary indicates the
measurement with the flashing icon
.
This may be an indicator for arrhythmia. Arrhythmia is a
condition where the heart rhythm is abnormal as a result of
defects in the bioelectrical system controlling the heart beat.
The symptoms (omitted or premature heart beats, slow or
excessively fast heart rate) may be caused, among other
things, by heart disease, age, physical predisposition, ex-
cessive use of stimulants, stress or lack of sleep. Arrhythmia
can only be ascertained through examination by your doctor.
Repeat the measurement if the flashing icon
is dis-
played after the measurement. Please note that you should
rest for 5 minutes between measurements and not talk or
move during the measurement. If the icon
appears
often, please contact your doctor. Any self-diagnosis and
treatment based on the test results may be dangerous. It is
vital to follow your doctor‘s instructions.
WHO classification:
In accordance with the guidelines/definitions of the World
Heath Organization and the latest findings, the measure-
ments can be classified and assessed according to the
following table.
However, these standard values serve only as a general
guideline, as the individual blood pressure varies in different
people and different age groups etc.
It is important to consult your doctor regularly for advice.
Your doctor will tell you your individual values for normal
blood pressure as well as the value above which your blood
pressure is classified as dangerous.
Range of blood pressure values
Systolic
(in mmHg)
Diastolic
(in mmHg)
Measure
Grade 3: Severe hypertension
> = 180
> = 110
Seek medical advice
Grade 2: Moderate hypertension
160 – 179
100 – 109
Seek medical advice
Grade 1: Mild hypertension
140 – 159
90 – 99
Have it checked regularly by doctor
High-normal
130 – 139
85 – 89
Have it checked regularly by doctor
Normal
120 – 129
80 – 84
Check it yourself
Optimal
< 120
< 80
Check it yourself
Source: WHO, 1999
