BECKHOFF DK9322-1109-0011 User Manual
Page 2
TwinCAT
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
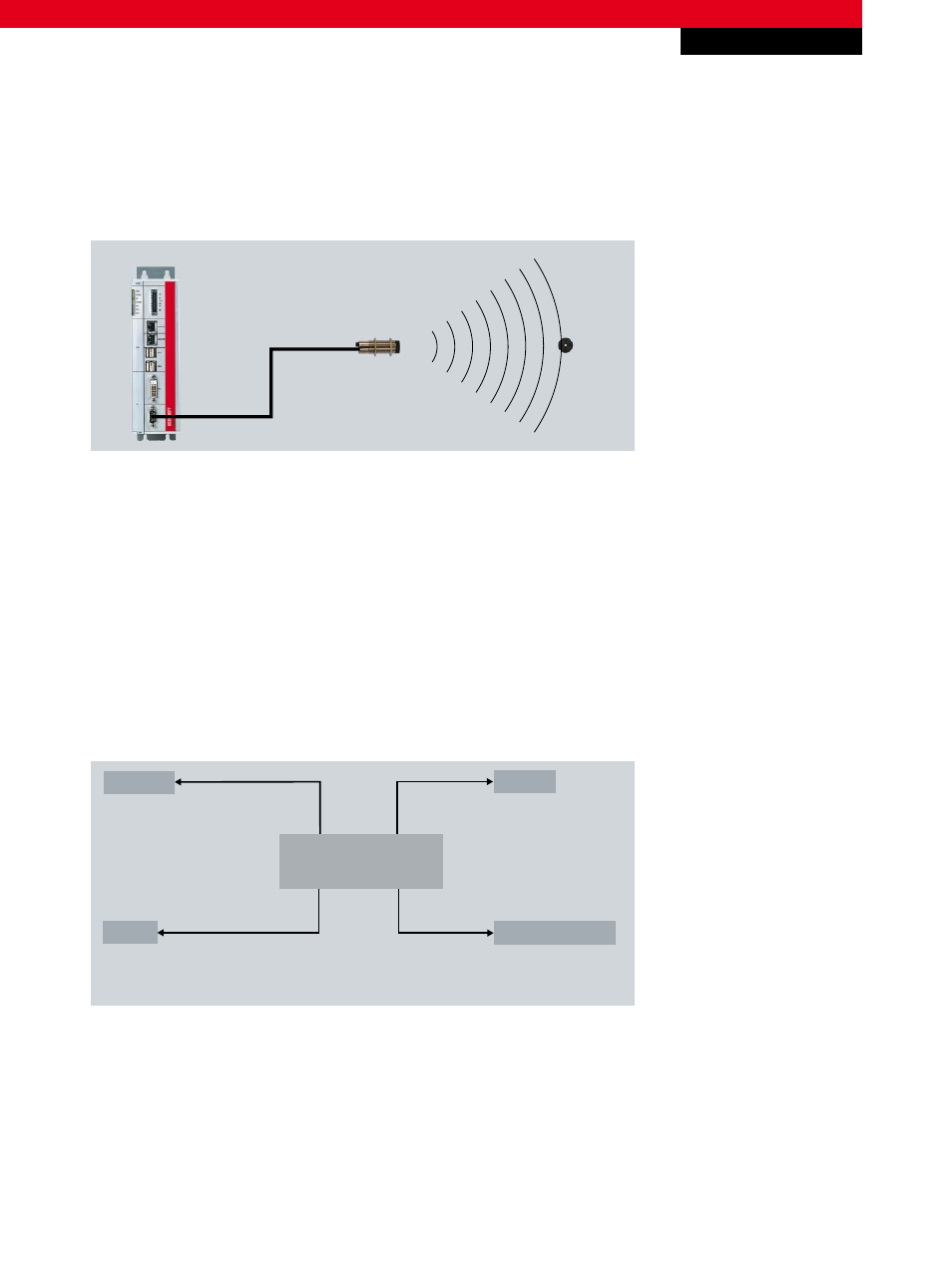
IPC
RFID reader
RFID tag
Fig. 1 Structure of an RFID connection
The object to be detected is fitted with a tag that transmits its data as soon as the object is within range of the reader.
A specific alignment of the tag and the readers, such as is required with a barcode, is not necessary, since the data is
received contactlessly within the range cone of the reader. As opposed to barcodes, tag detection is also assured in poor
lighting conditions and in the case of dirty surfaces. Since RFID has short detection times and many tags can be detected
simultaneously (bulk reading ability), the individual goods on an entire pallet of different goods, for example in a goods
reception area, can be identified individually without having to take the container apart. Thus, all goods can be identified
within a very short space of time and their data made available for further processing. RFID offers many advantages over other
identification systems and is now used as an industrial standard in almost all industries.
Areas of application
for RFID
Access systems
Payment systems
Credit chips
Immobiliser
Parts tracking
Tool identification
Product history
Process management
Security
Membership card
Time recording
Personnel
Tracking of hazardous goods
Servicing
Tracing
Waste management
Forgery-proofing
Goods marking
Goods flow
Fig. 2 Areas of application of RFID
New Automation Technology
Beckhoff
2
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
