Lingenfelter L450080000 Lingenfelter TVS Diode v1.4 User Manual
Page 2
Page 2 of 3
Description:
A Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diode is a voltage clamping/limiting device used to
protect sensitive electronics from voltage spikes. The TVS diode is NOT a normal diode.
Rather, it is a bi-directional device that allows the voltage to swing from -28 volts to +28 volts
before clamping the flyback voltage. This allows the field of the solenoid to collapse faster and
in most applications allows the solenoid to turn OFF faster while still maintaining the flyback
voltage level and reducing electrical noise. Because these TVS diodes are rated at 600 watts
each, there is a possibility of surpassing the total power dissipation limit if multiple solenoids
are placed on the same diode.
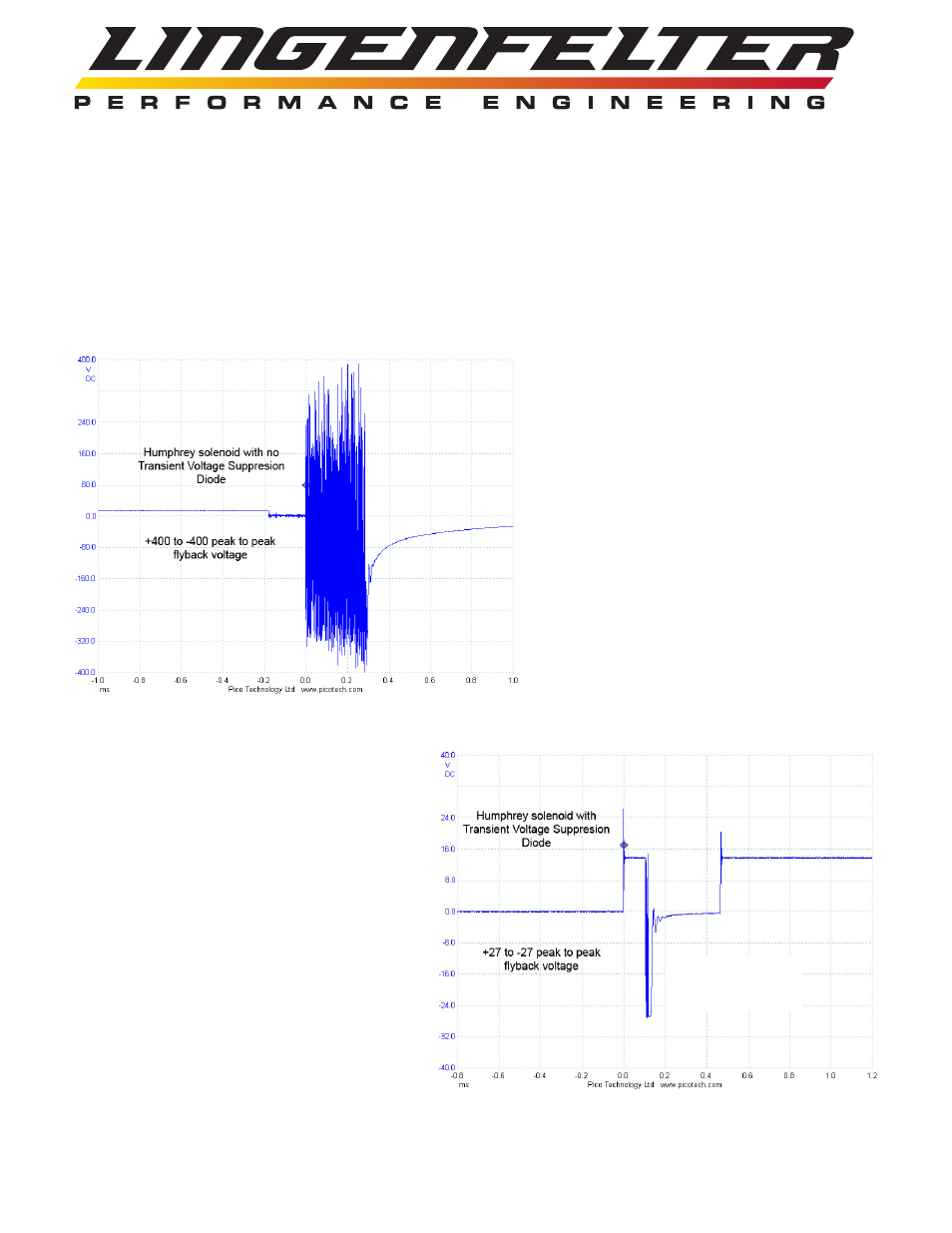
In an automotive environment there
can be many sources that can create
harmful voltage spikes. The captured
scope image to the left is the actual
flyback voltage produced when a
common control solenoid is switched
OFF. Peak voltages of +/- 400 volt
are present. This flyback voltage
can and will cause intermittent and
permanent failure of electronic
devices.
What it does:
The transient voltage suppression diode
clamps and/or limits the voltage peaks. The
captured scope image to the right shows
the same solenoid flyback voltage shown
above with a 27 volt TVS diode installed.
The +/-400 volt peak voltages are clamped
at +/-27 volts.
The addition of the TVS diode eliminates
harmful voltage transients produced by
the turning ON/OFF of solenoids. One key
benefit of a TVS Diode over a standard
Rectifier diode is the TVS diode still allows
a negative voltage to be developed in the
solenoid windings to aid in the collapse of
the magnetic field, which in turn allows for a
faster turnoff.
Note that the above graph is on a +/- 40 V DC scale
instead of a +/- 400 V DC scale of the graph at the top of
the page .
TVS diode allows negative
voltage to develop to aid in
de-energizing the solenoid
for faster turn off.
