ENMET SPECTRUM CO-RAL User Manual
Page 16
ENMET Corporation
S
PECTRUM
CO RAL
14
Appendix A: Characteristics and Effects of Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide is a colorless odorless toxic gas generated by incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon fuel in air. It may be
present where internal combustion engines, furnaces, boilers, and other combustion devices are present. It is toxic when
inhaled because of its great affinity to hemoglobin, the oxygen carriers in the red cells of the blood. CO replaces the oxygen
normally carried by the hemoglobin, and thus inhibits the delivery of oxygen throughout the body; the victim suffers from
oxygen deficiency, and may die from asphyxiation. The symptoms and degree of danger resulting from exposure to CO depend
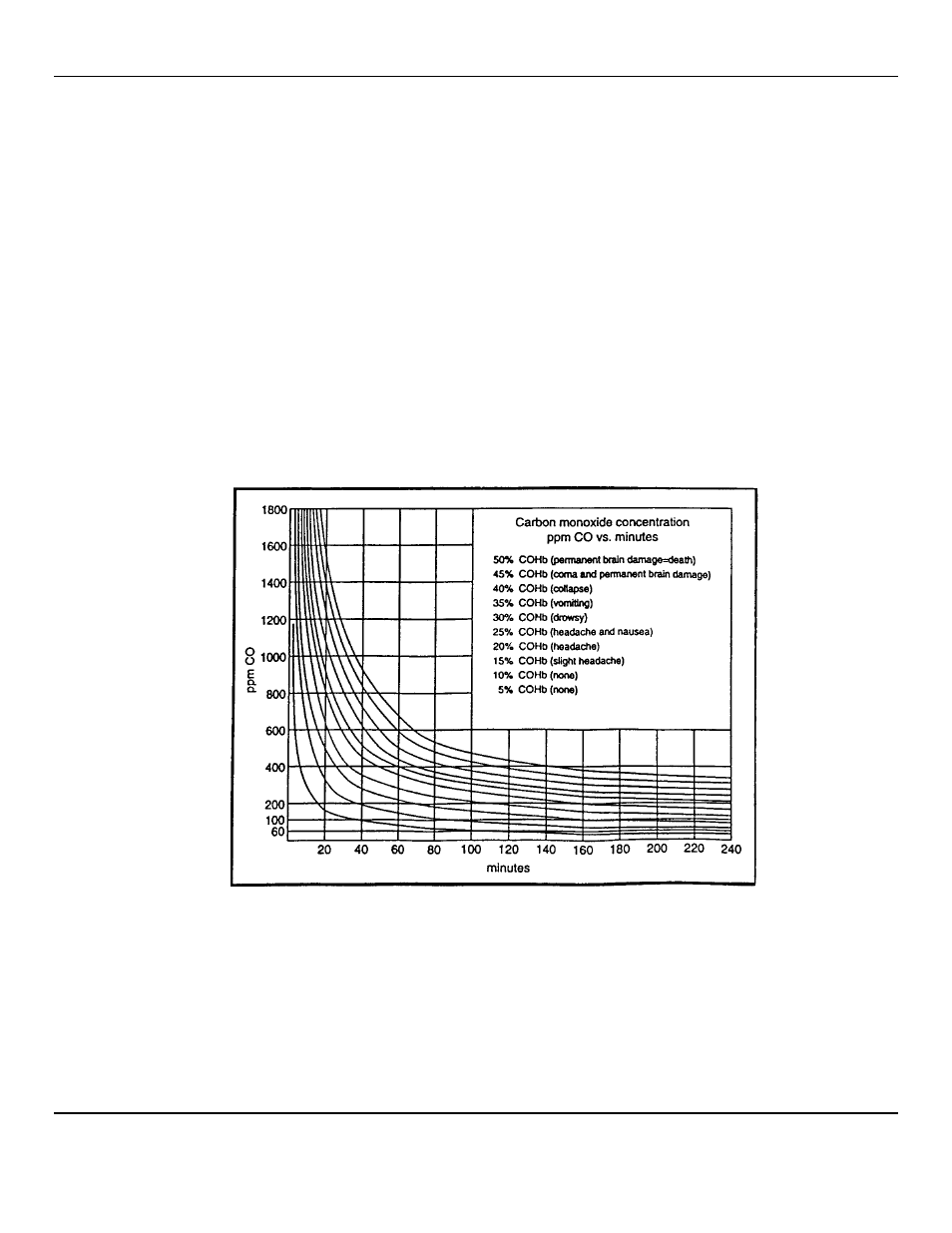
upon the concentration of the gas and the length of exposure; this is shown in Figure 5. The
S
PECTRUM
CO RAL
instrument is
employed to warn the user of the presence of CO, and to facilitate the assessment of the degree of danger that he or she is
exposed to
Based upon knowledge of the effects of CO, the Occupational Safety and Health Authority (OSHA) has set limits on exposure
to CO in the workplace. These are 35 ppm (parts CO per million parts air) as an time weighted average for an eight hour day,
and a maximum exposure of 200 ppm. The
S
PECTRUM
CO RAL
is shipped with the adjustable alarm set at 35 ppm; this alarm
cannot be adjusted above 200 ppm.
The curves in Figure 7 below are for percent carboxalhemoglobin with 50% being the top curve, 5% the bottom. %COHb is a
measure of the amount of hemoglobin occupied by CO rather than oxygen. CO effects upon children, adults engaging in
physical activity and smokers are more pronounced.
Figure 7: CO Exposure over Time
