Elenco Green Projects User Manual
Page 23
5V
-22-
Project #17
Voltage & Current
Light Emitting Diode
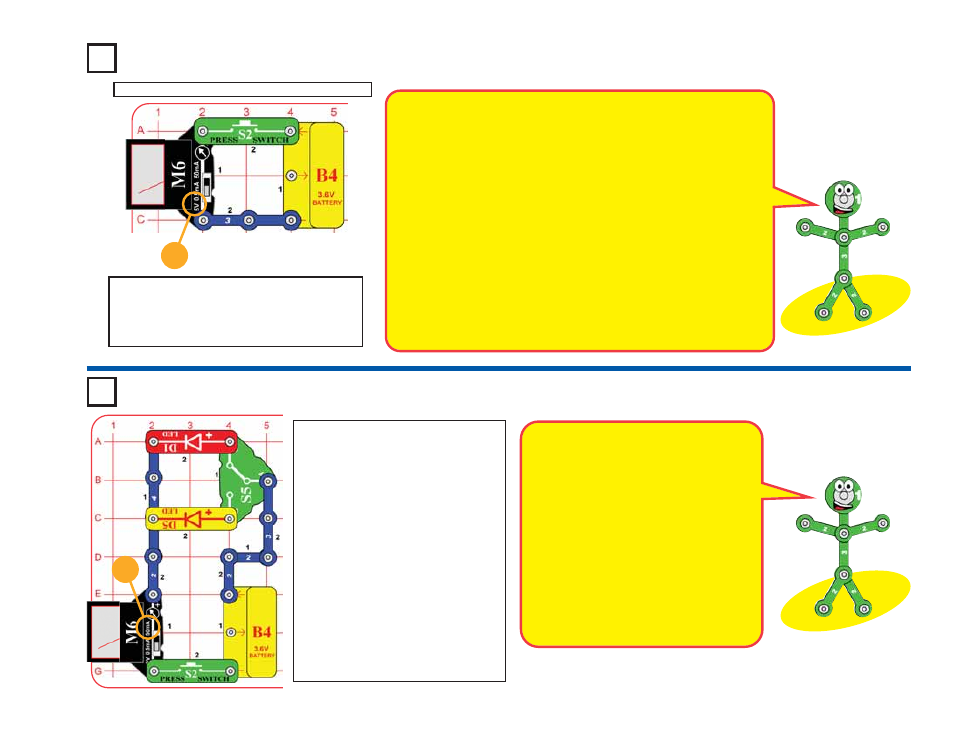
Project #18
Build the circuit shown. Set the meter
(M6) to the 50mA setting.
For each of the slide switch (S5)
positions, push the press switch (S2)
to measure the current through one of
the LEDs (D1 & D5). Then change the
slide switch (S5) to measure the
current with the other LED, and
compare them.
Now set the meter to the 5V setting,
and compare the voltage measured
with each LED. The voltage for both
should be lower than what you
measured directly at the battery in the
preceding project, due to the voltage
needed to turn on the LEDs.
Build the circuit shown. Set the meter (M6) to
the 5V setting. Push the switch (S2) to
connect the meter to the battery and measure
its voltage.
Electricity is the movement of sub-
atomic charged particles (called
electrons
) through a material due
to electrical pressure across the
material, such as from a battery.
The electrical pressure exerted by
a battery or other power source is
called
voltage
and is measured in
volts
(V). Notice the “+” and “–”
signs on the battery. These
indicate which direction the battery
will “pump” the electricity.
Circuits need the right voltage to
work properly. For example, if the
voltage to a light bulb is too low
then the bulb won’t turn on; if too
high then the bulb will overheat
and burn out.
The
electric current
is a measure
of how fast electricity is flowing in a
wire, just as the water current
describes how fast water is flowing
in a pipe. It is expressed in
amperes
(A) or
milliamps
(mA,
1/1000 of an ampere).
The “
power
” of electricity is a
measure of how fast energy is
moving through a wire. It is a
combination of the voltage and
current (Power = Voltage x Current).
It is expressed in
watts
(W).
50mA
Light emitting diodes (LEDs) are one-way
lights with a turn-on voltage threshold. If the
voltage is high enough, they will light. The
yellow LED (D5) requires a higher voltage
to turn it on, but can get brighter.
When electric current flows through an
LED, energy is released as light; the color
depends on the material. LEDs are much
more energy efficient and last longer than
ordinary light bulbs but were only used in
low-power applications due to power limits,
cost, and limited colors. However, LEDs are
rapidly being improved and are increasingly
being used in home lighting.
See projects 1 & 3 if you need to recharge the battery (B4).
