Ecler CKL SERIES User Manual
Page 12
12
8. APPENDIX – BRIEF EXPLANATION OF ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS
The following paragraphs give brief explanations of frequently used concepts in acoustics, which will
help you understand the problematic involved in designing high-quality PA systems.
8.1. Definition of acoustic parameters
8.1.1. Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
Defined as:
6
10
·
20
log
20
−
=
ef
p
SPL
(dB SPL)
The numerator corresponds to the effective sound pressure.
The denominator corresponds to the hearing threshold, i.e. the minimum sound pressure which causes
hearing sensation in the human auditory system.
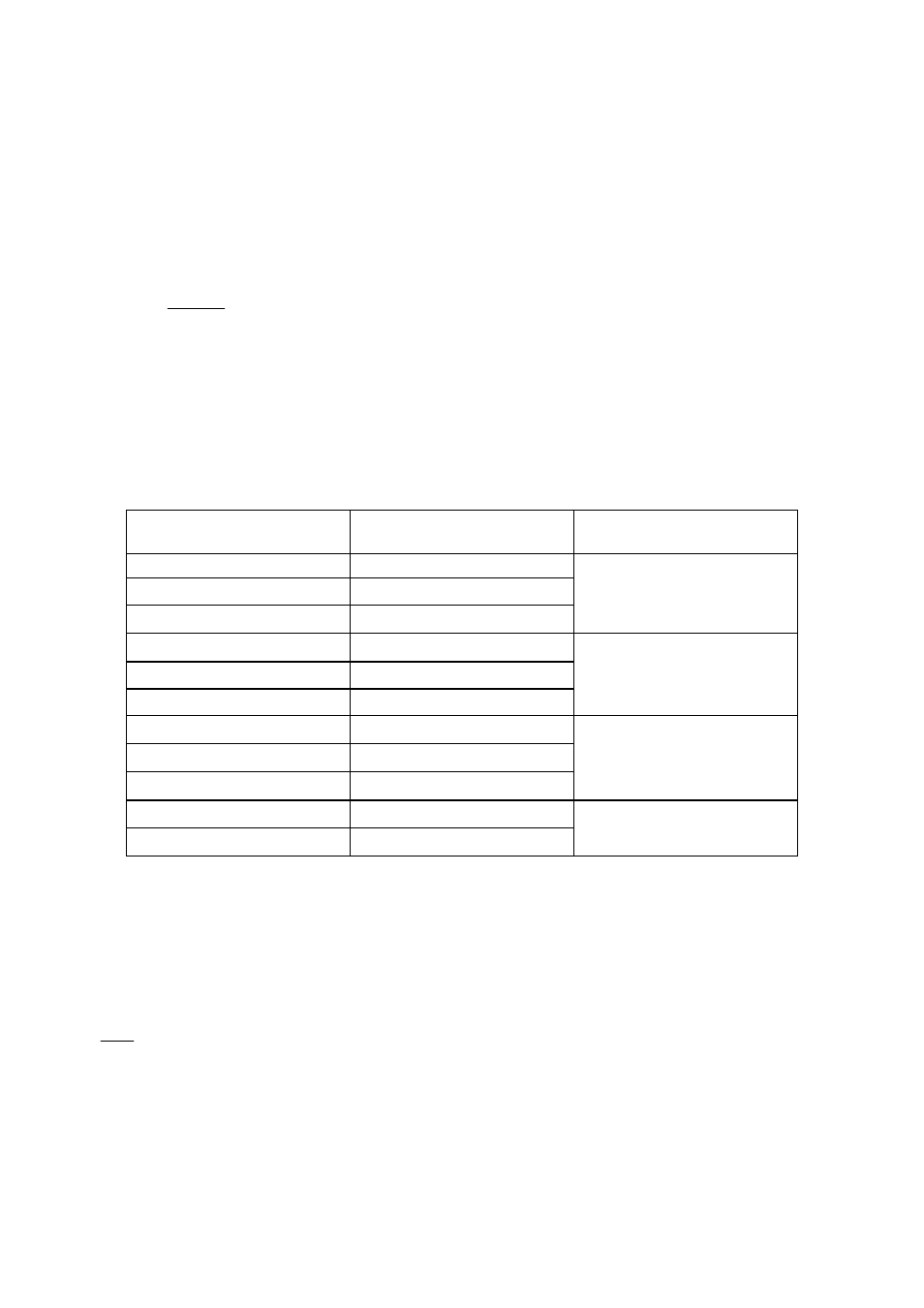
Following table shows the sound pressure levels of several typical sound sources, together with their
subjective level sensation.
SOUND SOURCE
SOUND PRESSURE
LEVEL (dB SPL)
SUBJECTIVE LEVEL
SENSATION
Jet take-off
120
Construction works
110
Pneumatic drill
100
Very high
Heavy truck (at 15m)
90
City street
80
Inside car
70
High
Normal conversation
60
Office
50
Living room
40
Moderate
Bed room (al night)
30
Recording studio
20
Low
Typical sound pressure levels (dB SPL)
8.1.2. Acoustic absorption
The acoustic absorption coefficient is defined as the ratio between absorbed acoustic energy by a
certain material and incident acoustic energy.
i
abs
E
E
=
α
Values of
α
range between 0 (no absorption) and 1 (maximum absorption). The absorption
characteristics of construction materials used for acoustic treatment of rooms, determine, amongst other
factors, the resulting reverberation time. (see paragraph 8.2.2)
