Getting started in soft solids testing, The constant rate test, Brookfield – Brookfield R/S-SST Rheometer User Manual
Page 5
BROOKFIELD
5 of 9
\\Bvserver\Data\RS Information\SSTManual.doc
Getting Started In Soft Solids Testing
Two test methods are most often used to evaluate soft solids with the SST2000: The
Constant Rate Test and The Creep Test.
The Constant Rate Test
For products like: Stiff pastes, slurries, set gels, waxes.
Properties measured: Yield stress or torque, equilibrium stress strain at yield, rigidity
modulus.
Description: In the constant rate test the vane is rotated at a constant low rotational
rate (typically 0.1 to 0.5 rpm) and torque or stress is measured against time, rotational
angle or strain.
Example method: Constant rotation at 0.2 rpm, linear data collection, 60 data points
over 60 seconds. A V30-15 vane (30mm high by 15mm across) is used in an open
configuration (see Setting Up Vanes).
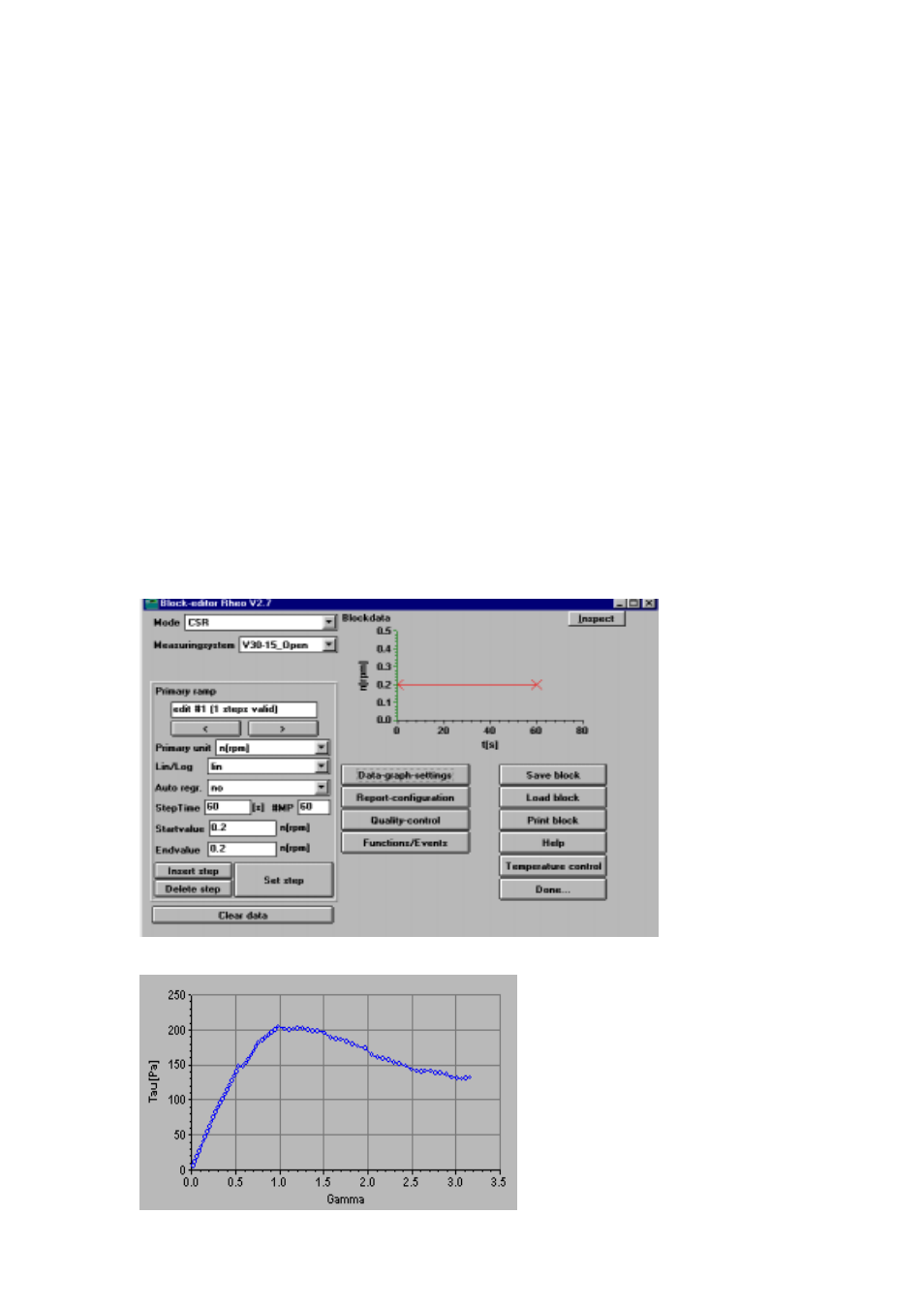
Typical results plots:
CR Test on mayonnaise with
stress (Tau, in Pascals) plotted
against strain (Gamma, unitless).
The peak value gives us yield
stress. The gradient of
stress/strain upcurve indicates gel
rigidity, a steeper curve: a stiffer
gel and vice-versa.
